(Press-News.org) About The Study: The intervention examined in this randomized clinical trial resulted in improvements in the receipt of preventive care services versus usual care for children insured by Medicaid by incorporating community health workers in a team-based approach to early childhood well-child care.
Authors: Tumaini R. Coker, M.D., M.B.A., of Seattle Children’s Research Institute in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.7197)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: This study is being released to coincide with presentation at the Pediatric Academic Societies 2023 meeting.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2023.7197?guestAccessKey=63659d5e-9e4d-4dc1-a6c0-c006c859d9eb&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=043023
END
Community health workers in early childhood well-child care for Medicaid-insured children
JAMA
2023-04-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Prostate cancer in transgender women in the VA health system
2023-04-29
About The Study: This case series demonstrated that prostate cancer occurs in transgender women and is not as rare as published case reports might suggest. However, rates were lower than expected based on prior prostate cancer incidence estimates in cisgender male veterans.
Authors: Farnoosh Nik-Ahd, M.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.6028)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
Transgender women are still at risk for prostate cancer
2023-04-29
Transgender women keep their prostates even after gender-affirming surgery, but the extent to which they remain at risk of prostate cancer has been unclear.
Now a first of its kind study led by UC San Francisco has estimated the risk at about 14 cases per 10,000 people.
The study drew on 22 years of data from the Veterans Affairs Health System. Although the sample size was necessarily small, it is still the largest study of its kind. It publishes Saturday, April 29, 2023 in the Journal ...
New Jersey’s temporary health care license program expanded mental health services during pandemic
2023-04-29
At least 3,700 out-of-state mental health providers utilized New Jersey’s COVID-19 Temporary Emergency Reciprocity Licensure program to provide mental health services to more than 30,000 New Jersey patients during the first year of the pandemic, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, published in The Journal of Medical Regulation, surveyed health care practitioners who received a temporary license in New Jersey to examine the impact of the temporary licensure program on access to mental health care.
“The New Jersey program enabled patients with ...
Scientists pinpoint where compound that helps metabolism hangs out in muscle cells
2023-04-29
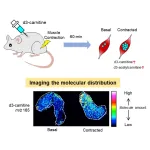
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a way of mapping the distribution of carnitine in skeletal muscle cells. Carnitine is a small compound that helps transport fatty acids and reduce metabolic byproducts. They discovered that slow-type muscle fibers contained the most, and that activity promptly led to rises in acetylcarnitine, a product of the immediate response of carnitine contained in the cell. Their technique promises new insights into how muscle cells work.
Our muscles require ...
Previously unknown intracellular electricity may power biology
2023-04-28
The human body relies heavily on electrical charges. Lightning-like pulses of energy fly through the brain and nerves and most biological processes depend on electrical ions traveling across the membranes of each cell in our body.
These electrical signals are possible, in part, because of an imbalance in electrical charges that exists on either side of a cellular membrane. Until recently, researchers believed the membrane was an essential component to creating this imbalance. But that thought was turned on its head when researchers at Stanford University discovered that similar imbalanced electrical ...
Doubling the number of sources of repeating fast radio bursts
2023-04-28
Astronomers from McGill University are part of an international team that has discovered 25 new sources of repeating fast radio bursts (FRBs), these explosions in the sky that come from far beyond the Milky Way. This discovery brings the total number of confirmed FRB sources to 50. Based on data gathered by the CHIME/FRB collaboration, the new study, published this week in The Astrophysical Journal, may also bring scientists closer to understanding the origins of these mysterious phenomena.
A new way of identifying FRBs
Thanks to the radio telescopes such as those at CHIME, which scan the entire northern sky every day, the number of detected FRBs has grown exponentially in recent years. ...
Previously unknown intercellular electricity may power biology
2023-04-28
The human body relies heavily on electrical charges. Lightning-like pulses of energy fly through the brain and nerves and most biological processes depend on electrical ions traveling across the membranes of each cell in our body.
These electrical signals are possible, in part, because of an imbalance in electrical charges that exists on either side of a cellular membrane. Until recently, researchers believed the membrane was an essential component to creating this imbalance. But that thought was turned on its head when researchers at Stanford University discovered that similar imbalanced electrical charges can exist between microdroplets of water ...
Texas A&M research redefines mammalian tree of life
2023-04-28
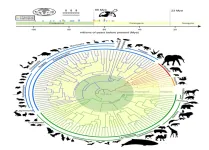
Research led by a team of scientists from the Texas A&M School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences puts to bed the heated scientific debate regarding the history of mammal diversification as it relates to the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs. Their work provides a definitive answer to the evolutionary timeline of mammals throughout the last 100 million years.
The study, published in Science, is part of a series of articles released by the Zoonomia Project, a consortium of scientists from around the globe that is using the largest mammalian genomic dataset in history to determine the evolutionary history of the human genome in the context of mammalian evolutionary history. ...
Twelve outstanding journalists named 2023 MBL Logan Science Journalism Fellows
2023-04-28
WOODS HOLE, Mass. –Twelve accomplished science and health journalists have been awarded a highly competitive fellowship in the Logan Science Journalism Program at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL).
Now in its 36th year, the Logan Science Journalism Program provides journalists with immersive, hands-on research training, giving them invaluable insight into the practice of science as well as some of the major news stories of today. The program, which offers a Biomedical course and an Environmental course, will run May 30-June 9 in Woods Hole.
Biographies ...
Improved gene editing method could power the next generation of cell and gene therapies
2023-04-28
PHILADELPHIA— A new approach to the genetic engineering of cells promises significant improvements in speed, efficiency, and reduction in cellular toxicity compared to current methods. The approach could also power the development of advanced cell therapies for cancers and other diseases, according to a study from researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
In the study, which appeared this week in Nature Biotechnology, researchers found that protein fragments used by some viruses to help them get into cells could ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Community health workers in early childhood well-child care for Medicaid-insured childrenJAMA