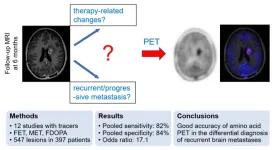
(Press-News.org) Reston, VA—A newly published meta-analysis indicates that amino acid PET can accurately differentiate recurrent or progressive brain metastases from treatment-related changes. A specificity of 84 percent suggests that it may reduce the number of invasive procedures and overtreatment in patients who in fact experience treatment-related changes. This research was published in the May issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Brain metastases occur in 20 to 40 percent of all cancer patients and are most likely to occur in those with lung, breast and renal cancer, melanoma, and cancers of the gastrointestinal tract. Management of patients with brain metastases usually includes surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Some patients develop treatment-related changes such as radiation necrosis or pseudoprogression.
“A differentiation between recurrent or progressive brain metastases and treatment-related changes is challenging,” said Igor Yakushev, senior physician in the department of nuclear medicine at Technical University of Munich in Germany. “As the management of patients with recurrent or progressive brain metastases and treatment-related changes is fairly different, accurate and early differential diagnosis is essential.”
The meta-analysis included 12 studies with amino acid PET radiotracers. The studies included a total of 397 patients with 547 lesions. Overall, 269 lesions (49 percent) were found to be recurrent or progressive brain metastases. Using a histologic examination and/or radiological and clinical follow-up as reference, pooled sensitivity and specificity of amino acid PET were found to be 82 and 84 percent respectively.
“This study provides IIa class evidence on diagnostic utility of amino acid PET in the differential diagnosis of recurrent or progressive brain metastases,” stated Yakushev. “These findings are in line with an increasing role of molecular imaging in the management of patients with brain tumors, yet the results also point to potential for further improvement of diagnostic accuracy.”
The authors of “Diagnostic utility of amino acid PET in the differential diagnosis of recurrent brain metastases and treatment-related changes: a meta-analysis” include Timo Schlürmann, Wolfgang Weber, and Igor Yakushev, Department of Nuclear Medicine, School of Medicine, Klinikum Rechts der Isar, Technical University of Munich, Germany; Birgit Waschulzik, Institute of AI and Informatics in Medicine, School of Medicine, Klinikum Rechts der Isar, Technical University of Munich, Germany; Stephanie Combs, Department of Radiation Oncology, Institute of Radiation Medicine (IRM), Department of Radiation Sciences (DRS), Helmholtz Zentrum München (HMGU), Oberschleißheim, Germany, Deutsches Konsortium für Translationale Krebsforschung (DKTK), Partner Sites; Jens Gempt, Department of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Klinikum Rechts der Isar, Technical University of Munich, Germany; and Benedikt Wiestler, Department of Neuroradiology, School of Medicine, Klinikum Rechts der Isar, Technical University of Munich, Germany.
Visit the JNM website for the latest research, and follow our new Twitter and Facebook pages @JournalofNucMed or follow us on LinkedIn.
###
Please visit the SNMMI Media Center for more information about molecular imaging and precision imaging. To schedule an interview with the researchers, please contact Rebecca Maxey at (703) 652-6772 or rmaxey@snmmi.org.
About JNM and the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging
The Journal of Nuclear Medicine (JNM) is the world’s leading nuclear medicine, molecular imaging and theranostics journal, accessed 15 million times each year by practitioners around the globe, providing them with the information they need to advance this rapidly expanding field. Current and past issues of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine can be found online at http://jnm.snmjournals.org.
JNM is published by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI), an international scientific and medical organization dedicated to advancing nuclear medicine and molecular imaging—precision medicine that allows diagnosis and treatment to be tailored to individual patients in order to achieve the best possible outcomes. For more information, visit www.snmmi.org.
END
Key takeaways
Researchers studied the way different generations in Romania determined the truth of information following the country’s transition from authoritarianism to democracy.
Those who were born and raised after the transition were more likely than older cohorts to compare and evaluate different perspectives before deciding who is right.
The factors associated with the youngest generation’s style of thinking were greater exposure to formal education and social media.
While people change and learn throughout life, experts recognize ...
NEW YORK – May 12, 2023 – The Cardiovascular Research Foundation (CRF) announced that TVT: The Structural Heart Summit will feature 15 Late-Breaking Clinical Science studies. An annual meeting featuring cutting-edge research and techniques for structural heart interventions, TVT will take place June 7-10, 2023, at the Phoenix Convention Center – West in Phoenix, Arizona.
TVT has become the epicenter of innovation and collaboration in the structural heart arena over its 16-year history. The meeting brings together world-renowned experts and master operators to help translate novel discoveries into practical therapies for patients with valvular heart disease.
TVT’s ...
Misael Cabrera has been selected through a nationwide search as the inaugural director of the School of Mining and Mineral Resources. The school was created in 2021 and is jointly housed in the College of Engineering and the College of Science, with strong partnerships to additional colleges and centers.
“Our role is to deliver talent and technology through research, but also to change the top-of-mind association with mining. We can create real solutions that both industry and our planet need,” said Cabrera.
Cabrera, who began the position in April, most ...
The spread of drug-resistant microbes has become a global health concern that threatens our ability to treat infections. The widespread use of antimicrobials in livestock, such as swine farms, exacerbates this problem. Therefore, we need surveillance systems to monitor these microbes to support the public health authorities. To this end, researchers have tracked the antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from swine.
Antimicrobials are essential for preventing and treating infections in humans and animals. According to the US Food and Drug Administration, 70% of all antibiotic ...
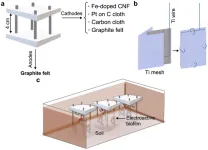
In the context of increasing energy demands and environmental concerns, renewable energy solutions are crucial for achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. Microbial electrochemical technologies, such as SMFCs, are cost-effective and environmentally friendly, making them an attractive option for green energy systems. SMFCs utilize endogenous microorganisms present in soil to convert organic matter into electricity, offering a sustainable energy source and a self-powered in situ bioremediation strategy for contaminated soils.
Cathode materials play a significant role in the performance of microbial fuel cells. In this study, researchers compared the performance ...
Ruminants like cows have developed an unusual way of digesting their food: they ingest plants, give them a rough chewing and then swallow the half-chewed mash before regurgitating it repeatedly and continuing to chew. This has clear advantages, as a research team including the University of Göttingen has shown: the regurgitated mushy food contains much less hard grit, sand and dust than the food that they first ingested. This protects the teeth from being ground down during the chewing process. This ...
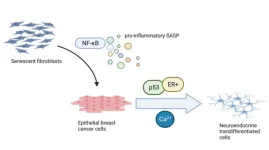
“We recently unveiled a new interesting role for SASP: its ability to induce neuroendocrine transdifferentiation (NED) in breast cancer epithelial cells [3].”
BUFFALO, NY- May 12, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 8, entitled, “The senescence-associated secretory phenotype induces neuroendocrine transdifferentiation.”
In this editorial, researchers Anda Huna, Nadine Martin and David Bernard from the Université de Lyon discuss the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). SASP, ...
Larry Steckel, row crop weed specialist and professor in the Department of Plant Sciences at the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture, has been named a Fellow of the Southern Weed Science Society (SWSS).
The award was given to honor Steckel’s years of research and contributions to weed prevention in row crop agriculture. Steckel was among only a small group of esteemed researchers to receive the honor, presented to him during the annual meeting of the SWSS.
Steckel says he is proud to be named a Fellow, and that he knows the research and extension work conducted by weed specialists across the ...
Manufacturing and metrology considerations are key when designing with freeform optics
Close communication between optics designers and manufacturers can help prevent problems
Québec City, Canada -- Although optical components such as lenses are traditionally spherical in shape, freeform optical components, which have little to no symmetry around the optical axis, are becoming more common. Freeform optical components are attractive because they can be designed to behave in ways traditional optics cannot, offering optical design flexibility ...
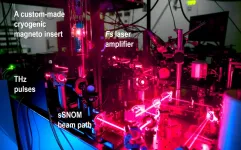
A team of scientists from the Department of Energy’s Ames National Laboratory have developed a way to collect terahertz imaging data on materials under extreme magnetic and cryogenic conditions. They accomplished their work with a new scanning probe microscope. This microscope was recently developed at Ames Lab. The team used the ultralow temperature terahertz microscope to take measurements on superconductors and topological semimetals. These materials were were exposed to high magnetic fields and temperatures below liquid helium (below 4.2 ...