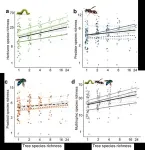
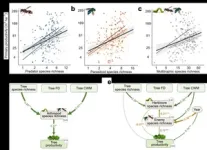
(Press-News.org) An international team of researchers led by Prof. MA Keping from the Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IBCAS) has shown that forests with higher tree species richness tend to have greater arthropod diversity.
The researchers showed that higher tree diversity promotes productivity through the suppression of herbivores by enemy arthropods.
These findings, published recently in Nature Ecology & Evolution, underscore the importance of arthropod diversity as a mediator of the effects of tree diversity on forest productivity.
Managing forests for increased productivity will require both increased tree diversity and multitrophic diversity, according to the researchers.
Forests are home to 80% of terrestrial plant and animal diversity, making them a critical component of global biodiversity conservation. However, forest biodiversity is under serious threat from anthropogenic disturbance and climate change. Species-rich groups such as arthropods are declining dramatically due to the degradation of forests and loss of plant diversity.
Most studies of biodiversity–ecosystem functioning (BEF) relationships have focused solely on plant diversity, neglecting the impact of the diversity of other trophic groups. As a result, it remains unclear how the diversity of herbivores and their enemies affects ecosystem functioning. Given the importance of forests in providing essential ecosystem services and global biodiversity, it is vital to understand these relationships and take action to protect them.
Using five years of data on aboveground herbivorous, predatory, and parasitoid arthropods, together with tree growth data from a large-scale forest biodiversity experiment in southeastern China (BEF-China), the researchers showed that the effects of increased tree species richness were consistently positive for species richness and abundance of herbivores, predators, and parasitoids.
This finding is consistent with a previous study from another large grassland biodiversity experiment (the Jena Experiment) and again shows that conserving plant diversity is important to conserving arthropod diversity.
However, in contrast to the bottom-up control of arthropod diversity by plant diversity in the central European grassland study, this new study in the species-rich forests of southeastern China shows that higher tree diversity can enhance the top-down control of herbivores by their enemies, thereby contributing to increased productivity.
"This study emphasizes that arthropod diversity plays an important role in mediating the effects of tree diversity on primary productivity," said Dr. LI Yi, a postdoc researcher at IBCAS and first author of the study.
A previous study conducted at the same sites showed that increasing plant diversity can promote forest productivity directly. The new study shows that increasing plant diversity can also indirectly increase forest productivity by promoting arthropod diversity and trophic interactions.
"It underscores the critical role of conservation efforts aimed at maintaining forest biodiversity," said Prof. LIU Xiaojuan, senior author and leader of the BEF-China management group.
To draw more reliable conclusions, the researchers conducted multi-year sampling. According to Prof. MA, chairman of the BEF-China platform, this approach takes into account the possibility that different arthropod groups may be affected inconsistently from year to year.
"It also highlights the value of the BEF-China platform, not only as the world’s largest experiment on forest biodiversity and ecosystem functioning, but also as an open and international platform for long-term ecological research," he said.
"The BEF-China platform provides valuable opportunities for international research teams and young researchers in different directions," said Prof. ZHU Chaodong, an author from the Institute of Zoology of CAS.
Overall, while several recent studies have documented declines in terrestrial arthropod biodiversity, few have examined the consequences for ecosystems.
"This work fills that gap by demonstrating the important role of arthropod diversity in BEF relationships," said Prof. Bernhard Schmid, an author from the University of Zurich.
In summary, these findings are of great importance in guiding the public to understand the conservation of forest biodiversity, plants, animals, and ultimately their associated microbes.
END
Arthropods in high-diversity forests contribute to improved productivity
2023-04-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Molecular autopsy sheds light on cause of sudden death of a child with COVID-19
2023-04-27
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) utilize an advanced DNA sequencing technique to reveal the factors that contributed to the death of a 5-year-old child with COVID-19
Tokyo, Japan – Sudden, unexplained child mortality is a tragedy; determining the cause of death is important for improving healthcare and providing loved ones with closure. Now, researchers from Japan have reported the use of an advanced DNA sequencing technique, whole-exome sequencing (WES), to determine why a young child died after a relatively mild infection.
In a study published ...
Bioinformatics specialists in Saarbrücken explore the molecular mechanisms of ageing
2023-04-27
A team led by bioinformatics experts Andreas Keller and Fabian Kern from Saarland University together with researchers at Stanford University have gained new insights into manifestations of ageing at the molecular level. They found that the process of reading genetic information does not run as smoothly in older individuals as it does in younger ones. These changes in the transcription process are due to particular RNA molecules that influence the activity of individual genes and thus determine which proteins the body produces – physiological ...
University of Cincinnati research examines the role of genetics in opioid use disorder
2023-04-27
New research out of the University of Cincinnati examines the association between genetics and the presence of opioid use disorder (OUD). The study identified six single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) or genetic variants that are linked to OUD.
The study was published in the journal Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics.
“We are trying to identify some of the genetic variants that might play into OUD,” says Caroline Freiermuth, MD, associate professor in the Department of Emergency ...
Light-based computing scheme reduces power needed to mine cryptocurrencies
2023-04-27
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new light-based computing scheme that uses a photonic integrated circuit to reduce the energy necessary for cryptocurrency and blockchain applications. Mining cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin—a process of verifying transactions and adding new cryptocurrency to the blockchain—consumes up to 1% of the world’s energy. This energy expenditure is expected to grow as cryptocurrency and blockchain applications become increasingly mainstream.
Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies created using encryption algorithms. These alternative currencies require ...
CityU establishes the first UNESCO Regional Training and Research Centre on coastal contaminant monitoring in Hong Kong for the Western Pacific region
2023-04-27
The State Key Laboratory of Marine Pollution (SKLMP) of City University of Hong Kong (CityU) received approval from the UNESCO Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) Sub-Commission for the Western Pacific (WESTPAC) to establish the first UNESCO regional training and research Centre (the Coastal-COMMIT Centre, also known as the “Centre”) on coastal contaminant monitoring and marine innovative technologies in Hong Kong for the Western Pacific region.
The Centre aims to strengthen the monitoring capacity for marine pollution in the Western Pacific region, promote the development of marine innovation ...
James Fast selected as Jefferson Lab EIC project manager
2023-04-27
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility and DOE’s Brookhaven National Laboratory partnered early on to take on the design and construction of the Electron-Ion Collider. To keep the project moving forward, Jefferson Lab tapped members of its experienced leadership team to ensure project success. Now, Jefferson Lab is proud to announce it has appointed a dedicated EIC project manager: James Fast will lead the lab’s EIC project team and honor the lab’s project commitments going forward.
“The EIC project is central to the future of ...
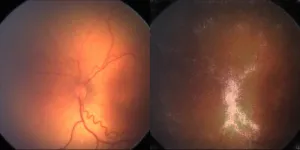
AI breakthrough in detecting leading cause of childhood blindness
2023-04-27
The team developed a deep learning AI model that can identify which at-risk infants have ROP that may lead to blindness if left untreated, and they hope their technique could improve access to screening in the many areas with limited neonatal services and few trained ophthalmologists.
The study, by an international team of scientists and clinicians in the UK, Brazil, Egypt and the US, supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at Moorfields Eye Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and UCL Institute of Ophthalmology, is published in The Lancet Digital Health.
Lead author Dr Konstantinos Balaskas ...
Why people include themselves in photos
2023-04-27
Embargoed until 9 AM ET on Thursday, April 27, 2023
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study may help explain why people choose to include themselves in some photos – and it is not vanity.
Researchers found that first-person photos (capturing the scene as it looks from one’s own eyes) best represent the physical experience of an event for people.
But third-person photos like selfies (documenting a moment with themselves in it) better depict the deeper meaning of the event in their lives.
“We found that people have a natural intuition about which perspective to take to capture what they want out ...
Selfies and other third-person photos help us capture the meaning of moments
2023-04-27
Imagine you are eating your dream meal and want to commemorate the moment: Should you snap a picture of the food by itself or take a selfie with your partner while you eat? New research suggests that people use first-person photography, taking a photo of the scene from one’s own perspective, when they want to document a physical experience, but opt for third-person photos, depicting themselves in the scene (like selfies), to capture the deeper meaning of events.
Previous research has focused how the photo-taker wants to present themselves to others. The current research, published today in Social Psychological and Personality Science, ...
How can we fight blood cancer more effectively?
2023-04-27
Multiple myeloma is a rare blood cancer caused by the uncontrolled multiplication of abnormal plasma cells. These plasma cells are a special type of white blood cells that play an important role in the immune system by producing essential antibodies in the bone marrow and lymph nodes.
Despite an increasing number of approved drugs and treatment approaches such as immunotherapy becoming available, the disease is still not curable. The average life expectancy of patients after diagnosis is only five years.
One of the main challenges is the cancer’s tendency to return even after treatment. This is because treatment makes the cancer cells ...