(Press-News.org) The spiral-shaped bacteria Helicobacter pylori are common and troublesome.
More than 13 percent of Americans have an H. pylori infection, although rates vary with age, race and socioeconomic status. The microorganism uses its corkscrew-like tail to power forward through viscous fluids such as stomach mucus. When it arrives at the epithelium of the stomach wall, it can cause everything from ulcers to cancer.
In a new study published by Physical Review Letters, FAMU-FSU College of Engineering researchers created a 3D model of this bacteria to better understand its movement, hoping to crack the code governing the organism’s motility and develop alternative treatments for infections, such as strengthening the gastric mucus barrier that stands against the bacteria.
“People around the world have treated ulcers with antibiotics because antibiotics kill bacteria, but it’s a double-edged sword,” said study co-author Hadi Mohammadigoushki, an associate professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomedical Engineering. “If we understand how these bacteria move, we can work toward providing other solutions for treatment.”
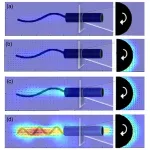
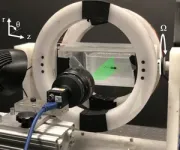
In the experiments, the team placed a model of the bacteria in a high-viscosity polymer gel, an example of what’s called a yield-stress fluid. Those fluids behave as solids under small stresses but flow like liquids beyond a critical stress point.
Then they used a magnetic field to rotate the 3D model, mimicking the behavior of the microorganism. Using particle tracking and imaging techniques, the researchers measured the speed of the bacteria and visualized the distribution and density of the fluid flowing around it.
The researchers identified two critical thresholds that the bacteria must overcome: the torque needed to rotate the swimming model and the force needed to propel the model forward.
“We found that if the tail propulsion was too weak, the bacteria remain stuck in the gel,” Mohammadigoushki said. “If the force was strong enough it could penetrate the gel. It’s kind of like when you are drilling a screw into a solid wall. If your drill isn’t strong enough and you are not pushing the screw with enough force, it won’t penetrate the wall, but with the right amount of force, it can break through.”
The swimming motions and force that allow H. pylori to move also apply to larger objects, such as earthworms that burrow in the soil, various parasites and more.
“If we understand how the bacteria successfully move to attack our body, we can use that information for whatever we can imagine,” said Kourosh Shoele, an assistant professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
Shoele is part of the multidisciplinary research team and is an expert in computational science. He explained how learning from nature can get a better response from mechanical and biological systems.
“In the future, we can design a micro-robot that can deliver a drug to a particular location in the body, in terms of fighting leukemia and other diseases,” Shoele said. “Or perhaps we can design tiny robots that use swimming motion and force, like H. pylori, that can dig deep in the sand to explore for water or oil. The possibilities are endless.”
Farshad Nazari, an FSU doctoral student in chemical and biomedical engineering, is working with the two researchers and is the leading author of this paper.
END
Researchers use 3D models to investigate bacteria movement
2023-05-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers at Purdue discover superconductive images are actually 3D and disorder-driven fractals
2023-05-12
Meeting the world’s energy demands is reaching a critical point. Powering the technological age has caused issues globally. It is increasingly important to create superconductors that can operate at ambient pressure and temperature. This would go a long way toward solving the energy crisis.
Advancements with superconductivity hinge on advances in quantum materials. When electrons inside of quantum materials undergo a phase transition, the electrons can form intricate patterns, such as fractals. A fractal is a never-ending pattern. When zooming in on a fractal, the image looks the same. Commonly seen fractals can be a tree or frost on a windowpane ...
Save the phages to protect Big Blue
2023-05-12
The plastic era has begun, and for sure, it will last for decades or even longer. Polymer-based materials are almost everywhere, reaching even the deepest regions of the oceans, and their global production is larger than recycling, leading to the generation of tremendous amounts of water pollution with microplastics. These tiny polymer particles not only release chemicals but also reduce the number of bacteriophages. Recently, researchers from the Institute of Physical Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences, led by Prof. Jan Paczesny, explored ...
Head and neck cancer organoids as a step towards personalized treatments
2023-05-12
Researchers from the Organoid group (Hubrecht Institute) and UMC Utrecht have developed a biobank with organoids derived from patients with head and neck cancer (HNC). They used this biobank to validate known HNC biomarkers and found that treatment responses in the organoids matched those seen in patients. The results of the study will be published in Med on 12 May 2023 and could aid treatment decisions and discovery of novel therapies for HCN patients in the future.
Head and neck cancer (HNC) is an overarching term used for several types of cancer, including the most ...
Intestinal bacteria influence the growth of fungi
2023-05-12
The bacteria present in the intestine provide information about the quantities of fungi of the potentially disease-causing Candida genus. Among them, and surprisingly, are lactic acid bacteria that are known for their protective effect against fungal infections. The findings of researchers at the Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology (Leibniz-HKI) and their collaborative partners from Denmark and Hungary add another piece to the puzzle of understanding the human gut microbiome.
The ...
Researchers discover novel "Shanghai APP" mutation in late-onset Alzheimer's disease, offering new avenues for treatment
2023-05-12
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder affecting tens of millions of people worldwide, and it is the most common cause of dementia. Early-onset AD is typically associated with mutations in the genes APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2, leading to a more aggressive form of the disease with atypical symptoms. In contrast, the newly discovered "Shanghai APP" mutation has been linked to LOAD, which affects a larger population of AD patients.
In a study published in Genes & ...
Breakthrough technology: Carbon nanotube membranes with Pd-Cu modification successfully reduce nitrate levels via electrocatalysis
2023-05-12
The adverse effects of excess nitrate in water on human productivity and lives have received increasing attention due to the discharge of industrial wastewater and the overuse of farmland fertilizers. An international team of researchers has conducted an in-depth study of the significant need and challenge of efficient nitrate removal.
Several techniques have been used to eliminate nitrate from water, such as biological denitrification is technologically mature, cost-effective, and widely used. However, biological processes are often sluggish and ...
Samsung Electronics – DGIST, establishment of ”Semiconductor Contracting Department” for fostering semiconductor development talent
2023-05-12
□ DGIST (President Yang Kook) (the following three science and technology institutions) will establish a "Semiconductor Contracting Department" with Samsung Electronics for fostering technical staff specialized in semiconductor manufacturing processes.
□ DGIST closed a business agreement on the 27th (Mon) at DGIST University Center Convention Hall for establishing and operating the Semiconductor Contracting Department, which was attended by Samsung Electronics President Seokwoo Nam and Wanpyo Kim, DGIST President Yang Kook, and other major stakeholders.
□ Owing to the recently increasing global semiconductor demand, safeguarding national competitiveness ...
The DGIST increases clinical diagnosis accuracy through the development of rare cell loss minimization technology.
2023-05-12
□ DGIST (President Yang Kook) Professor Minseok Kim of the Department of Neurobiology and his team developed lossless immunocytochemistry technology, which facilitates analysis of rare cells that present in trace amounts in clinical specimens. The corresponding technology developed together with CTCELLS, Inc. involves the use of an ultra-thin film hydrogel to facilitate fluid exchange while inhibiting cell loss, and a higher preservation rate and reproducibility were achieved compared to existing cell ...
DGIST and Seoul National University signed MOU to develop open innovation business model
2023-05-12
Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology (DGIST; President Kuk Young) and Seoul National University (President Ryu Hong-lim) signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on Wednesday, April 26 to develop an open innovation business model. Under this MOU, Senior Researcher Yun Jin-hyo at the Division of Electronics & Information Systems, DGIST provides consulting services required to develop an open business model to students in the Engineering Project Management Program at the Graduate School of Engineering Practice, Seoul National University. The first seminar was held on the day of the MOU.
□ Senior Researcher ...
Portugal participates in the development of a first-class instrument for the largest telescope in the world
2023-05-12
A research team from the University of Lisbon and University of Oporto (Portugal) participate in the development of METIS (Mid-infrared ELT Imager and Spectrograph). This powerful instrument will equip the largest telescope in the world - the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) - under construction by the European Southern Observatory (ESO) in Armazones, Chile.
At this critical acceptance stage of the complete and final METIS design, ESO is presenting an illustrative film demonstrating the exceptional capabilities of the instrument. The presentation will take place on May 12, at 4:00pm (CEST).
METIS will detect ...