(Press-News.org) A prototype quantum sensor with potential applications in GPS-free navigation, developed at Imperial College London, has been tested in collaboration with the Royal Navy.
The test marks an important step in bringing new quantum technologies out of the lab and into real-world settings.
Many navigation systems today rely on global navigation satellite systems (GNSS), such as GPS, which uses signals from satellites orbiting the Earth. However, GPS navigation is not always accessible, obstacles like tall buildings can easily block the satellite signals, and they are also susceptible to jamming, imitation, or denial, thereby preventing accurate navigation. It has been estimated that a single day of satellite service denial would incur a cost of £1 billion to the UK.
Self-contained satellite-free navigation systems do exist; however, current technologies drift over time, meaning they lose accuracy unless regularly calibrated with satellites. The quantum sensor has the potential to remove this drift, significantly improving the accuracy over long timescales.
The Imperial College London team unveiled their first ‘quantum compass’ prototype in 2018, and have since been refining the technology to the point where it can now be tested in the field.
Real-world environments
The latest Imperial quantum sensor was integrated into a Qinetiq NavyPOD – an interchangeable rapid prototyping platform, before setting sail to London aboard a new Royal Navy research ship the XV Patrick Blackett.
The experiment is the first step towards understanding the application and exploitation of quantum-enabled navigation, which could provide significant navigational advantages when operating in satellite-denied areas.
Dr Joseph Cotter, lead scientist on the quantum sensor from the Department of Physics at Imperial, said: “Access to the Patrick Blackett provides us with a unique opportunity to take quantum sensors out of the lab and into the real-world environments, where they are needed.”
Commander Michael Hutchinson, Commanding Officer of XV Patrick Blackett, said: “Working with Imperial College London on this project has been an exciting and interesting opportunity for all of us. So far, the testing has gone well but the technology is still in its very early stages. It’s great to be a part of Royal Navy history.”
Exploiting ultracold atoms
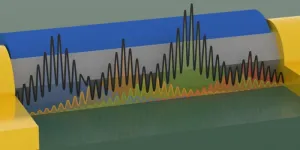
The Imperial quantum sensor is a new type of accelerometer. Accelerometers measure how an object’s velocity changes over time. By combining this information with rotation measurements and the initial position of the object, the current location can be calculated.
Conventional accelerometers are used in many different devices such as mobile phones and laptops. However, these sensors cannot maintain their accuracy over longer periods of time without an external reference.
The quantum accelerometer uses ultracold atoms to make highly accurate measurements. When cooled to extremely low temperatures the atoms start to display their ‘quantum’ nature, resulting in wave-like properties. As the atoms move through the sensor, an ‘optical ruler’ is formed by using a series of laser pulses. This allows the acceleration of the atoms to be precisely measured.
Quantum legacy
These new tests build on a legacy of quantum research at Imperial. Imperial has formed the Centre for Centre for Quantum Engineering, Science and Technology (QuEST) to translate discoveries in quantum science into transformative quantum technologies.
Professor Peter Haynes, Director of QuEST at Imperial, says: “The quantum accelerometer is a pioneering technology at the forefront of quantum innovation. It has the potential to transform navigation by making it more accurate and secure.
"This work represents the latest advance in Imperial's long track record of world-leading research in quantum science and technology. With deep expertise in basic science, engineering and translation, we are focussed on making quantum technologies - and the benefits they hold - a reality."
The XV Patrick Blackett ship also has another Imperial connection. The 1948 Nobel Prize winner Professor Lord Blackett was head of the Imperial College Department of Physics from 1953 to 1963 and the main building on the South Kensington campus still bears his name.
END
Quantum sensor for a future navigation system tested aboard Royal Navy ship
2023-05-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Hydrogen sulfide in cancer treatment
2023-05-26
Hydrogen sulfide is usually a highly toxic gas. However, with careful preparation, it can be used to support photothermal therapy (PTT) in treating cancer, as a team of researchers reporting in the journal Angewandte Chemie has recently discovered. As the team reports, an adjuvant releasing hydrogen sulfide causes tumor cells to lose their natural heat protection and thus to become significantly more sensitive to PTT.
Breathing in gaseous hydrogen sulfide usually causes us to suffocate, because the gas suppresses the respiratory chain in the mitochondria, ...
First death in the UK associated with Xylazine
2023-05-26
The death of a 43-year-old male is the first in the UK to be associated with Xylazine and marks the entry of the drug into the UK drug supply.
New research published in the Journal of Forensic and Legal Medicine from King’s College London details the death of the man in May 2022 from the effects of Xylazine alongside heroin, fentanyl and cocaine.
Xylazine is a non-opioid sedative, painkiller and muscle relaxant used in veterinary medicine as a tranquiliser for large animals. The drug – known ...
Developing a blueprint for mobile data visualisation
2023-05-26
By Jovina Ang
SMU Office of Research – It is predicted that by 2025, almost three quarters of the internet users in the world will be mobile-only users.
While mobile devices provide ready access to data, there are limitations to how the data can be optimally presented due to the small form factor and limited screen size.
For example, it is a lot easier to show 10,000 data points on a desktop compared to a smartphone, which typically has a screen size of 2.82 inches (71.5 mm) ...
Optimising outcomes for older adults
2023-05-26
By Alistair Jones
SMU Office of Research – The contribution of team members on a research project can get taken for granted, with storied senior leaders gaining most of the attention.
A recent exception is Micah Tan, an associate researcher at the Centre for Research on Successful Ageing (ROSA) at Singapore Management University (SMU). For his collaborative work at ROSA, Tan was recognised with an inaugural 2022 Research Staff Excellence Award.
“Winning the award has given me a strong sense of fulfilment and has inspired me to want to do more, both for the SMU community but also more generally in terms of ...
Harnessing large vision-language models
2023-05-26
By Alistair Jones
SMU Office of Research – The terminology of artificial intelligence (AI) and its many acronyms can be confusing for a lay person, particularly as AI develops in sophistication.
Among the developments is deep learning – a machine learning technique that teaches computers to learn by example.
“Deep learning has brought many major changes to AI, especially in natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision, two sub areas of AI,” says Jing Jiang, a Professor of Computer Science at Singapore Management University (SMU).
“In my field, which is NLP, the solution ...
State policies can boost use of anti-opioid medication
2023-05-26
States that want to increase access to buprenorphine, a lifesaving medication used to treat opioid use disorder, should consider efforts to enhance professional education and clinician knowledge, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Examining six state-level policies aimed at boosting use of buprenorphine, researchers found that requiring buprenorphine prescribers to receive additional education beyond the initially required instruction, as well as continuing medical education related to substance misuse, were both associated with a significant increase in use of the treatment.
The findings are published in the latest edition of the journal JAMA Health Forum.
“Many ...
Association of healthy lifestyle factors and obesity-related diseases in adults in the UK
2023-05-26
About The Study: In this study of 438,000 UK Biobank participants, adherence to a healthy lifestyle was associated with reduced risk of a wide range of obesity-related diseases, but this association was modest in adults with obesity. The findings suggest that although a healthy lifestyle seems to be beneficial, it does not entirely offset the health risks associated with obesity.
Authors: Sebastien Czernichow, M.D., Ph.D., of the Hopital Europeen Georges Pompidou in Paris, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.14741)
Editor’s ...
Effect of free medicine distribution on health care costs in Canada
2023-05-26
About The Study: In this secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial of primary care patients in Ontario, Canada, eliminating out-of-pocket medication expenses for patients with cost-related nonadherence in primary care was associated with lower health care spending over three years. These findings suggest that eliminating out-of-pocket medication costs for patients could reduce overall costs of health care.
Authors: Nav Persaud, M.D., of the University of Toronto, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
Kentucky, Michigan scientific researchers awarded $2 million to study new heart disease, stroke treatments
2023-05-26
DALLAS, May 26, 2023 — A Lexington, Ky., research scientist studying ways to repair damaged major vessels with medication rather than surgery and a physician-scientist from Ann Arbor, Mich., exploring the mechanisms of how exercise can heal heart muscle and brain tissue following a heart attack or stroke are the most recent American Heart Association Merit Award recipients. Each researcher will receive $1 million in funding from the Association, the world’s leading voluntary organization focused on heart and brain health and research.
Alan Daugherty, Ph.D., D.Sc., FAHA, the associate vice president for research, ...
Scepticism about Microsoft results
2023-05-26
In March 2022, Microsoft published research results about the realisation of a special type of particle that might be used to make particularly robust quantum bits. Researchers at the University of Basel are now calling these results about so-called Majorana particles into doubt: through calculations they have shown that the findings can also be explained differently.
In 1938 a genius suddenly vanished without a trace: after buying a ferry ticket from Palermo to Naples, the young Italian physicist Ettore Majorana seemingly ...