(Press-News.org) A study from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago found that parents with children who were not yet vaccinated against COVID-19 were most likely to vaccinate their child after reading the following hypothetical scenario:
You hear from other parents you trust that they have vaccinated their children against COVID-19. Some of them say that they weren’t sure at first about whether the vaccine is safe for kids. But they ended up deciding that it was the best way to fight COVID-19, and the vaccination went fine. They want to keep their kids protected.
This “trusted parents” message was particularly effective among unvaccinated parents and Black parents, who tend to be the most hesitant to vaccinate their children.
In another hypothetical scenario, parents read that their child’s doctor or nurse delivered a different message that emphasized that the COVID-19 vaccine is safe and thoroughly tested in children. After reading this message paired with the “trusted parents” message, parents responded with significantly higher intentions to vaccinate their children.
Strikingly, all racial and ethnic differences in intentions to vaccine their children disappeared when parents received the “trusted parents” and “safe and tested” messages together. Findings suggest that these two messages were especially encouraging to unvaccinated parents and Black parents.
The study was published in the journal Pediatrics.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has had a disproportionately negative impact on historically marginalized racial and ethnic groups, and we wanted to understand if some message types would be better at reducing the inequities in vaccination intentions among parents,” said lead author Marie Heffernan, PhD, Assistant Professor at Mary Ann & J. Milburn Smith Child Health Outcomes, Research, and Evaluation Center at Lurie Children’s and the Department of Pediatrics at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. “In our study overall, Black parents were least likely to intend to vaccinate their children against COVID-19. Our findings that the ‘trusted parents’ and ‘safe and tested’ message types increased Black parents’ intentions to vaccinate their children could inform vaccination campaigns and hopefully help to effectively reach these families.”
One message type – that the vaccine was “well-tolerated” with few side effects, delivered by the child’s doctor or nurse in a hypothetical scenario – was found to be ineffective. Intentions to vaccinate children among parents who received this message did not differ significantly from the “control” message, which simply provided information about the anticipated timeline for authorization of vaccine in children.
“Our study helps clarify how different types of messages influence parents’ intentions to vaccinate their children against COVID-19. This is an urgent need because some methods to encourage vaccination, such as correcting myths about vaccines, have been shown to be counterproductive and inadvertently discourage vaccination,” said senior author Matthew M. Davis, MD, MAPP, Chair of the Department of Medicine at Lurie Children’s, Executive Vice President and Chief Community Health Transformation Officer at the Patrick M. Magoon Institute for Healthy Communities at Lurie Children’s, and Chair of Pediatrics at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. “In addition to aiding public health campaigns, our findings may help guide clinicians’ discussions with vaccine-hesitant families. Given the importance of effective vaccination among children in controlling future waves of COVID-19 illness, such messages may be some of the most important communications that pediatricians are currently providing.”
Data were collected through the Voices of Child Health in Chicago Parent Panel Survey, a tri-annual survey of Chicago parents from all 77 neighborhoods in the city on topics related to child, adolescent, and family health. The survey was administered October-November 2021, when the FDA’s emergency use authorization (EUA) for COVID-19 vaccines in children 5-11 years old was still new and the EUA for COVID-19 vaccines in children under 5 years old had not yet occurred.
In this study, any parent who responded that they had at least one child who was not yet vaccinated was randomly assigned to read one of four distinct messages about COVID-19 vaccines – “trusted parents,” “safe and tested,” “well-tolerated” and “control.” Analyses were based on responses from 898 parents about 1,453 children who had not yet received a COVID-19 vaccine at the time of the survey. Parent and child demographics did not differ significantly between message randomization groups.
Research at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago is conducted through Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute. The Manne Research Institute is focused on improving child health, transforming pediatric medicine and ensuring healthier futures through the relentless pursuit of knowledge. Lurie Children’s is ranked as one of the nation’s top children’s hospitals by U.S. News & World Report. It is the pediatric training ground for Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine.
END
Study identifies messages about vaccinating children against COVID-19 that resonate best with vaccine-hesitant parents
2023-05-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
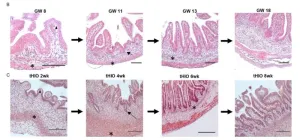
Organoids validated as tool for studying fetal intestine development
2023-05-04
Developmental biologists have learned a great deal about how the human digestive tract functions through many years of studies involving fish, frogs, and rodents along with detailed explorations of individual human cells. But nothing quite matches the learning that could be achieved from studying actual human organ systems as they form.
Yet for obvious reasons, running experiments on growing human fetuses is both unethical and illegal.
Now a study led by researchers at Cincinnati Children’s, published online April 18, 2023, in the journal Development, reports that lab-grown tissues called organoids accurately mimic key development stages of the human intestine.
“Achieving ...
New free-to-read collection shares research on the Southwest Asian and North African region
2023-05-04
Sage has launched a free-to-read collection of research and other resources that explore the Southwest Asian and North African (SWANA) region. Categories in the collection include:
gender role and oppression
governments, laws, and policies
information and media
mental health, healthcare, and medicine
protests, conflicts, and war
refugees, displaced, and stateless people
Readers can access the Southwest Asia and North Africa microsite free for a limited time. END ...
Cleveland Clinic Rare Disease Center recognized as a National Center of Excellence by National Organization for Rare Disorders
2023-05-04
May 4, 2023, Cleveland: Cleveland Clinic has been designated a Rare Disease Center of Excellence by the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD). The new Cleveland Clinic Center for Rare Diseases is one of 40 U.S. academic medical centers selected to join the first-of-it-kind national network dedicated to diagnosing, treating and researching all rare diseases.
The NORD Rare Disease Centers of Excellence program provides a much-needed national infrastructure to help accelerate advancements for rare diseases. The network of medical institutions, led by NORD, is designed to improve rare disease patient care by connecting patients to appropriate specialists regardless of disease ...
Adding epigenetic drug to standard chemotherapy was effective in pilot study for T-cell lymphoma
2023-05-04
Nearly 90 percent of patients with an aggressive subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma had their cancer go into remission in a small phase 2 clinical trial testing a treatment aimed at making chemotherapy more effective, according to Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian investigators.
The clinical trial, whose results were published May 4 in Blood, included 17 patients with a type of blood cancer called peripheral T-cell lymphoma with T-follicular helper phenotype (PTCL-TFH), also known as angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Fifteen of them (88.2 percent) had complete ...
What really killed COVID-19 patients: it wasn’t a cytokine storm
2023-05-04
· No evidence of cytokine storm in critically ill patients with COVID-19
· Nearly half of patients with COVID-19 develop a secondary bacterial pneumonia
· Crucial to find and aggressively treat secondary bacterial pneumonia in ICU patients
CHICAGO --- Secondary bacterial infection of the lung (pneumonia) was extremely common in patients with COVID-19, affecting almost half the patients who required support from mechanical ventilation. By applying machine learning to medical record data, scientists at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine found that secondary bacterial pneumonia that does not resolve was a key ...
Many older adults take multiple medications; an updated AGS Beers Criteria® will help ensure they are appropriate
2023-05-04
New York (May 4, 2023) — Today, the American Geriatrics Society (AGS) released the 2023 update to the AGS Beers Criteria® for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults (DOI: 10.1111/jgs.18372). The AGS Beers Criteria® serves as a comprehensive list of medications that older people should potentially avoid or consider using with caution because they often present unnecessary risks for this population. Given that, according to the National Center for Health Statistics, United States (NCHSUS), more than 88% of older people use at least one prescription and more than 66% use ...
Study presents new clues about the rise of earth’s continents
2023-05-04
Continents are part of what makes Earth uniquely habitable for life among the planets of the solar system, yet surprisingly little is understood about what gave rise to these huge pieces of the planet’s crust and their special properties. New research from Elizabeth Cottrell, research geologist and curator of rocks at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History, and lead study author Megan Holycross, formerly a Peter Buck Fellow and National Science Foundation Fellow at the museum and now an assistant professor at Cornell University, deepens the understanding of Earth’s crust by testing ...
Converging ocean currents bring floating life and garbage together
2023-05-04
The North Pacific “Garbage Patch” is home to an abundance of floating sea creatures, as well as the plastic waste it has become famous for, according to a study by Rebecca Helm from Georgetown University, US, and colleagues, publishing April 27th in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
There are five main oceanic gyres — vortexes of water where multiple ocean currents meet — of which the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre (NPSG) is the largest. It is also known as the North Pacific “Garbage Patch”, because converging ocean currents have concentrated large amounts ...
Gutless marine worms on a Mediterranean diet: Animals can synthesize phytosterols
2023-05-04
Cholesterol and phytosterol are sterols, fatty compounds essential for many biological processes such as the functioning of cell membranes. Up to now, it has been assumed that phytosterols are characteristic for plants, and cholesterol for animals, and that only plants can make phytosterols, while animals typically make cholesterol. Dolma Michellod, Nicole Dubilier and Manuel Liebeke from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology in Bremen, Germany, were therefore surprised when they discovered that a small marine worm called Olavius ...
Scientists begin to unravel global role of atmospheric dust in nourishing oceans
2023-05-04
CORVALLIS, Ore. – New research led by an Oregon State University scientist begins to unravel the role dust plays in nourishing global ocean ecosystems while helping regulate atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
Researchers have long known that phytoplankton – plantlike organisms that live in the upper part of the ocean and are the foundation of the marine food web – rely on dust from land-based sources for key nutrients. But the extent and magnitude of the impact of the dust – ...