(Press-News.org) NAIROBI, Kenya, 20 April 2023_An international team of researchers, led by Africans, has fully sequenced the genome of a climate resilient bean that could bolster food security in drought-prone regions.
The sequencing of the hyacinth bean or ‘lablab bean’ [Lablab purpureus] paves the way for wider cultivation of the crop, bringing nutritional and economic benefits, as well as much needed diversity to the global food system.
The plant is native to Africa and is cultivated throughout the tropics producing highly nutritious beans, which are used for food and livestock feed. It’s extremely drought-resilient and thrives in a range of environments and conditions, contributing to food and economic security, and improving soil fertility by fixing nitrogen. Lablab is also used medicinally in some areas and contains bioactive compounds with
Diversifying the global food system
The lablab bean is one of a long list of ‘orphan crops’: indigenous species that play an important role in local nutrition and livelihoods, but that receive little attention from breeders and researchers.
The three major crops that currently provide over 40 percent of global calorie intake – wheat, rice, and corn – receive the bulk of breeding and crop improvement efforts. With so little diversity in crop cultivation, the global food system is vulnerable to environmental and social instabilities. Underutilised crops like lablab hold the key to diversified and climate-resilient food systems and genome-assisted breeding is one promising strategy to improve their productivity and adoption.
Oluwaseyi Shorinola, another of the study’s lead authors from the International Livestock Research Institute, and a visiting scientist at the John Innes Centre in the United Kingdom, said, “The first green revolution was achieved with major crops like wheat and rice. Orphan crops like lablab could pave the way for the next green revolution.”
African-led research
The research process itself was ground-breaking not only for its inclusivity but also for its leadership by African scientists. “Although many African indigenous crops have been sequenced in the past few years, in most of that work African scientists have been underrepresented, and when we’ve been involved we have been in the back seat,” said Meki Shehabu, another co-author of the study and a scientist at ILRI in Ethiopia. “What makes this project special is that it is led by African scientists, in collaboration with scientists from international institutes.”
--
Notes for Editors
For further information and interviews with Chris Jones or Meki Shehabu at the International Livestock Research Institute, please contact: David Aronson, Media Relations, d.aronson@cgiar.org +254 717 868916.
The International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) works with partners worldwide to enhance the roles that livestock play in food security and poverty alleviation, principally in Africa and Asia. ILRI’s mission is to improve food and nutritional security and to reduce poverty in developing countries through research for efficient, safe and sustainable use of livestock—ensuring better lives through livestock. www.ilri.org
The University of Southampton drives original thinking, turns knowledge into action and impact, and creates solutions to the world’s challenges. We are among the top 100 institutions globally (QS World University Rankings 2023). Our academics are leaders in their fields, forging links with high-profile international businesses and organisations, and inspiring a 22,000-strong community of exceptional students, from over 135 countries worldwide. Through our high-quality education, the University helps students on a journey of discovery to realise their potential and join our global network of over 200,000 alumni. www.southampton.ac.uk
The John Innes Centre is an independent, international centre of excellence in plant science and microbiology. Our mission is to generate knowledge of plants and microbes through innovative research, to train scientists for the future, to apply our knowledge of nature’s diversity to benefit agriculture, the environment, human health, and wellbeing.
END
New bean genome unveils potential to boost food security and resilience in drought-prone regions
Results pave way for genetic improvements of native legume to promote widespread cultivation that could yield nutritional and economic benefits
2023-04-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
El Niño–Southern Oscillation correlates well with following-summer cloud-to-ground lightning in China
2023-04-28
Large-scale circulation anomalies are a key factor in the transportation of water vapor and changes in climate. For tropical and subtropical regions, an atmospheric circulation field not only determines the characteristics of the weather situation but also influences the atmospheric circulation in the middle and high latitudes, as well as the global climate, through the transport of energy and angular momentum. At the same time, whilst lightning can serve as a global tropical “thermometer” and an indicator of water vapor in the upper troposphere, the driving role of the circulation situation for it needs to be further analyzed.
In a paper recently ...
An artificial intelligence method for rapid plant phenotyping under complex conditions
2023-04-28
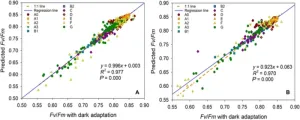
During photosynthesis, the green pigment chlorophyll in algae and plants absorbs most of the energy from incoming light. Chlorophyll gets excited and transfers this energy to the energy-harvesting protein complexes photosystem I (PSI) and II (PSII). However, some of this energy dissipates as heat or chlorophyll a fluorescence (ChlF).
Changes in the environment or plant physiology that affect PSII also alter ChlF, which can therefore be used as a fast, sensitive, and non-destructive indicator of PSII status. Indeed, ChlF is a powerful tool for assessing multiple aspects of photosynthesis. Though ChlF measurements ...
Tip sheet: Studies on behavioral concerns tied to a commonly used chemical and youth COVID-19 vaccination rates among Johns Hopkins research to be featured at National Pediatrics Meeting
2023-04-28
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
What: Pediatric Academic Societies (PAS) 2023 Meeting
When: April 27 to May 1
Where: Walter E. Washington Convention Center (801 Mt Vernon Pl NW, Washington, DC 20001)
Johns Hopkins Children’s Center researchers will present on numerous topics during the PAS 2023 meeting, including:
System-Level Approach to Improve First COVID-19 Vaccine Dose Uptake in a Primary Care Setting: The Value of Health Educators
Monday, May 1, 1 to 2:30 p.m. Eastern time
Convention Center: 204 C
Oral Abstract
COVID-19 vaccination rates among youth ...
Study shines light on impact of environment on neurocognitive outcomes
2023-04-28
To gain a clearer understanding of the differences between childhood cancer patients when it comes to the impact of radiation therapy on cognition, scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital studied the effect of their environment. Their work showed that children with supportive environments fared better than children living in neighborhoods with economic hardship. Those in areas with greater economic hardship had worse baseline and long-term cognitive outcomes. The results imply that policies and resources providing support at a neighborhood level ...
6% of nations provide for citizens in just, sustainable manner
2023-04-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers at The Ohio State University have developed a framework for quantifying how well countries around the world are doing at providing adequate food, energy and water to their citizens without exceeding nature’s capacity to meet those needs.
They found that only 6% of 178 countries provide for all their citizens in an ecologically sustainable way in both carbon sequestration and water consumption.
The study found that while 67% of nations operate safely and sustainably in regard to water use, only 9% do in regard to carbon sequestration, ...
IVI begins clinical development of DuoChol oral cholera vaccine
2023-04-28
The International Vaccine Institute, an international organization with a mission to discover, develop, and deliver safe, effective, and affordable vaccines for global health, began clinical development of DuoChol, a new low-cost oral cholera vaccine (OCV) in capsule form. With funding support from the Wellcome Trust and the Swedish government, IVI is preparing to conduct a Phase I clinical trial of the vaccine in Sweden.
Scientists at the University of Gothenburg developed DuoChol, a dry formulation inactivated bacterial whole cell/cholera toxin B subunit OCV with a similar composition as the world’s first WHO-prequalified OCV, DUKORAL®. ...
Astronomers detect the closest example yet of a black hole devouring a star
2023-04-28
Once every 10,000 years or so, the center of a galaxy lights up as its supermassive black hole rips apart a passing star. This “tidal disruption event” happens in a literal flash, as the central black hole pulls in stellar material and blasts out huge amounts of radiation in the process.
Astronomers know of around 100 tidal disruption events (TDE) in distant galaxies, based on the burst of light that arrives at telescopes on Earth and in space. Most of this light comes from X-rays and optical radiation.
MIT astronomers, tuning past the conventional X-ray and UV/optical bands, have discovered a new ...
Old dogs with dementia sleep less deeply, just like people with Alzheimer’s
2023-04-28
In people with Alzheimer’s, the earliest symptoms are commonly disruptions in sleep rhythms. These include daytime sleepiness, showing agitation or confusion around dusk, staying awake longer, and waking up often at night. These changes are thought to result from damage to sleep-regulating areas in the brain. Alzheimer patients tend to spend less time in both REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, in which most dreaming occurs, and non-REM (NREM) sleep. But they show the greatest reduction in so-called slow-wave sleep (SWS) – a stage of non-dreaming deep sleep, characterized by slow ‘delta’ brain waves (0.1 to ...
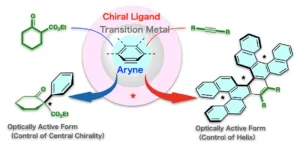
Review article on asymmetric synthesis using arynes
2023-04-28
Arynes, synthetic intermediates in which a portion of the benzene ring is a triple bond, have been applied in various organic molecular transformations and have long been of interest to chemists as extremely useful compounds. Furthermore, with the advancement in aryne chemistry, the development of “asymmetric synthesis” reactions of arynes, which are expected to increase the efficiency of the synthesis of compounds with complex steric structures and facilitate the creation of new compounds, has attracted increasing attention.
However, asymmetric synthesis based on arynes, which are extremely reactive and unstable, presents several challenges. Therefore, asymmetric ...
Study: Hypothermia more likely in Black, Asian newborns
2023-04-28
Newborns of Black and Asian mothers are significantly more likely to experience hypothermia than those born to white mothers, according to a new study. The research will be presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies (PAS) 2023 Meeting, held April 27-May 1 in Washington, D.C.
Researchers reviewed electronic medical records of 23,549 infants born at 35 weeks or later and admitted to a children’s hospital-affiliated newborn nursery between 2015 and 2021. The study evaluated all recorded temperatures ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
[Press-News.org] New bean genome unveils potential to boost food security and resilience in drought-prone regionsResults pave way for genetic improvements of native legume to promote widespread cultivation that could yield nutritional and economic benefits