(Press-News.org) The green hydrogen economy is a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. However, one of the challenges of constructing a global hydrogen economy is hydrogen transportation by sea. A new paper proposes solid air as a medium for recycling cold energy across the hydrogen liquefaction supply chain.
The world is undergoing an energy transition to reduce CO2 emissions and mitigate climate change. The COVID-19 pandemic and the Russia-Ukraine war have further increased the interest of Europe and Western countries to invest in the hydrogen economy as an alternative to fossil fuels. Hydrogen can significantly reduce geopolitical risks if the diversity of future hydrogen energy suppliers is increased.
Hydrogen is a particularly challenging product to transport safely. One option is to liquefy hydrogen, which requires cooling to 20 Kelvin (-253 °C). This is an expensive process and requires around 30% of the energy stored within the hydrogen.
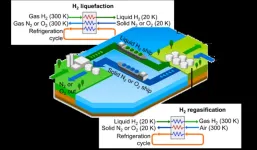
A pioneering approach developed by IIASA researchers and colleagues proposes solid air (nitrogen or oxygen) as a medium for recycling cooling energy across the hydrogen liquefaction supply chain. At standard temperature and pressure, air is a gas, but under certain conditions, it can become a liquid or solid. Solid Air Hydrogen Liquefaction (SAHL) consists of storing the cooling energy from the regasification of hydrogen, by solidifying air, and transporting the solid air back to where the hydrogen was liquefied. The solid air is then used to reduce the energy consumption for liquefying hydrogen. The process is divided into four main steps: hydrogen regasification, solid air transportation, hydrogen liquefaction, and liquid hydrogen transportation.
Another advantage of solidifying air for energy recovery in the hydrogen liquefaction supply chain is the extra production of oxygen. The oxygen could be used to increase the efficiency of power generation with oxy-combustion and to facilitate the capture, use, and storage of carbon (CCUS).
“Using solid air as a medium for recycling cooling energy across the hydrogen liquefaction supply chain can reduce the cost and energy consumption for transporting hydrogen between continents,” says lead author Julian Hunt, a researcher in the Integrated Assessment and Climate Change Research Group of the IIASA Energy, Climate, and Environment Program. “This would increase the viability of a global hydrogen economy in the future and increase the number of hydrogen suppliers for energy-demanding regions, such as China, Europe, and Japan. The possibility of selling hydrogen could result in a further expansion of solar and wind power in developing countries, contributing to their economies.”
In their paper, the authors also address the ongoing debate in industry and academia to find the best alternative to transport hydrogen by sea:
“Compared to ammonia or methanol, liquefied hydrogen is the best option for several reasons. Transporting hydrogen with ammonia and other molecules would require around 30% of the energy transported to extract the hydrogen. The hydrogen is liquefied where electricity is cheap. Also, SAHL can lower energy consumption for hydrogen liquefaction by 25 to 50%,” Hunt concludes.
Reference
Hunt, J., Montanari, P., Hummes D., Taghavi M., Zakeri, B., Romero, O., Zhou, W., Castro, J., Schneider, P., Wada, Y. (2023). Solid air hydrogen liquefaction, the missing link of the hydrogen economy. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.03.405
About IIASA:
The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) is an international scientific institute that conducts research into the critical issues of global environmental, economic, technological, and social change that we face in the twenty-first century. Our findings provide valuable options to policymakers to shape the future of our changing world. IIASA is independent and funded by prestigious research funding agencies in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Europe.
END
How solid air can spur sustainable development
2023-04-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Deep-learning system explores materials’ interiors from the outside
2023-04-28
CAMBRIDGE, MA — Maybe you can’t tell a book from its cover, but according to researchers at MIT you may now be able to do the equivalent for materials of all sorts, from an airplane part to a medical implant. Their new approach allows engineers to figure out what’s going on inside simply by observing properties of the material’s surface.
The team used a type of machine learning known as deep learning to compare a large set of simulated data about materials’ external force fields and the corresponding internal structure, and used that to generate a ...
Solving computationally complex problems with probabilistic computing
2023-04-28
According to computational complexity theory, mathematical problems have different levels of difficulty in the context of their solvability. While a classical computer can solve some problems (P) in polynomial time — i.e., the time required for solving P is a polynomial function of the input size — it often fails to solve NP problems that scale exponentially with the problem size and thus cannot be solved in polynomial time. Classical computers based on semiconductor devices are, therefore, inadequate ...
York University leads $318.4M first-of-kind inclusive next-gen technology research initiative
2023-04-28
TORONTO, April 28, 2023 — Is an equitable world that includes humans and machines possible? York University researchers believe it must be and have set out to make it so through a first of its kind interdisciplinary research initiative called Connected Minds: Neural and Machine Systems for a Healthy, Just Society.
From universities to industries, hospitals and policymakers, artists and Indigenous communities, York’s Connected Minds will engage 50+ community partners and research collaborators over seven years supported by a historic $318.4 million in funding. Connected Minds has received a combined $105.7 million from the Canada First Research ...
Shocking implications of electric fishes’ tailless sperm
2023-04-28
Betting on tailless sperm that evolved from brave swimmers to hapless floaters seems like a crazy evolutionary gamble, but a group of fish seems to have done just that. Understanding that tradeoff holds promise to shed light on human disease and shake up biology lessons on traditional gender roles.
Michigan State University associate professor of integrative biology Jason Gallant and colleagues are using nearly $1 million from the National Science Foundation to understand the implications from a small African fish which ...
Insilico Medicine founder and CEO Alex Zhavoronkov, Ph.D., presents at LSX World Congress
2023-04-28
Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD, founder and CEO of Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”) will present at the 9th LSX World Congress happening in London May 3 and May 4. Zhavoronkov, an expert in generative artificial intelligence (AI) for drug discovery, will present on May 3, 2:45pm (London time) on “‘Death By Pilot’” to Asset Licensing – the Evolution of Pharma-AIDD Partnerships” as part of the Biotech Growth CEO Forum and on May 4, 9:30am (London time) on “Building a Galvanizing ...
Texas Neurologist and Professor elected New American Academy of Neurology President
2023-04-28
MINNEAPOLIS – The American Academy of Neurology (AAN), the world’s largest professional association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, has elected as its 38th president Carlayne E. Jackson, MD, FAAN, a neurologist, researcher and professor of neurology and otolaryngology at the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. Jackson succeeds Orly Avitzur, MD, MBA, FAAN, who completed her two-year term as president during the recent AAN Annual Meeting.
“It’s humbling to have been chosen by my colleagues to follow such talented and dedicated individuals ...
First comprehensive care plan to prevent preeclampsia published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology
2023-04-28
Recommendations for high-risk expecting parents and health care providers to promote the prevention of preeclampsia, a leading cause of pregnancy-related death in the United States
SAN FRANCISCO - April 28, 2023 – A new special report published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology (AJOG) provides a groundbreaking approach to preeclampsia, one of the most pressing issues in maternal health today, and will translate the prediction of risk into prevention of disease.
The report, ...
Max-difference maximization criterion: A feature selection method for text categorization
2023-04-28
For text categorization, it is necessary to select a set of features(terms) with high discrimination by using feature selection. In text feature selection, Accuracy2(ACC2)treats terms with same absolute document rate difference but different discrimination equally, which is unreasonable. Existing improved methods (normalized difference measure(NDM), max-min ratio(MMR)and trigonometric comparison measure(TCM)) based on ACC2 may confuse the importance of rare and sparse terms on account of challenge for parameter selection.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Li Zhang published their new research on 15 February 2023 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published ...
U of T receives $200-million grant to support Acceleration Consortium's ‘self-driving labs’ research
2023-04-28
The University of Toronto has been awarded a $200-million grant from the Canada First Research Excellence Fund (CFREF) to revolutionize the speed and impact of scientific discovery through its Acceleration Consortium. The funding – the largest federal research grant ever awarded to a Canadian university – will support the consortium’s work on “self-driving labs” that combine artificial intelligence, robotics and advanced computing to discover new materials and molecules in a fraction of the usual time and cost. Applications include everything from life-saving medications ...
Scientists identify antivirals that could combat emerging infectious diseases
2023-04-28
A new study has identified potential broad-spectrum antiviral agents that can target multiple families of RNA viruses that continue to pose a significant threat for future pandemics. The study, led by Gustavo Garcia Jr. in the UCLA Department of Molecular and Medical Pharmacology, tested a library of innate immune agonists that work by targeting pathogen recognition receptors, and found several agents that showed promise, including one that exhibited potent antiviral activity against members of RNA viral families.
The ongoing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, which ...