Research reveals longstanding cultural continuity at oldest occupied site in West Africa
2023-05-04
(Press-News.org) Evidence from West Africa about human evolution remains scarce, but recent research has indicated unique patterns of cultural change in comparison to other regions of the continent. A new article in the journal Nature Ecology and Evolution adds to our understanding with a study of the oldest directly dated archaeological site in West Africa. The site shows technological continuity spanning roughly 140,000 years and offers insights into the ecological stability of the region.
Our species emerged in Africa around 300 thousand years ago and until around 30-60 thousand years ago typically used tools and tool-making techniques referred to as Middle Stone Age toolkits. Around that time, distinct Later Stone Age toolkits began to emerge in northern, eastern, and southern Africa. While recent evidence suggests Middle Stone Age toolkits persisted in West Africa much later, to around 10 thousand years ago, the antiquity of these technologies is poorly understood.
The new study, led by scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Geoanthropology, Université Cheikh Anta Diop de Dakar, University of Sheffield, and University of South Florida, extends the timeframe in which Middle Stone Age toolkits are known from West Africa to 150 thousand years ago, based on excavations from the near-coastal site of Bargny 1.
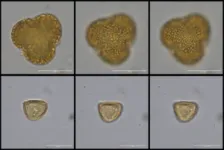
“The stone tool assemblage dating from 150 thousand years ago shows classic features of the Middle Stone Age, with the use of Levallois and discoidal reduction methods and the use of small retouched flake tools rather than larger implements,” says Dr Khady Niang, lead author of the study. “The assemblage from Bargny 1 is closely comparable to those of a similar age from across the continent, and is the first site from West Africa dating to the Middle Pleistocene, prior to the onset of substantial technological regionalization elsewhere in Africa.”
The site itself is located close to the modern coastline, south of Dakar, Senegal. While no artefacts indicating direct human engagement with coastal resources were recovered at the site, study of the associated environments offer a wider perspective.
“We found mangrove and brackish wetland plant microfossils associated with the site’s occupation,” adds Dr Chris Kiahtipes of the University of South Florida, co-author on the study. “This is particularly interesting because it shows that the site was located near an estuary and demonstrates how important these habitats are to humans past and present.”
The study highlights long-term durability of core elements of Middle Stone Age toolkits in West Africa without evidence for the appearance of specialized technological developments observed elsewhere.
“Middle Stone Age populations adapted to a wide range of habitats and engaged with climatic changes across Africa. But in West Africa, we see considerable environmental stability over the past 150 thousand years,” adds Dr Jimbob Blinkhorn. “One explanation for the enduring cultural continuity we observe is that it was a stable behavioural adaptation to stable environmental conditions, whilst potential isolation from other populations across Africa may have led to demographic stability too. Ultimately, our study helps illustrate the persistent utility of Middle Stone Age technologies to inhabit the diverse habitats found across Africa.”
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-05-04
BRONX, NY—May 4, 2023—Acute radiation dermatitis (ARD)—characterized by red, sore, itchy or peeling skin—affects up to 95% of people undergoing radiation treatment for cancer. Severe cases can cause significant swelling and painful skin ulcers that can severely impair quality of life, yet little is known about why this condition occurs and no standardized treatments for preventing severe ARD have been widely adapted.
Researchers at Montefiore Einstein Cancer Center (MECC) have found that many cases of ARD involve a common skin bacterium and that a simple, low-cost treatment ...
2023-05-04
SEATTLE, WA — May 4, 2023 — A new Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center study in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology investigated how endometriosis, uterine leiomyomas (also known as fibroids) and a common intervention for these conditions—hysterectomy—changed ovarian cancer risk in Black and white women.
Scientists found fibroids were associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer in both Black and white women, with hysterectomy modifying the risk of cancer in both groups. However, researchers also found that while Black and white women with endometriosis had a higher risk of ovarian cancer overall, hysterectomy only ...
2023-05-04
Vanishing glaciers threaten alpine biodiversity
With glaciers melting at unprecedented rates due to climate change, invertebrates that live in the cold meltwater rivers of the European Alps will face widespread habitat loss, warn researchers.
Many of the species are likely to become restricted to cold habitats that will only persist higher in the mountains, and these areas are also likely to see pressures from the skiing and tourism industries or from the development of hydroelectric plants.
The research study – led jointly by the University of Leeds and ...
2023-05-04
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Neuropathic pain — abnormal hypersensitivity to stimuli — is associated with impaired quality of life and is often poorly managed. Estimates suggest that 3 percent to 17 percent of adults suffer from neuropathic pain, including a quarter of people with diabetes and a third of people with HIV.
In a paper published in the journal Neuron, researchers report that a mechanism involving the enzyme Tiam1 in dorsal horn excitatory neurons of the spinal cord both initiates and maintains neuropathic pain. Moreover, they show that targeting spinal Tiam1 with anti-sense oligonucleotides injected ...
2023-05-04
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions have identified a strategy cancerous tumors use to remotely disrupt the development of an immune response that could stop their growth.
Published in the journal Cell Stem Cell, the study shows in animal models that breast cancer tumors send molecular signals to the bone marrow, the birthplace of immune cells. The signals alter the natural environment of the bone marrow in such a way that it suppresses the response to fight back the tumor. Interestingly, ...
2023-05-04
Young men with cannabis (marijuana) use disorder have an increased risk of developing schizophrenia, according to a study led by researchers at the Mental Health Services in the Capital Region of Denmark and the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) at the National Institutes of Health. The study, published in Psychological Medicine, analyzed detailed health records data spanning 5 decades and representing more than 6 million people in Denmark to estimate the fraction of schizophrenia cases that could be attributed ...
2023-05-04
About The Study: In this observational study of 1,340 women with high-risk breast cancer, strongest collective adherence to cancer prevention lifestyle recommendations was associated with significant reductions in disease recurrence and mortality. Education and implementation strategies to help patients adhere to cancer prevention recommendations throughout the cancer care continuum may be warranted in breast cancer.
Authors: Rikki A. Cannioto, Ph.D., Ed.D., of the Roswell Park Comprehensive ...
2023-05-04
About The Study: Results of this diagnostic study including 4,095 retinal fundus images collected from 245 neonates suggest that it can be very challenging to remove information relevant to self-reported race from fundus photographs. As a result, AI algorithms trained on fundus photographs have the potential for biased performance in practice, even if based on biomarkers rather than raw images. Regardless of the methodology used for training AI, evaluating performance in relevant subpopulations is critical.
Authors: J. ...
2023-05-04
Proteins that act like air traffic controllers, managing the flow of signals in and out of human cells, have been observed for the first time with unprecedented detail using advanced microscopy techniques.
Described in new research published today in Cell, an international team of researchers led by Professor Davide Calebiro from the University of Birmingham has seen how beta-arrestin, a protein involved in managing a common and important group of cellular gateways, known as receptors, works.
Beta-arrestin is involved in controlling the activity of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) which are the largest group of receptors ...
2023-05-04
Neuropathy is a type of chronic pain triggered by nerve injury or certain diseases. It affects millions of people worldwide, significantly deteriorating their quality of life. Neuropathy, for example, might emerge from hurting the sciatic nerve on the lower back or the spinal cord, in diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes or after chemotherapy drugs. Current therapies attempt to suppress the symptoms with pain medications like opioids, but their efficacy is low, and they carry undesirable side effects.
A group led by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and University of Alabama at Birmingham took on the challenge of investigating the process ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Research reveals longstanding cultural continuity at oldest occupied site in West Africa