Alternating estrogen and anti-estrogen therapies is effective in treating metastatic breast cancer
Results from a new clinical trial show that cycling between estrogen-stimulating and estrogen-blocking therapies is an effective treatment for patients with metastatic or advanced ER+ breast cancer.
2023-05-15
(Press-News.org) LEBANON, NH— Advanced or metastatic estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer is commonly treated with drugs that block the estrogen receptor. However, estrogens that stimulate the receptor can also be effective. Building on their previous studies, researchers at Dartmouth Cancer Center recently concluded a Phase II clinical trial aimed to test the efficacy of alternating between estrogen stimulation and estrogen deprivation in patients with metastatic ER+ breast cancer, and to identify tumor characteristics that predict who might benefit from this strategy. The results, newly published ahead of print in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, support cyclical estrogen/anti-estrogen therapy as a promising strategy to treat advanced/metastatic ER+ breast cancer.
The POLLY trial stands for “Phase II study of Pre-emptive oscillation of ER activity levels through alternation of estradiol/anti-estrogen therapies prior to disease progression in ER+/HER2- metastatic or advanced breast cancer.” Among 19 patients enrolled in the trial, 3 (16%) experienced tumor shrinkage during cyclical treatment and another 5 (26%) had disease stabilization for at least 24 weeks, yielding an overall benefit rate of 42%. Treatments were well-tolerated, and no patients discontinued drug treatment due to side effects. Following cancer progression on cyclical treatment, 12 patients elected to receive non-cycling treatment with a single drug—5 of these patients (42%) had further disease stabilization lasting at least 24 weeks.
“Estrogen therapy has been used for more than 50 years to treat breast cancer. Strategies to maximize estrogen efficacy and minimize side effects, as well as research on cancers that develop resistance to the new tumor-targeted drugs coming to market in the past decade such as Ibrance, Kisqali, Verzenio and Afinitor, remain under-developed,” says Dartmouth Cancer Center breast oncologist and lead author, Gary N. Schwartz, MD. “The POLLY study addressed this gap.”
“Tumor features called biomarkers that predict which patients will benefit from estrogen therapy have also not been reported,” adds cancer researcher and co-corresponding author, Todd W. Miller, PhD. “In the POLLY trial, we found that mutations in the gene encoding ER, which often arise in tumors that become resistant to anti-estrogen drugs, were present in tumors from the only two patients whose tumors shrank in response to estrogen therapy within the first 8 weeks. This suggests that ER mutations may be useful in identifying patients who are likely to benefit from this treatment strategy.”
The team will build on POLLY findings by conducting a follow-up clinical study, “Estradiol therapy to target ER-mutant and ER-wild-type ER+ metastatic breast cancer (ESTHER),” that will test the effectiveness of estrogen therapy in patients with or without tumor mutations in ER.
###
About Dartmouth Cancer Center: Dartmouth Cancer Center combines the advanced cancer research in partnership with Dartmouth and the Geisel School of Medicine, with award-winning, personalized, and compassionate patient-centered cancer care based at the Norris Cotton Cancer Care Pavilion at Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center. With 14 locations around New Hampshire and Vermont, Dartmouth Cancer Center is one of only 53 National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Centers. Each year the Dartmouth Cancer Center schedules 74,000 appointments seeing more than 4,500 newly diagnosed patients, and currently offers patients more than 240 active clinical trials. Celebrating its 50th anniversary in 2022, Dartmouth Cancer Center remains committed to excellence, outreach and education. We strive to prevent and cure cancer, enhance survivorship and to promote cancer health equity through pioneering interdisciplinary research and collaborations. Learn more at http://cancer.dartmouth.edu.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-05-15
Oxytocin, the so-called “love hormone,” plays a key role in the process of how a young zebra finch learns to sing by imitating its elders, suggests a new study by neuroscientists at Emory University. Scientific Reports published the findings, which add to the understanding of the neurochemistry of social learning.
“We found that the oxytocin system is involved from an early age in male zebra finches learning song,” says Natalie Pilgeram, first author of the study and an Emory PhD candidate in psychology. “It’s basic science that may lead to insights into the ...
2023-05-15
Resistance to antibiotics is a problem that alarms the medical and scientific community. Bacteria resistant to three different classes of antibiotics, known as multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacteria, are far from rare. Some are even resistant to all currently available treatments and are known as pan-drug resistant (PDR). They are associated with dangerous infections and listed by the World Health Organization (WHO) as priority pathogens for drug development with maximum urgency.
An article published in a special issue of the journal Antibiotics highlights a compound with antibacterial activity that presented promising ...
2023-05-15
Post-secondary education (PSE) has a potential for improving the IQ of adults with mild intellectual disability (ID), according to a new Bar-Ilan University study.
The study examined the impact of PSE on students with mild ID who study in a university-based program, known as the Empowerment Project, at the Bar-Ilan University Faculty of Education.
The study sample included 24 participants, divided into 12 students with ID who participate in the Empowerment Project and 12 adults with ID with the same background, who did not participate. The results were published in the European Journal of Special Needs Education.
The findings revealed significant IQ improvement ...
2023-05-15
New synthetic metabolic pathways for fixation of carbon dioxide could not only help to reduce the carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere, but also replace conventional chemical manufacturing processes for pharmaceuticals and active ingredients with carbon-neutral, biological processes. A new study demonstrates a process that can turn carbon dioxide into a valuable material for the biochemical industry via formic acid.
In view of rising greenhouse gas emissions, carbon capture, the sequestration of carbon dioxide from large emission sources, is an ...
2023-05-15
Astronomers have described the first radiation belt observed outside our solar system, using a coordinated array of 39 radio dishes from Hawaii to Germany to obtain high-resolution images. The images of persistent, intense radio emissions from an ultracool dwarf reveal the presence of a cloud of high-energy electrons trapped in the object’s powerful magnetic field, forming a double-lobed structure analogous to radio images of Jupiter’s radiation belts.
“We are actually imaging the magnetosphere of our target by observing the radio-emitting ...
2023-05-15
Recently published in PeerJ Life and Environment, researchers successfully use aircraft surveys with novel instrumentation to capture airborne nucleic acids and probe biodiversity in the atmosphere, uncovering surprising findings.
[Clemson, May 2023] - A groundbreaking research article titled "Aircraft Surveys for Air eDNA: Probing Biodiversity in the Sky" unveils a revolutionary approach to studying genetic material in the atmosphere. Scientists have developed a durable and sterilizable probe and supporting system to capture air environmental nucleic acids (eDNA) with full-flow filtration and a high-integrity chamber.
Using this innovative probe, ...
2023-05-15
ITHACA, N.Y. – A Cornell University-led experiment in which two people play a modified version of Tetris revealed that players who get fewer turns perceived the other player as less likable, regardless of whether a person or an algorithm allocated the turns.
Most studies on algorithmic fairness focus on the algorithm or the decision itself, but researchers sought to explore the relationships among the people affected by the decisions.
“We are starting to see a lot of situations in which AI makes decisions on how resources should be distributed among people,” ...
2023-05-15
The cerebellum, a major part of the hindbrain in all vertebrates, is important for motor coordination, language acquisition, and regulating social and emotional behaviors. A study led by Dr. Roy Sillitoe, professor of Pathology and Neuroscience at Baylor College of Medicine and investigator at the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute (Duncan NRI) at Texas Children’s Hospital, shows two distinct types of cerebellar neurons differentially regulate motor and non-motor behaviors during development and in adulthood.
The study, published in Nature Communications, provides the first in ...
2023-05-15
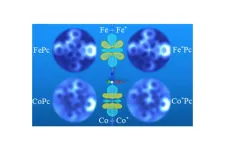
No one will ever be able to see a purely mathematical construct such as a perfect sphere. But now, scientists using supercomputer simulations and atomic resolution microscopes have imaged the signatures of electron orbitals, which are defined by mathematical equations of quantum mechanics and predict where an atom’s electron is most likely to be.
Scientists at UT Austin, Princeton University, and ExxonMobil have directly observed the signatures of electron orbitals in two different transition-metal atoms, iron (Fe) and cobalt ...
2023-05-15
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Investors in commercial real estate are rethinking the values of coastal properties exposed to flood risk — even in northern U.S. locales that haven’t suffered flood damage, according to researchers. This shift in perspective has implications for investors and developers alike as they determine the value of coastal properties amid a changing climate.
Eva Steiner, associate professor of real estate and King Family Early Career Professor in Real Estate in the Penn State Smeal College of Business, and her co-authors published these findings recently in Real Estate Economics.
Steiner and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Alternating estrogen and anti-estrogen therapies is effective in treating metastatic breast cancer
Results from a new clinical trial show that cycling between estrogen-stimulating and estrogen-blocking therapies is an effective treatment for patients with metastatic or advanced ER+ breast cancer.