(Press-News.org) The 819-day calendar used by ancient Mayans has long stumped researchers, but anthropologists from Tulane University may have finally deciphered its secrets.
Researchers long suspected the calendar followed astronomical events, specifically how long it takes a planet to appear in the same place in the night sky as seen from Earth, known as the synodic periods of planets. But, according to the study published in Ancient Mesoamerica, the cycles in the Maya calendar cover a much larger timeframe than scholars previously thought.
“Although prior research has sought to show planetary connections for the 819-day count, its four-part, color-directional scheme is too short to fit well with the synodic periods of the visible planets,” wrote anthropologists John Linden, a Tulane alumnus, and Victoria Bricker, PhD, professor emerita at Tulane University School of Liberal Arts. “By increasing the calendar length to 20 periods of 819-days, a pattern emerges in which the synodic periods of all the visible planets commensurate with station points in the larger 819-day calendar.”
Previously, researchers thought the calendar referred to four cycles of 819, but that time span didn’t sync neatly with the synodic periods of all the planets that can be seen with the naked eye: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. The researchers discovered it takes 20 cycles of 819 days, which is about 45 years, to align with the synodic periods of all visible planets.
Within 20 cycles, each planet goes through some number of synodic periods a whole number of times: Mercury every cycle, Venus every 5 cycles, Saturn every 6 cycles, Jupiter every 19 cycles, and Mars every 20 cycles.
Each synodic period is less than 819 days, but only Mercury has one that happens a whole number of times within a single cycle. Combining the cycles allows for prediction of the placement of the planets, which Linden and Bricker say is also connected to important dates and celebrations.
“Rather than limit their focus to any one planet, the Maya astronomers who created the 819-day count envisioned it as a larger calendar system that could be used for predictions of all the visible planet's synodic periods,” the authors wrote.
This research is a key part of understanding how the ancient Maya studied astronomy and is part of a decades-long quest to understand the complexity of ancient Maya calendars.
END
Researchers solve ancient mystery of Maya calendar
2023-04-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
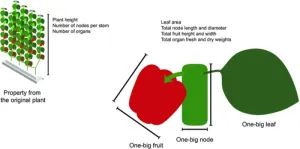
A versatile deep-learning model for accurate prediction of plant growth
2023-04-27
Crop yield can be maximized when the best genetic variety and most effective crop management practices are used for cultivation. Scientists have developed various machine learning models to predict the factors that produce the greatest yield in specific crop plants. However, traditional models cannot accommodate high levels of variation in parameters or large data inputs. This can lead to the failure of models under certain circumstances. Also, since crop models are restricted to the types of input they can accommodate, ...
Speedy robo-gripper reflexively organizes cluttered spaces
2023-04-27
When manipulating an arcade claw, a player can plan all she wants. But once she presses the joystick button, it’s a game of wait-and-see. If the claw misses its target, she’ll have to start from scratch for another chance at a prize.
The slow and deliberate approach of the arcade claw is similar to state-of-the-art pick-and-place robots, which use high-level planners to process visual images and plan out a series of moves to grab for an object. If a gripper misses its mark, it’s back to the starting point, where the controller must map out a new plan.
Looking to give ...
Mason researchers explore techniques to successfully reintroduce captive birds into the wild
2023-04-27
Studies show that some species may require breeding in captivity within the next 200 years to avoid extinction. This reality places heavy importance on the reintroduction practices used to successfully transfer species from captivity to the wild. A new study from George Mason University looks at some of the most popular conservation techniques and identifies which have the highest likelihood of success for the reintroduction of bird species back into the wild.
George Mason doctoral student Jessica Roberts and biology professor Dr. David Luther examined various conservation management methods from the past 50 years to identify the most successful ...
New test reveals existing antibiotics, hiding in plain sight on pharmacy shelves, can cure superbugs
2023-04-27
A new test revealed that FDA-approved antibiotics — available at your neighborhood pharmacy — can effectively treat superbugs. They are not prescribed, however, because the gold-standard test predicts they will not work. The new test may improve the way antibiotics are developed, tested and prescribed — and it is openly available to all.
The research has significant implications in the fight against bacterial resistance by optimizing the prescription and use of currently available antibiotics and enhancing the efforts to discover new ones.
Developed by a research team of UC Santa Barbara scientists, the antibiotic study was published in the ...
As the California sea lion population got bigger, so did male sea lions
2023-04-27
Animals tend to get smaller as their populations grow because of increased competition for food resources among members of the same species. That’s not what has happened with California sea lions, however, according to a new study led by scientists at UC Santa Cruz.
Published April 27 in Current Biology, the study found that male California sea lions have gotten bigger as the population grew over the past 50 years, while female body size has remained stable.
“It’s counterintuitive. You would expect that their body size would decrease as dietary resource competition intensified,” said coauthor Paul Koch, professor of Earth and planetary sciences at UCSC.
The ...
In a ‘rapid autopsy’ study, UCLA researchers identify lethal molecular alterations after present-day therapies fail patients with metastatic melanoma
2023-04-27
In a new translational study from UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, researchers analyzed genetic changes in the organs of recently deceased patients to understand how metastatic cutaneous melanoma spreads in those who had initially benefited from precision therapies. Results are published online ahead of print in Nature Medicine.
The researchers, including collaborators at the Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center in Chapel Hill, North Carolina, and the Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center in Nashville, Tennessee, said unveiling the landscape of DNA and RNA alterations ...
New pancreatic cancer research could boost survival rates
2023-04-27
A unique treatment combining radiation and immunotherapy can eradicate pancreatic tumors while stopping the cancer from spreading, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Colorado Cancer Center.
The study, published today in the journal Cancer Cell, offers new hope to those with this often deadly disease.
“This is the first time we’ve seen the eradication of a pancreatic tumor that suggests the cancer cell has memory, meaning we can stop the disease from coming back,” said lead author Sana Karam, MD, PhD, member of the CU ...
ChatGPT scores nearly 50 per cent on board certification practice test for ophthalmology, study shows
2023-04-27
A study of ChatGPT found the artificial intelligence tool answered less than half of the test questions correctly from a study resource commonly used by physicians when preparing for board certification in ophthalmology.
The study, published in JAMA Ophthalmology and led by St. Michael’s Hospital, a site of Unity Health Toronto, found ChatGPT correctly answered 46 per cent of questions when initially conducted in Jan. 2023. When researchers conducted the same test one month later, ChatGPT scored more than 10 per cent higher.
The potential of AI in medicine and exam preparation ...
Ecology: Over 64% of suitable elephant habitat lost across Asia since 1700
2023-04-27
Habitats suitable for Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) across Asia have decreased by over 64% – equating to 3.3 million square kilometres of land – since the year 1700, estimates a study published in Scientific Reports. The authors suggest that habitat loss from 1700, after centuries of relative stability, coincides with the colonial-era use of land and subsequent agricultural intensification in South Asia.
Asian elephants live in a range of habitats including grasslands and rainforests, but with increasing human use of land and habitat loss, elephants can come ...
Citing growing evidence of harm to child health and learning ability, advocates call for faster replacement of diesel school buses
2023-04-27
Health and environmental advocates today called on communities, school boards and governments at every level to accelerate the electrification of school buses, replacing tens of thousands of diesel-powered school buses spewing toxic fumes that can seriously harm child health and interfere with learning.
Led by the Canadian Partnership for Children’s Health and Environment (CPCHE), a coalition of 34 organisations made the goal of all-electric school bus fleets in Canada the central focus of this year’s national Healthy Environments for Learning Day (April 27).
The joint call for urgent action by ...