(Press-News.org) Prior to Putin’s invasion of Ukraine, Europe sourced a great deal of natural gas from Russia. But as a result of EU sanctions on Russia, this supply is no longer there. European countries have scrambled to find and secure new suppliers. But if both the war and these sanctions last into next winter, gas will remain in short supply – especially if next winter is a cold one and people need a lot of gas for heating. There is a distinct possibility that a shortage of gas will mean homes go unheated and will force industry to halt production. As a result, some countries might be tempted to prioritise the needs of their own citizenry and economy over showing solidarity to other countries.
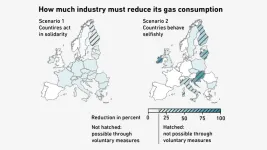
But how would the effects of such a selfish behaviour play out? And how far removed from a show of solidarity would such a scenario be? Researchers in the group of Giovanni Sansavini, Professor of Reliability and Risk Engineering at ETH Zurich, have examined this using model calculations. One of the study’s key findings is that collaborating in solidarity is worthwhile. At the very least, it would allow European countries to avert drastic and involuntary energy demand curtailment.
Collaborating in solidarity means countries helping each other out when gas is in short supply and signing bilateral agreements to that effect. This would involve a country voluntarily lowering its energy demand in order to supply gas to other countries should they desperately need some. Only eight such agreements have been reached in Europe to date.
The alternative to collaborating in solidarity is acting selfishly. Several Central European countries such as Germany, Belgium and the Netherlands would be better off acting selfishly as they would then have more gas available. However, this would cause shortages in other countries. Hardest hit would be countries along the eastern edge of Europe: from Finland down through the Baltic States to the Balkans.
Redirected gas flows in Europe
The main reason for all of this is that the disappearance of Russia as a supplier caused a fundamental shift in Europe’s supply channels. Russia used to supply eastern European countries as well as Finland. Although Finland shares a border with Norway, a big producer of natural gas, there is no gas pipeline between these two Nordic countries.
Europe is now offsetting its need for Russian gas largely with liquefied natural gas (LNG), which arrives by sea chiefly from the US, Qatar and Nigeria. Most of the ports for handling LNG are found on the Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea, with Spain being the largest transfer zone. Production in Norway remains high, as do imports from Algeria, reaching Europe through pipelines to Spain and Italy.
In other words, it’s now countries in Western Europe that are serving as the continent’s gateway to gas. And countries in the east and southeast suddenly find themselves at the end of the supply chain.
“The trouble is that Europe’s gas infrastructure wasn’t designed for such a shift,” says Paolo Gabrielli, a senior researcher in Sansavini’s group and co-author of the study. Cross-border pipelines are operating at maximum capacity, especially in Southeastern Europe. “This is why Southeastern Europe is particularly vulnerable to gas shortages and relies on agreements with other countries.” Gabrielli adds that existing bottlenecks can be removed by additional investments in the gas infrastructure.
Voluntary action is less painful
Based on their results, the researchers are calling on policymakers to coordinate the distribution and consumption of gas at the international level. Moreover, private individuals and companies throughout Europe must be given greater incentives to effect a measured reduction in their gas consumption wherever possible – even when there is no acute shortage. This would help keep gas storage as full as possible so as to be prepared for a cold winter.
“Voluntarily reducing demand to distribute the burden evenly is far less painful than forcing a country to massively reduce its demand because there’s no energy available,” says Jacob Mannhardt, doctoral student in Sansavini's group and lead author of the study. “International collaboration together with anticipatory energy savings are the most cost-effective way of preventing a severe energy crisis.”
Reducing climate impact and dependence
In their study, the ETH researchers analysed the entire energy system by looking not just at gas but also at other energy sources and the electricity grid. This allowed them to calculate that turning off gas-fired power stations and instead generating more electricity through coal would offset 15 percent of the supply gap left by Russian natural gas. The downside would be climate damage: such a move alone would trigger a 5 percent increase in greenhouse gas emissions in the electricity and heating sector.
“We show that diversification in natural gas supply, and especially LNG imports, have stabilised Europe’s gas supply,” Gabrielli says. “But Europe must learn its lesson from this energy crisis, namely that it is dangerous to be dependent on foreign countries for its energy supply. Switching to a different foreign supplier merely shifts the dependency.”
To avoid damaging the climate and simply forging new dependencies, the researchers recommend channelling the current momentum into investing in domestic energy supply, expanding renewable technologies, pursuing electrification efforts, and ensuring electricity trading across Europe.
END
Countries would be well advised to assist each other with regard to gas
If European countries collaborate, they can avoid severe energy scarcity due to a gas shortage. This is the finding of a new study by ETH Zurich researchers
2023-05-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ETRI commercializes a light source device capable of transmitting 25Gbps 30km
2023-05-17
Korean researchers and an SME have successfully commercialized a light source1) capable of transmitting 25 billion bits per second over long distances for the first time in Korea.
1) Light source: An element that converts electrical signals into optical signals and is manufactured by a compound semiconductor process
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute(ETRI) announced that it has succeeded in commercializing an electro-absorption modulator-integrated laser(EML)2) capable of transmitting data over 30 km at a speed of 25 Gbps with ELDIS Co., Ltd., a III-V semiconductor laser ...
Interventions with drug-coated balloons – a PCR Statement
2023-05-17
Paris, France, 17 May 2023. The field of coronary drug-coated balloon (DCB) angioplasty looks set to assume growing importance in the years to come and the potential for increased use of these devices in clinical practice is considerable.
DCB catheters became available for coronary use in Europe more than 14 years ago and have become widely used in clinical practice around the world since then. In recent years there has been renewed interest in this therapy linked to the development of novel devices coated with drugs from the limus family and a wider experience in the treatment of de novo lesions. As of today, for coronary use, there are no less ...
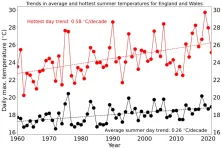
Extremely hot days are warming twice as fast as average summer days in North-West Europe
2023-05-17
New study analysed data on near-surface air temperatures recorded for North-West Europe over the past 60 years.
The findings show that the maximum temperature of the hottest days is increasing at twice the rate of the maximum temperature of average summer days.
The results highlight the need for urgent action by policy makers to adapt essential infrastructure to the impacts of climate change.
New research led by the University of Oxford has found that climate change is causing the hottest days in North-West Europe to warm at double the rate of average ...
Coronary bioresorbable scaffolds nearly as safe and effective as conventional metal stents for heart disease patients
2023-05-17
First-generation bioresorbable vascular scaffolds (BVS) may be just as effective as drug-eluting metallic stents, which are currently the standard treatment for heart disease patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
These are significant findings from a global clinical trial led by a researcher from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. The work could lead to advancements and improvements in new BVS technology and future clinical use among interventional cardiologists across the ...
Evidence of ‘pandemic brain’ in college students
2023-05-17
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Decision-making capabilities of college students – including some graduating this spring – were likely negatively affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, new research suggests.
Students in the small study conducted by researchers at The Ohio State University were less consistent in their decision making during the 2020 fall semester compared to students who had participated in similar research over several previous years.
The researchers compared responses to a hypothetical situation made by students during the pandemic to responses made by students in earlier studies. They found evidence that students in 2020 ...
Researchers to advocate for fundamental science on Capitol Hill
2023-05-17
Researchers from universities across the United States will arrive at the U.S. House and Senate on Wednesday for meetings with lawmakers and their staffs about the importance of fundamental science and funding for the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation and the Department of Energy Office of Science.
Their advocacy is particularly crucial this year in light of the current tense negotiations over raising the debt ceiling, which threatens non defense discretionary funding, including for scientific research, public health and many other aspects of federal government funding.
The researchers ...
Lesbian, bisexual women more likely to have worse heart health than heterosexual women
2023-05-17
Research Highlights:
In a study of nearly 170,000 adults in France, lesbian and bisexual women had lower cardiovascular health scores compared to heterosexual women.
In contrast, gay and bisexual men had higher ideal cardiovascular health scores compared to heterosexual men.
The study is the first to examine ideal cardiovascular health scores in sexual minorities.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, May 17, 2023
DALLAS, May 17, 2023 — Lesbian and bisexual women were less likely to have ideal cardiovascular health scores compared to heterosexual women, which ...
Learning to save lives can start as early as age 4, according to new scientific statement
2023-05-17
Statement Highlights:
School-aged children are highly motivated to learn basic life-saving skills, such as recognizing a cardiac arrest, calling for help and performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), according to a new scientific statement from the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR), the American Heart Association and the European Resuscitation Council.
The statement identifies age-appropriate best practices to help children learn various skills that are part of the cardiac arrest chain of survival.
Teaching children about CPR at regular intervals as they age will develop their ...
Diagnosing inflammatory diseases with synthetic peptides
2023-05-17
Common inflammatory disorders such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease can be diagnosed or monitored by measuring the protein calprotectin in stool samples, while serum levels of calprotectin could be used to monitor the inflammation status in rheumatoid arthritis. Calprotectin concentrations in patient samples are typically determined using antibodies that bind and detect the protein, e.g. in lateral flow assays like the now all-too-familiar home COVID-19 test kits.
But there is a problem with antibody-based calprotectin assays: the results can vary depending on the type of antibody ...
Study reveals cardiovascular health disparities based on sexual orientation
2023-05-17
In a recent nationwide study from France, lesbian and bisexual women had worse cardiovascular health scores than heterosexual women. The study, which is published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, also found that gay and bisexual men tended to have better cardiovascular health scores compared with heterosexual men; however, rural-residing sexual minority men had worse cardiovascular health compared with heterosexual men.
The study included 169,434 cardiovascular disease–free adults and assessed nicotine exposure, diet, physical activity, body mass index, sleep health, blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood lipids.
“Overcoming preventive ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Countries would be well advised to assist each other with regard to gasIf European countries collaborate, they can avoid severe energy scarcity due to a gas shortage. This is the finding of a new study by ETH Zurich researchers