(Press-News.org) A UBC Okanagan researcher has been testing the effectiveness of a mobile app that encourages people living with a spinal cord injury—but can walk—to get active.
Dr. Sarah Lawrason, a researcher in the School of Health and Exercise Sciences, has focused her career on working with people who live with a spinal cord injury (SCI) but are ambulatory. She describes this population as an isolated, often misunderstood group of people because while they live with an SCI, they may not rely on a wheelchair all of the time for mobility.
“When people think of someone with an SCI, they picture a person who might be a paraplegic or quadriplegic—and that’s a person who has had a complete spinal cord injury,” she explains. “But a person who has had an incomplete spinal cord injury—who might be able to walk some of the time or with a device—can be ambulatory with an SCI. And this group is often marginalized.”
Dr. Lawrason, who conducts research with Centre for Chronic Disease Prevention and Management based at UBCO, says about half of spinal cord injuries are incomplete. The ambulatory SCI population is often seen as different from others and not a lot of research has been conducted with this cohort.
Her latest study, completed while working on her doctorate, investigates the potential of a mobile health intervention app called SCI Step Together. Some participants were provided with the app to help set goals, track activity, connect or chat with fellow participants, as well as access an online coach and weekly educational components. The other participants did not use the app.
None were prescribed specific exercises, but they were encouraged to do activities that bring them joy. Participants were also provided The Physical Activity Guidelines for Adults with Spinal Cord Injuries, established by UBCO’s Dr. Kathleen Martin Ginis, Dr. Lawrason’s faculty supervisor.
To achieve essential cardiorespiratory fitness and muscle strength benefits, the guidelines recommend adults with an SCI engage in at least 20 minutes of moderate to vigorous aerobic exercise and strength training on functioning muscle groups twice per week.
During the eight-week study, Dr. Lawrason checked weekly with participants to determine if they were accomplishing goals or facing barriers. Those with the app said they had greater fulfillment of basic psychological needs—including a sense of independence, competence and belonging—and knowledge than those without the app. And general results suggest the program is feasible, well-accepted and engages participants. The program significantly improved the satisfaction of basic psychological needs, knowledge and self-monitoring for leisure-time physical activity.
“This study is important because it’s the first exercise intervention for people with an SCI who walk, and one of the first mobile health programs for people with SCI in general,” Dr. Lawrason adds. “It is also indicative of a great partnership. SCI Step Together was developed in collaboration with Curatio Inc. to provide the mobile health platform. We also worked with several ambulators with SCI to make sure the content, delivery and format of the program met their needs.”
The study, published recently in the Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology, was supported by a doctoral fellowship with the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada and a WorkSafe BC Doctoral Research Training Award.
END
Getting active, while living with a partial spinal cord injury
Mobile app helps specific population group meet suggested activity guidelines
2023-05-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New, free online language course helps you learn Ojibwe
2023-05-11
TORONTO – May 11, 2023 – With funding from Canada’s Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC), Baycrest, the Kingston Indigenous Language Nest (KILN) and the University of Toronto have released a free online language course to learn the Indigenous language Ojibwe, also known as Anishinaabemowin.
The Ojibwe language is spoken in Indigenous communities around the Great Lakes in Canada and the US, but serious efforts are needed to ensure the long-term survival of the language.
“Due to the aging of people who ...
New research sheds light on the causes of fatigue after COVID 19
2023-05-11
Experts from Newcastle University found the nervous system of people with post-Covid fatigue was underactive in three key areas. Fatigue is one of the most common symptoms of long Covid.
The breakthrough could lead to better treatment and tests to identify the condition and the team are already progressing the work having just started a trial. They have begun recruiting patients to test the effectiveness of a TENS machine – commonly used for pain relief in childbirth – to alleviate the fatigue in patients with long Covid.
Newcastle University ...
Into the Blue: Securing a sustainable future for kelp forests
2023-05-11
Into the Blue: Securing a Sustainable Future for Kelp Forests global synthesis report is the most comprehensive knowledge review on kelp to date, revealing the state of science on the world’s kelp forests and providing recommended actions to build the recovery of the world’s kelp forests.
Aiming to improve our understanding of the value of kelp forests and provide recommendations to protect and sustainably manage them, the report also provides a range of policy and management interventions and options that can be used to maintain these remarkable ecosystems into the future and to support the people and economies that have depended on them for generations.
Despite ...
Heavy drinking poses even greater risk for one in three Americans
2023-05-11
LOS ANGELES — Two people regularly have a few alcoholic drinks daily. One develops liver disease. The other doesn’t.
What explains the different outcomes?
The answer may lie in a condition known as metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that together raise the risk of coronary heart disease, diabetes, stroke and other serious health problems. This syndrome, characterized by symptoms such as abdominal fat, high blood pressure, high cholesterol and high blood sugar, affects more than one in three Americans.
A new ...
Gene linking circadian and circatidal rhythms is discovered in tiny crustacean
2023-05-11
Scientists at UMass Chan Medical School and the Marine Biological Laboratory at Woods Hole have identified the first gene—Bmal1—to play a crucial role in regulating circatidal behavior in the crustacean Parhyale hawaiensis. Circatidal rhythms help animals cope with the rise and fall of the tides in coastal areas.
Published in Current Biology, the study by neurobiologists Patrick Emery, PhD, Joshua Rosenthal, PhD, and colleagues demonstrates the first molecular link between circatidal and circadian ...
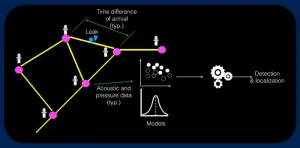
Fire hydrant hydrophones find water leaks #ASA184
2023-05-11
CHICAGO, May 11, 2023 – Access to clean drinking water is essential for healthy communities, but delivering that water is growing increasingly difficult for many utilities. Corroding pipes and land shifts in aging water distribution networks can create frequent leaks, wasting water before it ever gets to the tap. Utilities in the U.S. lose about 6 billion gallons of water a day — enough to fill 9,000 swimming pools — due to leaks, in addition to wasted energy and resources spent in collecting and treating that water.
Pranav Agrawal and Sriram Narasimhan from the University ...
InVADER mission to test its robotic laser divebot on a deep-sea expedition
2023-05-11
InVADER Mission to Test its Robotic Laser Divebot on a Deep-Sea Expedition
Team to test technologies for use in future planetary exploration while providing data to survey deep-sea ecosystems and minerals on Earth
May 11, 2023, Mountain View, CA – A team of scientists and engineers from the SETI Institute, Impossible Sensing, NASA JPL, and other institutions will test their innovative robotic laser system on a deep-sea expedition aboard the E/V Nautilus. The mission, called InVADER (In-situ Vent Analysis Divebot for Exobiology Research), aims to advance technologies to explore, ...
Rensselaer researcher uses artificial intelligence to discover new materials for advanced computing
2023-05-11
A team of researchers led by Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute’s Trevor David Rhone, assistant professor in the Department of Physics, Applied Physics, and Astronomy, has identified novel van der Waals (vdW) magnets using cutting-edge tools in artificial intelligence (AI). In particular, the team identified transition metal halide vdW materials with large magnetic moments that are predicted to be chemically stable using semi-supervised learning. These two-dimensional (2D) vdW magnets have potential applications in data storage, spintronics, and even quantum computing.
Rhone ...
Having dementia and reduction in social participation are associated with increased depression and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-05-11
Tokyo, May 8, 2023 -- An increased risk of depression and anxiety among US older adults with dementia and poor activity participation has been demonstrated through an analysis of data from the National Health and Aging Trends Study (NHATS), a nationally representative population-based study.
These findings were reached by a team of researchers from the Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Exploratory Oncology Research and Clinical Trial Center in National Cancer Center, and Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science, Japan. This study is published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports 7(1).
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) ...
Targeting uncontrolled inflammation may hold the key to treating therapy-resistant cancers
2023-05-11
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (May 11, 2023) — Van Andel Institute scientists have pinpointed how a specific gene mutation triggers an inflammatory cascade that may drive development of treatment-resistant cancers.
The new findings, published today in Molecular Cell, reveal for the first time the molecular circuitry by which mutations in the gene STK11 cause inflammation to spiral out of control. The resulting chemical firestorm damages healthy cells and can enable cancer development. Tumors that lose the STK11 gene are tough ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Getting active, while living with a partial spinal cord injuryMobile app helps specific population group meet suggested activity guidelines