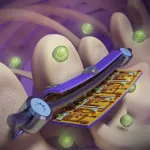
(Press-News.org) CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Newly developed “smart” coatings for surgical orthopedic implants can monitor strain on the devices to provide early warning of implant failures while killing infection-causing bacteria, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researchers report. The coatings integrate flexible sensors with a nanostructured antibacterial surface inspired by the wings of dragonflies and cicadas.
In a new study in the journal Science Advances, a multidisciplinary team of researchers found the coatings prevented infection in live mice and mapped strain in commercial implants applied to sheep spines to warn of various implant or healing failures.
“This is a combination of bio-inspired nanomaterial design with flexible electronics to battle a complicated, long-term biomedical problem,” said study leader Qing Cao, a U. of I. professor of materials science and engineering.
Both infection and device failure are major problems with orthopedic implants, each affecting up to 10% of patients, Cao said. Several approaches to fighting infection have been attempted, but all have severe limitations, he said: Biofilms can still form on water-repelling surfaces, and coatings laden with antibiotic chemicals or drugs run out in a span of months and have toxic effects on the surrounding tissue with little efficacy against drug-resistant strains of bacterial pathogens.
Taking inspiration from the naturally antibacterial wings of cicadas and dragonflies, the Illinois team created a thin foil patterned with nanoscale pillars like those found on the insects’ wings. When a bacterial cell attempts to bind to the foil, the pillars puncture the cell wall, killing it.
“Using a mechanical approach to killing bacteria allowed us to bypass a lot of the problems with chemical approaches, while still giving us the flexibility needed to apply the coating to implant surfaces,” said pathobiology professor Gee Lau, a coauthor of the study.
On the back side of the nanostructured foil, where it contacts the implant device, the researchers integrated arrays of highly sensitive, flexible electronic sensors to monitor strain. This could help physicians watch the healing progress of individual patients, guide their rehabilitation to shorten the recovery time and minimize risks, and repair or replace devices before they hit the point of failure, the researchers said.
The engineering group then teamed up with veterinary clinical medicine professor Annette McCoy to test their prototype devices. They implanted the foils in live mice and monitored them for any sign of infection, even when bacteria were introduced. They also applied the coatings to commercially available spinal implants and monitored strain to the implants in sheep spines under normal load for device failure diagnosis. The coatings performed both functions well.
The prototype electronics required wires, but the researchers next plan to develop wireless power and data communications interfaces for their coatings, a crucial step for clinical application, Cao said. They also are working to develop large-scale production of the nanopillar-textured bacteria-killing foil.
“These types of antibacterial coatings have a lot of potential applications, and since ours uses a mechanical mechanism, it has potential for places where chemicals or heavy metal ions – as are used in commercial antimicrobial coatings now – would be detrimental,” Cao said.
The National Science Foundation and the U.S. Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs supported this work.
Editor’s notes: To reach Qing Cao, email: qingcao2@illinois.edu.
The paper “A smart coating with integrated physical-antimicrobial and strain-mapping functionalities for orthopedic implants” is available online.
END
Smart surgical implant coatings provide early failure warning while preventing infection
2023-05-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Artificial intelligence identifies anti-aging drug candidates targeting ‘zombie’ cells
2023-05-05
SAN CARLOS, California – A new publication in the May issue of Nature Aging by researchers from Integrated Biosciences, a biotechnology company combining synthetic biology and machine learning to target aging, demonstrates the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to discover novel senolytic compounds, a class of small molecules under intense study for their ability to suppress age-related processes such as fibrosis, inflammation and cancer. The paper, “Discovering small-molecule senolytics with deep neural networks,” authored in collaboration with ...
How to make the faculty job search less discouraging
2023-05-05
Finding a full-time faculty job can be a daunting challenge for doctoral graduates.
University of Cincinnati anthropologist Kathleen Grogan says postdoctoral researchers can benefit from having peers review their applications.
She learned this herself while working as a postdoctoral researcher. She realized that she and other postdocs routinely solicited feedback in an online messaging app dedicated to aspiring scientists.
“I was on the job market and wanted people with broad scientific expertise to look at my stuff,” said Grogan, an assistant professor in UC’s College ...
Markey Cancer Center earns National Pancreas Foundation Center designation for treatment of pancreatic cancer
2023-05-05
LEXINGTON, Ky. (May 5, 2023) — The University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center has been recognized by the National Pancreas Foundation (NPF) as an approved NPF Center of Excellence.
The designation is awarded after a rigorous audit review to determine that an institution's focus is on multidisciplinary treatment of pancreatic cancer, treating the “whole patient” with a focus on the best possible outcomes and an improved quality of life.
“We are honored to receive the NPF designation, which highlight’s Markey’s commitment to multidisciplinary ...
Scientists capture elusive chemical reaction using enhanced X-ray method
2023-05-05
Researchers at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory captured one of the fastest movements of a molecule called ferricyanide for the first time by combining two ultrafast X-ray spectroscopy techniques. They think their approach could help map more complex chemical reactions like oxygen transportation in blood cells or hydrogen production using artificial photosynthesis.
The research team from SLAC, Stanford and other institutions started with what is now a fairly standard technique: They zapped a mixture of ferricyanide and water with an ultraviolet laser and bright X-rays generated by the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) X-ray free-electron laser. ...
Providing legal counsel at initial bail hearings lowers incarceration rates
2023-05-05
Providing defendants with legal counsel during their initial bail hearing decreases use of monetary bail and pretrial detention, without increasing the likelihood that defendants fail to appear at the subsequent preliminary hearing, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Researchers found that having legal counsel at bail hearings increased the probability of being released without monetary bail by 21% and reduced the probability that an individual was in jail three days after their bail hearing by 10%.
The analysis, based on a field experiment in Pittsburgh where public defenders were assigned to a limited number of initial bail hearings, is ...
Yale study reveals insights into post-vaccine heart inflammation cases
2023-05-05
New Haven, Conn. — When new COVID-19 vaccines were first administered two years ago, public health officials found an increase in cases of myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart muscle, particularly among young males who had been vaccinated with mRNA vaccines. It was unclear, however, what exactly was causing this reaction.
In a new study, Yale scientists have identified the immune signature of these heart inflammation cases.
These findings, published May 5 in the journal Science Immunology, rule out some of the theorized causes of the heart inflammation and suggest potential ways to further ...
nTIDE April 2023 Jobs Report: Despite sharp decline, employment remains above pre-pandemic levels for people with disabilities
2023-05-05
East Hanover, NJ – May 5, 2023 –Declines in the April job numbers for people with disabilities raise concerns about the future of the job market, according to today’s National Trends in Disability Employment – semi-monthly update (nTIDE), issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD). To assess whether this change signals a slowing of job gains for people with disabilities, nTIDE experts will look closely at the direction of next month’s employment indicators.
Month-to-Month ...
Systemic AL amyloidosis: Current approach and future direction
2023-05-05
“AL amyloidosis is a fatal disease and systemic therapy is required to prevent deposition of amyloid in other organs and prevent progressive organ failure.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 5, 2023 – A new review paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on April 26, 2023, entitled, “Systemic AL amyloidosis: current approach and future direction.”
In this review, researchers Maroun Bou Zerdan, Lewis Nasr, Farhan Khalid, Sabine Allam, Youssef Bouferraa, Saba Batool, Muhammad Tayyeb, Shubham Adroja, Mahinbanu Mammadii, Faiz Anwer, Shahzad Raza, and Chakra P. Chaulagain from SUNY Upstate Medical University, University of Texas MD Anderson ...
Boston Children’s Hospital to help lead research in NSF AI Institute for Societal Decision Making
2023-05-05
Artificial intelligence (AI) tools can drive cars, monitor and adjust the temperature in your home, and chat with you online. AI could help public health officials, community workers, and clinics efficiently direct and allocate resources and better target interventions to improve health outcomes during disasters and public health emergencies.
“The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted a need for new approaches to resource allocation during public health crises—approaches that simultaneously serve our society’s most vulnerable communities, improve our overall health and well-being, and maximize impact,” ...
U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs offers unlimited opportunities for emergency physicians
2023-05-05
Des Plaines, IL — There are unlimited opportunities for career growth in the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health system and this option should be recognized by medical students considering emergency medicine as a potential career, and by emergency medicine residents as well. This is the message of a perspective piece titled, The hidden jewel of emergency medicine careers: Why it's time to explore the VA. The piece introduces the April 2023 special issue of Academic ...