(Press-News.org) New University of Colorado Boulder research shows the number of farms globally will shrink in half as the size of the average existing farms doubles by the end of the 21st century, posing significant risks to the world’s food systems.
Published today in the journal Nature Sustainability, the study is the first to track the number and size of farms year-over-year, from the 1960s and projecting through 2100.
The study shows that even rural, farm-dependent communities in Africa and Asia will experience a drop in the number of operating farms.
“We see a turning point from widespread farm creation to widespread consolidation on a global level, and that's the future trajectory that humanity is currently on,” said Zia Mehrabi, assistant professor of environmental studies at CU Boulder. “The size of the farm and the number of farms that exist are associated with key environmental and social outcomes.”
To evaluate the global state of farming, Mehrabi used data from the UN Food and Agricultural Organization on agricultural area, GDP per capita and rural population size of more than 180 countries to first reconstruct the evolution of farm numbers from 1969-2013 and then to project those numbers through 2100.
His analysis found that the number of farms around the world would drop from 616 million in 2020 to 272 million in 2100. A key reason: As a country’s economy grows, more people migrate to urban areas, leaving fewer people in rural areas to tend the land.
Reap what you sow
A decline in the number of farms and an increase in farm size has been happening in the United States and Western Europe for decades. The most recent data from the U.S. Department of Agriculture indicates there were 200,000 fewer farms in 2022 than in 2007.
Mehrabi’s analysis found that a turning point from farm creation to widespread consolidation will begin to occur as early as 2050 in communities across Asia, the Middle East, North Africa, Oceania, Latin America and the Caribbean. Sub-Saharan Africa will follow the same course later in the century, the research found.
It also shows that even if the total amount of farmland doesn't change across the globe in coming years, fewer people will own and farm what land there is available. The trend could threaten biodiversity in a time where biodiversity conservation is top of mind.
“Larger farms typically have less biodiversity and more monocultures,” Mehrabi said. “Smaller farms typically have more biodiversity and crop diversity, which makes them more resilient to pest outbreaks and climate shocks.”
And it’s not just biodiversity: Food supply is also at risk. Mehrabi’s previous research shows the world’s smallest farms make up just 25% of the world’s agricultural land but harvest one-third of the world’s food.
Moreover, fewer farms mean fewer farmers who may carry with them valuable Indigenous knowledge dating back centuries. As farms consolidate, that knowledge is replaced by new technology and mechanisation.
Building a diverse food portfolio
Just as a diverse investment portfolio performs better than one that is not diversified, having diversity in the world’s food source portfolio is beneficial in the long run, said Mehrabi.
“If you’re investing in today’s food systems with around 600 million farms in the world, your portfolio is pretty diverse,” Mehrabi said. “If there’s damage to one farm, it’s likely the impact to your portfolio will be averaged out with the success of another. But if you decrease the number of farms and increase their size, the effect of that shock on your portfolio is going to increase. You’re carrying more risk.”
There are also upsides to the shift in corporate farm ownership: The paper points out that consolidation in farming can lead to improved labor productivity and economic growth with a larger workforce in non-farm employment and improved management systems.
One of the biggest benefits of farm consolidation, Mehrabi said, is improved economic opportunity for people, and the ability to choose their own career path within our outside of the agricultural sector.
But those future farm workers may need more support as suicide rates in the agriculture industry are among the highest rates by occupation in the U.S.
“Currently, we have around 600 million farms feeding the world, and they’re carrying 8 billion people on their shoulders,” Mehrabi said. “By the end of the century, we’ll likely have half the number of farmers feeding even more people. We really need to think about how we can have the education and support systems in place to support those farmers."
By raising awareness of global agricultural trends, Mehrabi hopes his analysis will lead to policies that ensure biodiversity conservation, maintain climate resilience, preserve Indigenous knowledge and provide incentives to improve the rural economy in countries around the world.
END
The number of the world's farms to halve by 2100, study shows
2023-05-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Investigation raises questions over lack of “substantial evidence” for FDA approved antibiotic
2023-05-16
Drugs approved in the US require “substantial evidence” that they are effective. But an investigation by The BMJ into the recent approval of the antibiotic Recarbrio from Merck suggests that these standards are being bypassed.
Peter Doshi, senior editor at The BMJ, describes how US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) scientists had serious doubts about Recarbrio - a product 40 times more expensive than an existing generic alternative - but the agency approved it anyway.
Did the FDA break its own rules in approving this antibiotic, and what does this case tell us about problems within the agency, he asks?
Recarbrio is a combination therapy made up ...
Chemical exposure may raise your risk for Parkinson’s
2023-05-16
Two years of heavy exposure to TCE, a liquid chemical that lingers in the air, water and soil, may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease by 70%.
Previous research has linked TCE, or trichloroethylene, to certain cancers, but a new study publishing in JAMA Neurology on May 15, 2023, is believed to be the first large-scale study to demonstrate its association with Parkinson’s.
TCE has been used for industrial and commercial purposes for nearly 100 years, and was used ...
How old are your bones?
2023-05-16
Researchers from The University of Technology Sydney (UTS) have measured the extent to which a bone fracture can lead to early death, and created a publicly available tool that doctors and patients can use to calculate risk.
The research, ‘Skeletal Age’ for mapping the impact of fracture on mortality has just been published in the prestigious scientific journal, eLife.
In the study of more than 1.6 million adults, the scientists found that a bone fracture was associated with a loss of one to ...
IU researchers find link between obesity and blood cancer
2023-05-16
Indiana University School of Medicine researchers studying clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP), a blood condition that may increase the risk of blood cancer, discovered that obesity was strongly associated with the condition. Their findings were recently published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
CHIP is a condition where blood cells accumulate genetic mutations, increasing the risk of developing blood cancer. Although CHIP is common in aging, the risk factors that contribute to the condition are poorly understood.
“Our study’s results showed being overweight ...
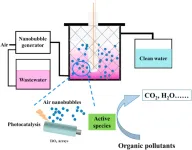
Degradation of Rhodamine B in the photocatalytic reactor containing TiO2 nanotube arrays coupled with nanobubbles
2023-05-16
The study is led by Xiaojun Han (School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology).
With the rapid development of urbanization and industrialization, environmental problems became increasingly serious. Dye wastewater is considered to be one of the biggest challenges due to its high toxicity. Organic dyes have mutagenic, teratogenic, and carcinogenic properties, and threaten the health and life of humans while hindering plant photosynthesis, which brings risks to the ecosystem. Traditional organic pollutant treatment ...
Occasional cannabis use during pregnancy may be enough to impact fetal growth significantly
2023-05-16
As more people use cannabis for recreational purposes, attitudes towards the drug have changed. For example, research has shown that dispensaries often recommend cannabis – also referred to as marijuana – to pregnant women to ease pregnancy symptoms, especially morning sickness.
There is a growing body of literature attesting to poor child outcomes if cannabinoids are consumed during pregnancy. The exact effects on the developing fetus, however, remain unclear. Researchers in the US have now examined how timing of cannabis exposure during pregnancy impacts fetal development.
“We show that even when marijuana use occurred only ...
Severe hot flashes after menopause increase metabolic syndrome risk in women
2023-05-16
EMBARGOED UNTIL SUNDAY 14 MAY 2023 AT 00:01 CET
Severe hot flashes after menopause increase metabolic syndrome risk in women
Women who experience more severe hot flashes after menopause are more likely to develop metabolic syndrome and high blood pressure, according to research presented at the 25th European Congress of Endocrinology in Istanbul. The findings of this long-term study highlight the importance of using hormone replacement therapy for menopause in these women.
Metabolic syndrome is a group of three or more ...
Newly discovered RNA molecules hold promise for detecting and treating esophageal cancer
2023-05-15
CLEVELAND—Irregularities in the body’s genetic coding to make proteins are linked to cancerous tumors. But most genetic material contains elements whose function isn’t clear.
Could abnormalities in non-coding material also impact a person’s health, or even be linked to cancers as well?
A new study by researchers at the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine suggests that the non-coding genetic molecules also play a key role in health and disease, including tumor development.
More specifically, ...
Henry Ford Health cardiologists look to the past to create new heart bypass procedure
2023-05-15
DETROIT (May 15, 2023) – Henry Ford Health Interventional cardiologists William O’Neill, M.D., and Khaldoon Alaswad, M.D., took a page out of the medical history books by performing a new coronary bypass procedure replicated from one not used in decades to treat a patient living with crippling angina ― a severe symptom of coronary artery disease.
Retired painting contractor Fred Casciano, 60, from Traverse City, became the first patient anywhere to receive the life-changing transcatheter procedure on April 12 at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit. The procedure was re-engineered from an operation first developed in the 1950s.
“This new ...
Novel AI-based software enables quick and reliable imaging of proteins in cells
2023-05-15
The more, the better
“TomoTwin paves the way for automated identification and localization of proteins directly in their cellular environment, expanding the potential of cryo-ET,” says Gavin Rice, co-first author of the publication. Cryo-ET has the potential to decipher how biomolecules work within a cell and, by that, to unveil the basis of life and the origin of diseases.
In a cryo-ET experiment, scientists use a transmission electron microscope to obtain 3D images, called tomograms, of the cellular volume containing complex biomolecules. To gain a more detailed image of ...