(Press-News.org) MELVILLE, N.Y., May 10 – The University of Arizona’s Husain Alqattan is the recipient of the APL Photonics 2022 Future Luminary Award for his work in utilizing pulse shaping and waveform synthesis to control electron motion and open the door for ultrafast electronics that process data at unprecedented speeds.
The winning paper, “Attosecond light field synthesis,” was published in the April 2022 issue of APL Photonics. In it, Alqattan and his team used an attosecond light field synthesizer to compress light field waveforms across two octaves, from near infrared to deep ultraviolet, controlling atomic and electronic motion.
“Our work was to advance the attosecond synthesis of optical laser pulses to a resolution comparable to the native time scale of electron motion in matter,” said Alqattan.
By synthesizing such powerful light field waveforms and establishing control over electron motion, Alqattan and his team have enabled the control of photo-induced current signals in potential dielectric nanocircuits — paving the way for ultrafast photonics that process and encode data at rates higher than 1 petabit per second.
“With the all-optical field sampling technique, the control has become on-demand so that such a synthesis scheme can find its way to the technology realm, too,” said Alqattan.
Alqattan received his doctorate in physics from the University of Arizona. In addition to his work with attosecond light field synthesis and electron motion control, his research also encompasses ultrafast electron diffraction and attosecond electron microscopy.
The APL Photonics Future Luminary Award, which recognizes early-career researchers with the potential to become luminaries in the field of photonics, includes a $3,000 honorarium, the opportunity to join the APL Photonics Early Career Editorial Advisory Board, and an invitation to write an Invited Article in APL Photonics.
“I am delighted to receive the prestigious Future Luminary Award,” said Alqattan. “I hope this helps us to find more venues for the application of our research in the scientific and industrial communities.”
###
ABOUT APL PHOTONICS
APL Photonics is the dedicated home for open access multidisciplinary research from and for the photonics community. The journal publishes fundamental and applied results that significantly advance the knowledge in photonics across physics, chemistry, biology, and materials science.
ABOUT AIP PUBLISHING
AIP Publishing’s mission is to advance, promote, and serve the physical sciences for the benefit of humanity by breaking barriers to open, equitable research communication and empowering researchers to accelerate global progress. AIP Publishing is a wholly owned not-for-profit subsidiary of the American Institute of Physics (AIP) and supports the charitable, scientific, and educational purposes of AIP through scholarly publishing activities on its behalf and on behalf of our publishing partners.
###
END
APL Photonics selects recipient for 2022 Future Luminary Award
Early-career researcher Husain Alqattan receives recognition for his work that paves the way for ultrafast data and information processing.
2023-05-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Using AI to predict important measure of heart performance
2023-05-10
Coronary heart disease is the leading cause of adult death worldwide. The coronary angiography procedure provides the clinical standard diagnostic assessment for nearly all related clinical decision-making, from medications to coronary bypass surgery. In many cases, quantifying left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) at the time of coronary angiography is critical to optimize clinical decision-making and treatment decisions, particularly when angiography is performed for potentially life-threatening acute coronary syndromes (ACS).
Since the left ventricle is the heart’s pumping center, measuring the ejection fraction in the chamber provides critical information about the percentage ...
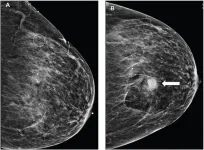
Bleeding after image-guided breast biopsies: Discontinuing vs. maintaining antithrombotic therapy
2023-05-10
Leesburg, VA, May 10, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), frequencies of imaging-apparent and palpable hematoma were not significantly different between patients temporarily discontinuing versus maintaining antithrombotic therapy (AT).
“The findings support safety of continuing AT during breast core-needle biopsy (CNB),” wrote lead researcher Melissa Reichman, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine at New York-Presbyterian ...
Ohio State professor elected to National Academy of Sciences
2023-05-10
COLUMBUS, Ohio - An Ohio State University astronomy professor has been elected to the National Academy of Sciences, one of the highest honors a scientist can receive in the U.S.
David Weinberg, Distinguished University Professor and chair of astronomy, is among 120 new members and 23 international members from 13 countries who were inducted this year in recognition of distinguished and continuing achievement in original research inside their chosen field.
“I have been lucky to have great students and great colleagues throughout ...
New Cleveland Clinic research links immune cell receptors to asthma, inflammatory lung disease
2023-05-10
CLEVELAND - Inhibiting a protein on the surface of immune cells could offer new strategies for treating severe asthma, Cleveland Clinic researchers found.
Researchers discovered a new way a protein called MCEMP1 contributes to severe inflammation in the airway and lungs. The discovery, published in Nature Communications, provides critical information for developing therapeutic interventions to treat long-term lung conditions, including asthma, on a biological level.
The study was conducted in a lab led by Jae Jung, PhD, chair ...
Entangled quantum circuits
2023-05-10
A group of researchers led by Andreas Wallraff, Professor of Solid State Physics at ETH Zurich, has performed a loophole-free Bell test to disprove the concept of “local causality” formulated by Albert Einstein in response to quantum mechanics. By showing that quantum mechanical objects that are far apart can be much more strongly correlated with each other than is possible in conventional systems, the researchers have provided further confirmation for quantum mechanics. What’s special about ...
Simple management steps for a high fertility cycle in your dairy herd
2023-05-10
Philadelphia, May 10, 2023 – The dairy industry has seen a revolution over the past two decades in fertility success within herds. Widely adopted fertility programs are at the heart of this leap forward, along with the industry’s increased understanding—and optimization—of the holistic interactions among the body condition, overall health, and fertility of a dairy cow. In a recent mini-review appearing in a special fertility issue of JDS Communications®, published by Elsevier, researchers from the University of ...
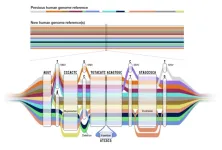
Scientists release a new human “pangenome” reference
2023-05-10
Researchers have released a new high-quality collection of reference human genome sequences that captures substantially more diversity from different human populations than what was previously available. The work was led by the international Human Pangenome Reference Consortium, a group funded by the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), part of the National Institutes of Health.
The new “pangenome” reference includes genome sequences of 47 people, with the researchers pursuing the goal of increasing that number to 350 by mid-2024. With each person carrying a paired set of chromosomes, the current reference actually includes 94 distinct genome ...
Crops evolved by swapping genetic modules between cells
2023-05-10
Comparing individual cells across corn, sorghum, and millet reveals evolutionary differences among these important cereal crops, according to a new study led by New York University researchers.
The findings, published in Nature, bring researchers closer to pinpointing which genes control important agricultural traits such as drought tolerance, which will help scientists faced with a changing climate adapt crops to drier environments.
Corn, sorghum, and millet provide food for humans and animals around the world. Corn and sorghum are ancient relatives that evolved into two different species roughly 12 million years ago, and millet is a more distant relative.
Despite ...
Behind the scenes of a major genomic discovery
2023-05-10
EMBARGOED UNTIL WEDNESDAY, MAY 10, 2023, AT 11AM ET
New York, NY (May 10, 2023)—Eimear Kenny, PhD, had just completed undergrad and was working in her first computational genomics job more than 20 years ago when scientists announced the first (nearly) complete sequencing of the human genome—what was considered at the time to be the fundamental blueprint for all humans. The Human Genome Project aimed to map the entire genome in an effort to accelerate the diagnosis and eventual treatment of common and rare diseases.
Now, Dr. Kenny, ...
Human pangenome reference will enable more complete and equitable understanding of genomic diversity
2023-05-10
UC Santa Cruz scientists, along with a consortium of researchers, have released a draft of the first human pangenome—a new, usable reference for genomics that combines the genetic material of 47 individuals from different ancestral backgrounds to allow for a deeper, more accurate understanding of worldwide genomic diversity.
By adding 119 million bases—the “letters” in DNA sequences—to the existing genomics reference, the pangenome provides a representation of human genetic diversity that was not possible with a single reference genome. It is highly accurate, more complete and dramatically increases ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] APL Photonics selects recipient for 2022 Future Luminary AwardEarly-career researcher Husain Alqattan receives recognition for his work that paves the way for ultrafast data and information processing.