(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, April 26, 2023 – Researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and Princeton University have discovered a novel genetic disorder associated with neurodevelopmental differences. The discovery identified the disorder in 21 families from all over the world. The findings were published today in Science Advances.
The as-yet unnamed disorder is the result of a series of rare variants in the MAP4K4 gene, which is involved in many signaling pathways, including the RAS pathway that normal cell growth, and is being investigated as druggable target for multiple disorders.
The researchers had documented several patients with craniofacial and neurodevelopmental issues that indicated a then-unknown genetic cause. They put out an international call for patients who seemed to fit these specific criteria. Ultimately, they were able to identify patients from 36 countries to determine whether there was a genetic variant linking them to their clinical issues.
“We were able to connect with patients from all over the world who had overlapping symptoms, and eventually we were able to pinpoint the overlapping genes that helped us identify the variants causing these issues,” said co-senior author Elizabeth Bhoj, MD, PhD, an attending physician in the Division of Human Genetics at CHOP.
At CHOP, research scientist Dong Li, PhD, identified variants that had not been linked to a particular disorder in families in which multiple patients exhibited the same symptoms. Once those variants of interest had been identified, researchers created a zebrafish model to confirm that these variants were indeed responsible for the symptoms among these patients.
“The zebrafish is an excellent model for testing identified variants for their potential pathogenicity,” said co-senior author Rebecca Burdine, PhD, a professor of molecular biology at Princeton University. “Given the accessible early development of the zebrafish, we were able to assess MAP4K4 variants quantitatively and rapidly in a living embryo. The approach is a powerful one we plan to continue to use to assess variants of unknown function for potential disease genes.”
The researchers showed that decreasing activity of MAP4K4 causes developmental defects in zebrafish, which is what is observed in these patients. Additionally, MAP4K4 activity can restrain signaling in the RAS pathway during embryonic stages, which is why these symptoms were being observed in children. However, overactive RAS activity can lead to cancer, which is why any therapeutic interventions targeting MAP4K4 need to be finely tuned to strike a balance between treating one disorder while also making sure not to increase the risk of cancer.
Since this is a newly discovered genetic variant that causes disease in certain patients, researchers would like to know if it is implicated in more general disease.
“With a new discovery like this, it’s possible we may have missed how these variants influence other diseases,” Bhoj said.
This study was supported by the National Institute of Child and Human Development grants K23HD088742 and R01HD105868, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences grant R21TR002770, the National Institute of Mental Health grant R01MH106826, the National Institutes of Health grants R01HD055651-11 and U01HG006487-05, and a Duke/UNC CTSA Consortium Collaborative Translational Research Grant DUR41703-UL1TR002553.
Patterson et al, “Abrogation of MAP4K4 protein function causes congenital anomalies in humans and zebrafish.” Sci Adv. Online April 26, 2023. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ade0631.
About Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia: A non-profit, charitable organization, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia was founded in 1855 as the nation’s first pediatric hospital. Through its long-standing commitment to providing exceptional patient care, training new generations of pediatric healthcare professionals, and pioneering major research initiatives, the 595-bed hospital has fostered many discoveries that have benefited children worldwide. Its pediatric research program is among the largest in the country. The institution has a well-established history of providing advanced pediatric care close to home through its CHOP Care Network, which includes more than 50 primary care practices, specialty care and surgical centers, urgent care centers, and community hospital alliances throughout Pennsylvania and New Jersey, as well as an inpatient hospital with a dedicated pediatric emergency department in King of Prussia. In addition, its unique family-centered care and public service programs have brought Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia recognition as a leading advocate for children and adolescents. For more information, visit https://www.chop.edu.
END
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Princeton researchers identify novel genetic disorder
The disorder was identified in 21 patients with neurodevelopmental and craniofacial symptoms; causal gene may be a valuable therapeutic target
2023-04-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Almost one in three adults aged 45 and older who had both TB and COVID-19 died during a pandemic cohort study in NYC between March 2020 and June 2022
2023-04-26
Almost one in three adults aged 45 and older who had both TB and COVID-19 died during a pandemic cohort study in NYC between March 2020 and June 2022.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0001758
Article Title: Cohort study of the mortality among patients in New York City with tuberculosis and COVID-19, March 2020 to June 2022
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Nifty nanoparticles help ‘peel back the curtain’ into the world of super small things
2023-04-26
Physicists at The Australian National University (ANU) are using nanoparticles to develop new sources of light that will allow us to “peel back the curtain” into the world of extremely small objects – thousands of times smaller than a human hair – with major gains for medical and other technologies.
The findings, published in Science Advances, could have major implications for medical science by offering an affordable and effective solution to analyse tiny objects that are too small for microscopes to see, let alone the human eye. The work could also be beneficial for the semiconductor industry ...
Tree diversity increases carbon storage, soil fertility in forests
2023-04-26
Keeping tree diversity intact in Canada’s many forests over the long term can help increase carbon capture and mitigate climate change, according to a new University of Alberta study.
The study, published in Nature, is the first of its kind to show the sustained benefits of tree diversity on a large spatial scale, in terms of storing carbon and nitrogen in the soil. It reinforces the importance of biodiversity conservation in forests, says Xinli Chen, lead author on the paper and postdoctoral fellow in the Faculty of Agricultural, ...
New findings indicate gene-edited rice might survive in Martian soil
2023-04-26
Andy Weir’s bestselling 2011 book, The Martian, features botanist Mark Watney’s efforts to grow food on Mars after he becomes stranded there. While Watney’s initial efforts focus on growing potatoes, new research presented at the 54th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference by a team of interdisciplinary researchers from the U of A suggests future Martian botanists like Watney may have a better option: growing rice.
As outlined in the team’s abstract, Rice Can Grow and Survive in Martian ...
New research sheds light on how circadian rhythms work
2023-04-26
ITHACA, N.Y. -- New research from a multidisciplinary team helps to illuminate the mechanisms behind circadian rhythms, offering new hope for dealing with jet lag, insomnia and other sleep disorders.
Using innovative cryo-electron microscopy techniques, the researchers have identified the structure of the circadian rhythm photosensor and its target in fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster), one of the major organisms used to study circadian rhythms. The research, “Cryptochrome-Timeless Structure Reveals Circadian Clock Timing ...
Brain aging expert Ashley Webb, Ph.D. joins faculty at Buck Institute for Research on Aging
2023-04-26
The Buck Institute for Research on Aging announces that Ashley Webb, PhD, will join its faculty as an associate professor on August 1, 2023. Webb’s research is focused on the molecular mechanisms underlying stem cells and brain aging. She joins the Buck from Brown University, where she is currently an associate professor in the Department of Molecular Biology, Cell Biology and Biochemistry. Webb uses a combination of mouse models, cell culture approaches and genomics technologies to investigate the epigenetic and transcriptional mechanisms that preserve healthy ...
Study: Tree diversity increases storage of carbon and nitrogen in forest soils, mitigating climate change
2023-04-26
Preserving the diversity of forests assures their productivity and potentially increases the accumulation of carbon and nitrogen in the soil, which helps to sustain soil fertility and mitigate global climate change.
That's the main takeaway from a new study that analyzed data from hundreds of plots in Canada's National Forest Inventory to investigate the relationship between tree diversity and changes in soil carbon and nitrogen in natural forests.
Numerous biodiversity-manipulation experiments have collectively suggested that ...
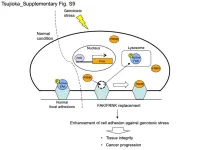
Hanging on for dear life
2023-04-26
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify a novel mechanism by which cells adhere more strongly to their surrounding matrix in response to stress
Tokyo, Japan – The DNA molecules in our cells can be damaged by various extrinsic and intrinsic factors called genotoxic stressors; persistent and unchecked damage can lead to developing diseases like cancer. Fortunately, our cells don’t sit idly by and let this happen.
In a recent article published in Cell Death & Disease, a team ...
Immune system sculpts rat brains during development
2023-04-26
Researchers have established that biological sex plays a role in determining an individual’s risk of brain disorders. For example, boys are more likely to be diagnosed with behavioral conditions like autism or attention deficit disorder, whereas women are more likely to suffer from anxiety disorders, depression, or migraines. However, experts do not fully understand how sex contributes to brain development, particularly in the context of these diseases. They think, in part, it may have something to do with the differing sizes of certain brain regions.
University ...
One Health surveillance in Viet Nam highlights hotspots for viral disease emergence and calls for One Health action
2023-04-26
HA NOI, Viet Nam (April 26, 2023) – A new study led by the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) identified a viral hotspot in Viet Nam where bat roosting sites, bat guano harvesting, and pig farms are all in close proximity. The findings of this collaborative One Health study, described in the latest issue of the journal Viruses, have important implications for public health and wildlife conservation.
The authors say that the collection of guano – commonly used as a fertilizer – if not stopped ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Princeton researchers identify novel genetic disorderThe disorder was identified in 21 patients with neurodevelopmental and craniofacial symptoms; causal gene may be a valuable therapeutic target