MTJ device with the world’s highest TMR performance developed through precision interfacial control
Technology may be applicable to the development of more sensitive magnetic sensors and larger capacity memory
2023-05-09
(Press-News.org)
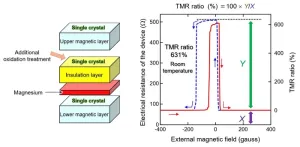
The National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) has achieved a tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) ratio of 631% at room temperature, breaking the previous world record which had stood for 15 years. This was accomplished by fine-tuning the interfaces in a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ). This MTJ exhibited very large TMR ratio oscillation effect with a peak-to-valley (PV) difference of 141%. This phenomenon may be exploitable to significantly increase the sensitivity of magnetic sensors and the capacity of magnetoresistive random access memory (MRAM).
Tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) is a dramatic change in the tunneling current in an MTJ—which consists of two ferromagnets separated by a thin insulator—when the relative magnetizations of the two ferromagnetic layers change in alignment. This effect has been used in highly sensitive, tiny magnetic sensors and energy-efficient MRAM. Sensor sensitivity and MRAM density can both be increased by using MTJs capable of producing larger TMR ratios (i.e., differences in electrical resistance generated by an MTJ when the magnetization orientation of its two ferromagnets switches between parallel and antiparallel). A room-temperature TMR ratio of 604% recorded in 2008 remained as the world record until recently. Because this record stood out for years, it had been widely believed that little room for improvement remained in magnetic sensor and MRAM performance.
This NIMS research team recently broke this TMR ratio record by precisely controlling interfaces in an MTJ consisting of two thin magnetic layers separated by a thin insulation layer. The team made atomic-scale modifications to the MTJ, including the fabrication of all of its layer components from single crystals and the addition of an ultrathin metallic magnesium layer between the magnetic and insulation layers. As a result, the team was able to create an MTJ with a maximum TMR ratio of 631%. In addition, the TMR ratio of this MTJ was found to oscillate with a PV difference of 141%—significantly greater than the PV difference of existing MTJs (up to a few dozen percent). This result was consistent with the previous finding that the oscillation PV difference of a TMR ratio is greatly influenced by the thickness of the insulation layer. In future research, the team will work to shed light on the poorly understood relationship between TMR ratios and their oscillation PV difference by investigating the mechanisms behind the large PV difference observed in this research. This understanding may enable the team to break its own room-temperature TMR ratio world record.
Using this breakthrough result, the team will work to accelerate the development of ultrasensitive magnetic sensors for medical use and very large capacity MRAM.
***
This project was carried out by a research team led by Thomas Scheike (Special Researcher, Research Center for Magnetic and Spintronic Materials (CMSM), NIMS) and Hiroaki Sukegawa (Group Leader, CMSM, NIMS). This work was partly based on the results obtained from a Project commissioned by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) via No. JPNP16007.
This research was published online in Applied Physics Letters (vol. 122, issue 11) on March 15, 2023.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-05-09
CLAY CENTER, Neb., May 9, 2023 -Scientists have collaborated to produce the first gene-edited calf with resistance to bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV), a virus that costs the U.S. cattle sector billions of dollars annually.
The recent study published in PNAS Nexus results from a collaboration between the USDA’s Agricultural Research Service (ARS), the University of Nebraska–Lincoln (UNL), the University of Kentucky, and industry partners, Acceligen and Recombinetics, Inc.
BVDV is one of the most significant viruses ...
2023-05-09
Cattle worldwide face major health threats from a highly infectious viral disease that decades of vaccinations and other precautions have failed to contain. Federal, private-sector and Husker scientists are collaborating on a new line of defense, by producing a gene-edited calf resistant to the virus.
If follow-up research confirms its efficacy, the gene-editing approach offers long-term potential to reduce antimicrobial and antibiotic use in the cattle industry.
The bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) devastates the bovine immune system and can cause severe respiratory and intestinal harm to infected beef and dairy cattle, said veterinary epidemiologist Brian Vander ...
2023-05-09
A team of scientists from the University of Ottawa has developed an innovative technique to manufacture complex chemical structures from easily accessible substrates, making it one of the simplest and most practical methods for converting alcohols into their arylated equivalents.
This innovative method for performing the reaction, namely the deoxygenative Suzuki-Miyaura arylation of aliphatic alcohols, uses two distinct metal catalysts. Their reaction operates under mild reaction conditions with minimal waste products and is expected to have a significant impact on the creation of new molecules. As a result, it will contribute to advances in pharmaceutical, agrochemical, ...
2023-05-09
Cameras used in harsh environments must be designed in a way that prevents temperature swings from influencing their optical performance. New research demonstrates that accounting for the exact lens mounting structure used is a critical step in ensuring that lens systems remain robust to temperature changes.
Eric M. Schiesser from Synopsys, Inc. will present the new research at the Optica Design and Fabrication Conference, which will take place 04 – 08 June 2023 in Quebec City, Canada.
“Most optical systems – from the camera in your smartphone to the eyes of the Mars rover - are used over a range of temperatures. To keep the image sharp ...
2023-05-09
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University]—When patients receive a low-dose computed tomography screen for lung cancer, doctors can see more than just the lungs. The screening test often picks up abnormalities or potentially “significant incidental findings” (SIFS) not associated with lung cancer. A new study led by Ilana Gareen, an associate professor of epidemiology at the Brown University School of Public Health, and published in JAMA Internal Medicine, highlights the need for proper reporting and management of these findings to reduce mortality, health care costs and unnecessary ...
2023-05-09
“In summary, single-cell transcriptomic analysis has allowed us to identify the specific populations and the dynamic transition states during senescence initiation and progression.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 9, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 8, entitled, “Single-cell transcriptomic analysis uncovers diverse and dynamic senescent cell populations.”
Senescence is a state of enduring growth arrest triggered by sublethal cell damage. Given that senescent cells actively ...
2023-05-09
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have linked specific variants or mutations of the gene myocardin-related transcription factor B (MRTFB) with a novel neurodevelopmental disorder. The team reports in the journal Genetics in Medicine that they were able to find variants in this gene in patients whose neurodevelopment disorders had previously gone undiagnosed. The research also revealed that the mutations disrupt the way the MRTFB protein controls other genes in the cell and this cascades to affect hundreds of other genes.
“We identified ...
2023-05-09
Many middle-aged and older women get mammograms every one to two years to screen for breast cancer, as recommended by their doctors. A study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis indicates that previous mammograms hold underutilized data that could help identify women at high risk of breast cancer and even reveal which breast is likely to be affected.
When doctors read mammograms, they assess breast density along with signs of cancer, comparing a woman’s previous mammograms to her most recent one to look for worrisome changes. But some changes are difficult to ...
2023-05-09
(Boston)—COVID-19, the disease resulting from SARS-CoV-2 infection, is associated with highly variable clinical outcomes that range from asymptomatic disease to death. For those with milder infections, COVID-19 can produce respiratory infection symptoms (cough, congestion, fever) and sensory phenotypes such as headache and loss of sense of smell. In more severe cases, SARS-CoV-2 infection can affect nearly every organ and result in strokes from vascular occlusion, cardiovascular damage and acute renal failure. ...
2023-05-09
New Method Uses Engineered Bacteria and AI to Sense and Record Environmental Signals
Columbia synthetic biologists first to engineer bacterial swarm patterns to visibly record environment, use deep learning to decode patterns; applications could range from monitoring environmental pollution to building living materials
New York, NY—May 9, 2023—Researchers in Biomedical Engineering Professor Tal Danino’s lab were brainstorming several years ago about how they could engineer and apply naturally-pattern-forming bacteria. There are many bacteria species, such as Proteus mirabilis (P. mirabilis), that self-organize into defined patterns on solid surfaces that are visible ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] MTJ device with the world’s highest TMR performance developed through precision interfacial control
Technology may be applicable to the development of more sensitive magnetic sensors and larger capacity memory