(Press-News.org) Glucocorticoid therapy is widely used during pregnancies at risk of premature delivery to promote fetal lung maturation. While it is an effective treatment, it can also trigger heart and blood vessel problems. New research published in The FASEB Journal uncovers the mechanisms behind the cardiovascular-related effects of the most commonly used glucocorticoids, Dexamethasone (Dex) and Betamethasone (Beta).
When investigators treated chicken embryos with these different glucocorticoids, they found that both caused growth restriction, with Beta being more severe. At the level of the heart, both treatments promoted cellular stress and changes to the cell cycle, but via different molecular pathways. Whereas Dex induced oxidative stress and lowered the activation of the glucocorticoid receptor, Beta treatment led to sustained glucocorticoid receptor activation, and it did not induce oxidative stress. Beta compared with Dex induced greater cardiac dysfunction. Also, Dex triggered an increase in heart muscle cell numbers, but Beta promoted a decrease. In blood vessels, Beta impaired blood vessel dilation, whereas Dex resulted in greater blood vessel constriction.
The findings indicate that Dex and Beta have different detrimental effects on the developing cardiovascular system.
“Antenatal glucocorticoid therapy to accelerate fetal lung maturation in human pregnancy threatened with preterm birth is a life-saving treatment that should be maintained. However, it can also lead to problems with the heart and circulation in offspring that need attention,” said senior author Dino A. Giussani, PhD, ScD, FRCOG, of the University of Cambridge, in the UK. “Here, we use a model system to isolate the direct effects of the two most common glucocorticoids used in the clinic worldwide to reveal the molecular pathways involved. Such knowledge is indispensable to improve current therapy and maintain the beneficial effects of steroids on the developing lung while weeding out adverse side effects on the developing heart and circulation—making therapy safer for the preterm infant.”
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1096/fj.202200676RR
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
The FASEB Journal publishes high quality and impactful multidisciplinary research covering biology and biomedical sciences at every level of organization: atomic, molecular, cell, tissue, organ, organismic, and population. The journal’s scope includes the spectrum of biological and biomedical sciences as well as interdisciplinary research cutting across multiple fields and extending in related areas.
About Wiley
Wiley is one of the world’s largest publishers and a global leader in scientific research and career-connected education. Founded in 1807, Wiley enables discovery, powers education, and shapes workforces. Through its industry-leading content, digital platforms, and knowledge networks, the company delivers on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
How does glucocorticoid therapy affect the developing cardiovascular system during pregnancy?
2023-05-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cigarette butts leak deadly toxins into the environment
2023-05-03
Cigarette filters are the world’s most common form of litter. Researchers from the University of Gothenburg can now show that the filters leak thousands of toxins and plastic fibres that are toxic to aquatic larvae. The researchers are therefore calling for these filters to be completely banned.
On the footpath, at the bus stop, in the park and on the beach. You can hardly avoid seeing cigarette butts in the streetscape. And these butts aren’t just butt-ugly to behold – they’re also really bad for the environment. A research ...
Study questions long term beta blocker use to curb further heart attack risk
2023-05-03
The accepted clinical practice of using beta blockers over the long term to curb the risk of further heart attacks or death doesn’t seem to be warranted in patients who don’t have heart failure, suggests a large study published in the journal Heart.
The researchers found no difference in these risks between patients taking beta blockers more than a year after their heart attack and those who weren’t on these drugs.
Beta blockers are a class of drugs that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms, ...
Fresh hope for Australians living with chronic back pain
2023-05-03
Long-term sufferers of chronic back pain experienced dramatic reductions in pain and related disability that remained at their one-year follow-up after taking part in a new treatment tested by Curtin-Macquarie-Monash University research.
Published today in the leading medical journal The Lancet, the research found large clinically significant improvements in the intensity of pain and pain-related disability among almost 500 people who had been seeking help for their pain for an average of four years before trialling the new treatment.
The treatment, which delivered a healthcare and work productivity saving of more than $5000 per person, took a whole-person approach ...
Dogs may be at risk from high levels of lead from shotgun pellets in raw pheasant dog food, study finds
2023-05-03
PRESS RELEASE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
EMBARGOED UNTIL: 01:00 BST / LONDON TIME WEDNESDAY 3 MAY 2023
Paper available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1GNT9-oVOFTREzjGTSGMK7nIUvlYR61PE?usp=sharing
Dogs may be at risk from high levels of lead from shotgun pellets in raw pheasant dog food, study finds
Researchers tested samples of raw pheasant dog food and discovered that the majority contained high levels of lead that could put dogs’ health at risk if they eat it frequently. ...
Why mosses are vital for the health of our soil and Earth
2023-05-03
Some people see moss growing in their gardens as a problem, but what they may not realise is this ancient ancestor of all plants is bringing lots of benefits to our green spaces, such as protecting against erosion.
Now a massive global study led by UNSW Sydney has found mosses are not just good for the garden, but are just as vital for the health of the entire planet when they grow on topsoil. Not only do they lay the foundations for plants to flourish in ecosystems around the world, they may play an important role mitigating against climate change by capturing ...
Hongkui Zeng elected to the National Academy of Sciences
2023-05-03
Hongkui Zeng, Ph.D., Executive Vice President and Director of the Allen Institute for Brain Science, a division of the Allen Institute, was today elected to the prestigious National Academy of Sciences for her work to understand the cells and connections in the mammalian brain, and leading the development of tools and openly available data resources that accelerate brain research worldwide.
“I am deeply honored to become a member of the National Academy of Sciences, joining more than 3,000 brilliant scientists around the country and the world,” said Zeng. “I feel incredibly fortunate to work at the Allen Institute alongside ...
Dementia and self-harm: why it's crucial to support patients in first year after diagnosis
2023-05-03
People diagnosed with dementia are more likely to self-harm within the first six to 12 months after initial diagnosis, highlighting the need for health services to offer more follow-up support in this crucial period.
In what is believed to be the largest study of its kind, researchers with expertise in medicine, psychiatry and psychology at UNSW Sydney looked at NSW hospital data captured for more than 180,000 people admitted to hospital between 2001 and 2015.
The researchers analysed statistics relating to two cohorts of patients admitted to hospital: 154,811 people recorded as having dementia, and ...
Boxing can take the fight to Parkinson’s Disease
2023-05-03
When we think of boxing, it’s understandable many of us wouldn’t associate it with being ‘good’ for our brains.
However, new Edith Cowan University (ECU) research undertaken in partnership with The Perron Institute and boxer Rai Fazio has shown the sport — without an opponent — could be a valuable way for people suffering Parkinson’s Disease (PD) to improve their quality of life.
Also collaborating with Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital and the University of Western Australia, ECU researchers had 10 people with early-stage PD perform three one-hour boxing sessions per week, over 15 weeks.
Rather ...
HKU’s innovative research novelties excel at 48th International Exhibition of Inventions of Geneva
2023-05-03
The University of Hong Kong (HKU) triumphed at the 48th International Exhibition of Inventions of Geneva, winning a total of 19 awards, including two special grand prizes Invention & Innovation CAI Award (China Delegation), and Prize of the Delegation of Malaysia. The results were announced yesterday (April 28).
Research teams from Faculty of Architecture, Faculty of Engineering, Faculty of Science, LKS Faculty of Medicine, and two HKU Inno Laboratories, established under the Hong Kong Government's InnoHK programme, garnered two special grand prizes, one Gold Medal with the Congratulations of the Jury, six Gold Medals, six Silver Medals ...
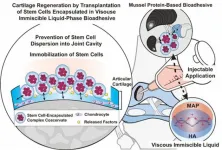
A novel stem cell adhesive using mussels
2023-05-03
Cartilage is a tissue that protects bones by providing shock absorption and facilitates smooth joint movement. Unfortunately, due to its limited intrinsic healing capacity, stem cell transplantation is a promising therapeutic approach to address cartilage inflammation and damage, as well as to promote cartilage regeneration. However, a major limitation of this technique is the rapid disappearance of transplanted stem cells from the smooth cartilage surface and fluidic environment around cartilage, resulting in less effective treatment outcomes. Recently, a joint team of researchers from POSTECH, Dongguk University Medical Center, and Nature Gluetech in Korea ...