(Press-News.org) Joan Casey lived through frequent wildfire-season power outages when she lived in northern California. While waiting for the power to return, she wondered how the multi-day blackouts affected a community’s health.
“For me it was an inconvenience, but for some people it could be life-threatening,” said Casey, now an assistant professor in the University of Washington’s Department of Environmental and Occupational Health Sciences. “If you had an uncle that had an electric heart pump, basically, his heart wouldn’t work without power. You could use a backup battery for eight hours, but after that, if you don’t have access to electricity, you have to go to the emergency room. This is a really dangerous situation.”
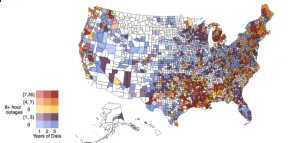
Years later, Casey has answers. A study published April 29 in the journal Nature Communications analyzed three years of power outages across the U.S., finding that Americans already bearing the brunt of climate change and health inequities are clustered in four regions — Louisiana, Arkansas, central Alabama and northern Michigan — and that they are most at risk of impact by a lengthy blackout.
The findings could help shape the future of local energy infrastructure, especially as climate change intensifies and the American power grid continues to age. Last year’s Inflation Reduction Act included billions of dollars to revamp energy systems, and Casey hopes federal agencies will consult the newly published findings to target energy upgrades.
The study is the first county-level analysis of power outages, which the federal government reports only at the state level. That poses a problem for researchers: a federally reported outage in Washington state could occur in Seattle, Spokane, or somewhere in between, making it difficult to understand specifically which population is affected.
Casey and her team found that between 2018 and 2020, more than 231,000 power outages lasting more than an hour occurred nationwide. Of those, 17,484 stretched at least eight hours — a duration widely viewed as medically relevant.
Most counties that experienced an electrical outage had at least one event lasting more than eight hours. These counties were most concentrated in the South, Northeast and Appalachia.
Next, researchers looked at how power outages overlapped with severe weather. They wanted to know which weather events are most likely to cause an outage, and which parts of the U.S. are most often hit with a blackout-causing storm.
They found that heavy precipitation in a given area makes a power outage five times more likely. Tropical cyclones, storms with high winds that originate over tropical oceans, make a power outage 14 times more likely. And a tropical cyclone with heavy precipitation on a hot day — like the hurricanes that each fall hit the Gulf Coast? They make power outages 52 times more likely.
“We look at weather reports and decide whether or not to bring an umbrella or stay home,” Casey said. “But thinking about being prepared for an outage when one of these events is rolling through is a new element to consider.”
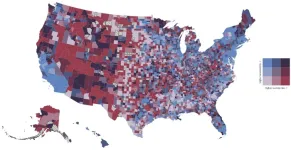
Then came questions of equity. Incorporating a combination of socioeconomic and medical factors, Casey’s team identified communities that would likely be especially vulnerable during a long power outage. Using that data, the researchers were able to identify communities that experienced both high social vulnerability and frequent power outages.
A map of those counties shows a bright cluster in Louisiana and Arkansas, with more clusters in central Alabama and northern Michigan. In those places especially, the country’s inevitable change in energy infrastructure provides the greatest opportunity to improve public health.
“Any time we can identify another factor that we can intervene on to get closer to health equity, it’s exciting,” Casey said. “I think we’re going to see tremendous change, especially in the way our energy systems are set up, in the next couple decades. It’s this huge opportunity to get equity into every conversation and talk about what we’re going to do to make two decades from now look different from where we are.”
This study began while Casey was a professor in Columbia University’s Mailman School of Public Health. Other authors are Vivian Do (first author), Heather McBrien, Nina Flores, Alexander Northrop and Jeffrey Schlegelmilch at Columbia University and Mathew Kiang at Stanford University. The research was funded by the National Institute on Aging and the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences.
For more information, contact Casey at jacasey@uw.edu.
END
Prolonged power outages, often caused by weather events, hit some parts of the U.S. harder than others
2023-05-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Columbia University study finds that improved access to mental health care is associated with reductions in suicide risk
2023-05-01
Amid historically high suicide rates and mental health care provider shortages, new research from Incite @ Columbia University suggests that interventions to alleviate mental health care access disparities can prevent unnecessary death and suffering. In an article pending publication in PNAS next week, “Differential Spatial-Social Accessiblity to Mental Health Care and Suicide," Daniel Tadmon and Peter S. Bearman find that in the United States improved access to mental health care is associated with reductions in suicide risk.
To enable this research, Tadmon and Bearman developed new methods of measuring access ...
Chances of eliminating HIV infection increased by novel dual gene-editing approach
2023-05-01
EMBARGO UNTIL: May 1, 2023 at 3 PM ET
Gene-editing therapy aimed at two targets – HIV-1, the virus that causes AIDS, and CCR5, the co-receptor that helps the virus get into cells – can effectively eliminate HIV infection, new research from the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University and the University of Nebraska Medical Center (UNMC) shows. The study, published online in the journal The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), is the first to combine a dual gene-editing strategy with antiretroviral ...
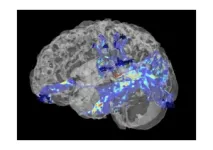
Scientists discover anatomical changes in the brains of the newly sighted
2023-05-01
CAMBRIDGE, MA — For many decades, neuroscientists believed there was a “critical period” in which the brain could learn to make sense of visual input, and that this window closed around the age of 6 or 7.
Recent work from MIT Professor Pawan Sinha has shown that the picture is more nuanced than that. In many studies of children in India who had surgery to remove congenital cataracts beyond the age of 7, he has found that older children can learn visual tasks such as recognizing ...
NYU Abu Dhabi study identifies brain structures that underlie sight recovery in blind teenagers
2023-05-01
Fast facts:
Congenital cataracts are the leading cause of treatable blindness in children worldwide. In nations where the surgery is widely available, surgery occurs during infancy and there is a good prognosis for the recovery of visual function.
It is widely accepted that the window for surgical intervention for congenital cataracts closes by the time a child reaches the ages of six to eight years old, as that is a critical period for visual brain development. Restoration of the visual input later in life is generally ...
Evidence of conscious-like activity in the dying brain
2023-05-01
[EMBARGOED UNTIL May 1, 2023 at 3:00 PM U.S. Eastern time]
Reports of near-death experiences--with tales of white light, visits from departed loved ones, hearing voices, among other attributes—capture our imagination and are deeply engrained in our cultural landscape.
The fact that these reports share so many common elements begs the question of whether there is something fundamentally real underpinning them—and that those who have managed to survive death are providing glimpses of a consciousness that does not completely disappear, even after the heart stops ...
50-year study offers insight into effects of climate on bird reproduction
2023-05-01
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new study reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences assessed changes in the reproductive output of 104 bird species around the world between 1970 and 2019. The study reveals that a warming climate appears to have more worrisome effects on larger birds and migratory birds than on smaller, sedentary species.
Study co-author Jeffrey Hoover, an avian ecologist at the Illinois Natural History Survey describes the findings in an interview with University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign life sciences editor Diana Yates.
Some highlights:
Increasing local temperatures during the chick-rearing part of the ...
Coal trains increase air pollution in San Francisco bay area
2023-05-01
Coal trains and terminal operations add a significant amount of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) pollution to urban areas, more so than other freight or passenger trains, according to a study conducted in Richmond, California, by the University of California, Davis.
The paper, published in the journal Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, is the first study of coal train particulate pollution in a U.S. urban area. It’s also the first to use artificial intelligence technologies to verify that the source of air pollution detected comes from coal.
It found that passing trains carrying ...
Silver nanoparticles spark key advance in thermoelectricity for power generation
2023-05-01
HOUSTON – Several high-performance thermoelectric materials have been discovered over the past two decades, but without efficient devices to convert the energy they produce into emission-free power, their promise has been unfulfilled. Now an international team of scientists led by a University of Houston physicist and several of his former students has reported a new approach to constructing the thermoelectric modules, using silver nanoparticles to connect the modules’ electrode and metallization layers.
The ...
A new method to test cancer drug toxicity
2023-05-01
For people with cancer, chemotherapy saves lives, but for some patients, the treatment comes with a side effect—heart damage. Screening cancer drugs for cardiotoxicity has been an ongoing challenge as heart cells don’t naturally grow in a dish, requiring researchers to do this critical testing using cardiac tissue from rodent models. A new study from researchers at Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University and Tufts Medical Center reports that heart tissue obtained through organ donations from dogs dying of other causes are a promising platform for testing cancer drug toxicity, offering scientists a new alternative.
The ...
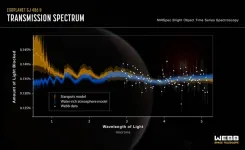
Webb finds water vapor, but from a rocky planet or its star?
2023-05-01
The most common stars in the universe are red dwarf stars, which means that rocky exoplanets are most likely to be found orbiting such a star. Red dwarf stars are cool, so a planet has to hug it in a tight orbit to stay warm enough to potentially host liquid water (meaning it lies in the habitable zone). Such stars are also active, particularly when they are young, releasing ultraviolet and X-ray radiation that could destroy planetary atmospheres. As a result, one important open question in astronomy is whether a rocky planet could maintain, or reestablish, an atmosphere in such a harsh environment.
To help answer that question, astronomers ...