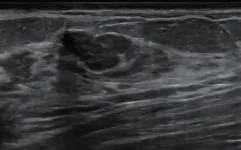
(Press-News.org) Leesburg, VA, May 17, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), deep learning–based computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) for breast lesion classification on ultrasound significantly improved radiologists’ diagnostic performance—particularly for reducing the frequency of benign breast biopsies.
Compared with the literature supporting CAD at tertiary and/or urban centers, results from this prospective multicenter study of radiologists without breast ultrasound expertise “support CAD in settings with incomplete access to breast imaging expertise,” wrote corresponding author Li-Gang Cui, MD, from Peking University Third Hospital in Beijing, China.
Cui et al.’s AJR study included patients scheduled to undergo biopsy or surgical resection of a breast lesion, classified as BI-RADS category 3-5 on prior breast ultrasound, at eight Chinese secondary or rural hospitals from November 2021 to September 2022. Patients underwent an additional investigational breast ultrasound, both performed and interpreted by a radiologist with no expertise in the modality. Hybrid body-breast imagers—radiologists lacking breast subspecialty training or in whom breast ultrasound accounted for less than 10% of their ultrasounds performed annually—then assigned a BI-RADS category. CAD results were used to upgrade reader-assigned BI-RADS category 3 lesions to category 4A, as well as for downgrading BI-RADS 4A lesions to 3. Histologic results of biopsy or resection served as the researchers’ reference standard.
Ultimately, application of CAD to interpretations by radiologists without breast ultrasound expertise resulted in upgrade of 6.0% (6/100) of BI-RADS category 3 assessments to category 4A, of which 16.7% (1/6) were malignant, and downgrade of 79.1% (87/110) of category 4A assessments to category 3, of which 4.6% (4/87) were malignant.
Because institutions lacking breast imaging expertise may also suffer from capacity issues to perform image-guided breast biopsies and pathologic evaluation of biopsy specimens, decreasing benign biopsies care of CAD “would be impactful,” the authors of this AJR accepted manuscript added.
North America’s first radiological society, the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) remains dedicated to the advancement of medicine through the profession of medical imaging and its allied sciences. An international forum for progress in radiology since the discovery of the x-ray, ARRS maintains its mission of improving health through a community committed to advancing knowledge and skills with the world’s longest continuously published radiology journal—American Journal of Roentgenology—the ARRS Annual Meeting, InPractice magazine, topical symposia, myriad multimedia educational materials, as well as awarding scholarships via The Roentgen Fund®.
END
Computer‐aided diagnosis improves breast ultrasound expertise in multicenter study
Deep learning–based computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) for breast lesion classification on ultrasound significantly improved radiologists’ diagnostic performance—particularly for reducing the frequency of benign breast biopsies.
2023-05-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Not Just for Sleep: Melatonin awakens scientists to its health benefits for cattle
2023-05-24
STARKVILLE, Miss.— Those needing extra sleep often reach for the bottle of melatonin, but Mississippi State scientists are discovering a host of other proven and potential health benefits for cattle who receive the supplement.
MSU faculty and students in the Department of Animal and Dairy Sciences and the Mississippi Agricultural and Forestry Experiment Station are making intriguing discoveries about the functions of melatonin in the bovine body and how this hormone can help support cattle health.
MSU Associate Professor Caleb Lemley has an extensive history of studying the use of melatonin as a supplement in cattle. He has been studying how the ...
Racial disparities in outcomes for pregnant and postpartum veterans and their infants
2023-05-24
A new study showed that despite there being no significant racial disparities in access or use of care during the perinatal period among veterans using Veterans Administration care, Black veterans were more likely than white veterans to experience postpartum re-hospitalization and to have a low-birth-weight infant. The study is published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Women’s Health. Click here to read the article now.
Jodie Katon, PhD, MS, from VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, and coauthors, reported that Black veterans were 67% more likely than white veterans to have a postpartum re-hospitalization and 67% more likely to have a low-birth-weight ...
Scientists from the Global South innovate to track ongoing amphibian pandemic
2023-05-24
The Panama Amphibian Rescue and Conservation Center at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) in Panama partnered with the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology in India to develop and validate a new test for chytridiomycosis strains, offering new insights into a wildlife disease that caused dramatic declines of over 500 amphibian species and the extinction of 90 others. Their novel assay, published in the journal Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, identified previously undetected Indian strains, and successfully detected ...
AI tool outperforms human emergency call handlers in identifying stroke, new study shows
2023-05-24
(24 May 2023, Munich, Germany) A team of researchers from Denmark have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) framework to address the number of strokes that go unrecognised by human emergency call handlers.1 The framework outperformed emergency call handlers in recognising stroke for both sexes and across all age groups studied, indicating its potential as a supplementary tool for early and precise stroke identification in the future.
The retrospective study, presented today at the European Stroke ...
Urban garden project seeks to reduce food insecurity and improve outcomes for people with HIV
2023-05-24
A University of Massachusetts Amherst public health scientist has received a five-year, $3.4 million grant from the National Institute of Mental Health to lead an urban gardening and peer nutritional counseling program aimed at improving the health of HIV-positive people with food insecurity in the Dominican Republic.
The project involving an international team of researchers and community partners is believed to the first full-scale trial to integrate nutritional counseling with food-generating ...
Propellers are louder over ground, researchers find
2023-05-24
The effects of the ground on propeller noise have been measured experimentally for the very first time by researchers in the Aeroacoustics research team at the University of Bristol.
In findings, published in the Journal of Sound and Vibration, the team found clear differences in the noise characteristics of propellers when over ground, known as ‘Ground Effect’, compared to when operated normally. They noted an overall noise increase when measuring at angles above the ground, with hydrodynamic and acoustic interaction effects being a key factor to the overall noise trends.
It is hoped this research, tested in the National Aeroacoustic Wind Tunnel ...
Establishing a wildflower meadow at King’s College, Cambridge bolstered biodiversity and reduced greenhouse gas emissions, study finds.
2023-05-24
A new study examining the effects of planting a wildflower meadow in the historic grounds of King’s College, Cambridge has demonstrated its benefits to local biodiversity and climate change mitigation.
The study, led by King’s Research Fellow Dr Cicely Marshall, found that establishing the meadow had made a considerable impact to the wildlife value of the land, while reducing the greenhouse gas emissions associated with its upkeep.
Marshall and her colleagues, among them three King’s undergraduate students, conducted biodiversity surveys over three years to compare the species richness, abundance ...
Breakthrough in computer chip energy efficiency could cut data center electricity use
2023-05-24
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Researchers at Oregon State University and Baylor University have made a breakthrough toward reducing the energy consumption of the photonic chips used in data centers and supercomputers.
The findings are important because a data center can consume up to 50 times more energy per square foot of floor space than a typical office building, according to the U.S. Department of Energy.
A data center houses an organization’s information technology operations and equipment; it stores, processes and disseminates ...
Study reveals unique molecular machinery of woman who can’t feel pain
2023-05-24
The biology underpinning a rare genetic mutation that allows its carrier to live virtually pain-free, heal more rapidly and experience reduced anxiety and fear, has been uncovered by new research from UCL.
The study, published in Brain, follows up the team’s discovery in 2019 of the FAAH-OUT gene and the rare mutations that cause Jo Cameron to feel virtually no pain and never feel anxious or afraid. The new research describes how the mutation in FAAH-OUT ‘turns down’ FAAH gene expression, as well as the knock-on effects on other molecular pathways linked to wound healing and mood. It is hoped the findings will ...
NTT and OIST make the first simultaneous atmospheric and marine observations directly beneath a violent, Category 5 typhoon in the North-West Pacific
2023-05-24
Joint Press Release
Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation (NTT, Head Office: Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo; President & CEO: Akira Shimada) and the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST, Head office: Onna-son, Kunigami-gun, Okinawa, Japan, Acting President: Dr. Albrecht Wagner) have successfully conducted the world’s first simultaneous marine and atmospheric measurements at multiple locations directly beneath a violent, Category 5*1, which is the strongest class, typhoon in the North-West Pacific, before it reached land.
These observations were made directly beneath typhoon No. 11, called “Hinnamnor”/”Henry”, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Computer‐aided diagnosis improves breast ultrasound expertise in multicenter studyDeep learning–based computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) for breast lesion classification on ultrasound significantly improved radiologists’ diagnostic performance—particularly for reducing the frequency of benign breast biopsies.