(Press-News.org) New UCLA-led research suggests that patient mortality rates, readmissions, length of stay, and health care spending were virtually identical for elderly hospitalized patients who were treated by physicians with Doctor of Medicine (MD) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degrees.
While both traditional, or allopathic, medical schools and osteopathic medical schools provide the same rigorous health education, osteopathic training adds a more holistic, hands-on component involving manipulation of the musculoskeletal system – for instance, the use of stretching and massage to reduce pain or improve mobility.
“These findings offer reassurance to patients by demonstrating that they can expect high-quality care regardless of whether their physicians received their training from allopathic or osteopathic medical schools,” said senior author Dr. Yusuke Tsugawa, associate professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine and health services research at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and associate professor of health policy and management at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health.
The study will be published May 30 in the peer-reviewed Annals of Internal Medicine.
Both types of physicians are licensed to practice medicine in every state. Currently about 90% of practicing physicians hold MD degrees and 10% have DO degrees. But the latter group is rapidly growing due to an increasing number of osteopathic medical schools, with their numbers having swelled by 72% between 2010 and 2020 compared with a 16% increase in MDs during the same period, and their ranks are expected to continue expanding.
In addition, osteopathic physicians are more likely than their MD counterparts to serve patients in rural and underserved areas.
The researchers relied on four data sources: a 20% sample of Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries, amounting to about 329,500 people aged 65 years and older who were hospitalized between Jan. 1, 2016 and Dec. 31 2019; Medicare Data on Provider Practice and Specialty; a comprehensive physician database assembled by Doximity, and the American Hospital Association’s annual survey on hospital characteristics. Of the patients, 77% were treated by MDs and 23% were treated by DOs.
The researchers found that patient mortality rates were 9.4% among MDs vs. 9.5% among DOs, patient readmission rates were 15.7% vs. 15.6% respectively, healthcare spending was $1004 vs. $1003, and lengths of stay were 4.5 days for both.
The results are similar because both types of medical schools deliver rigorous, standardized medical education and comply with comparable accreditation standards, including four-year curriculums mixing science and clinical rotations, Tsugawa said.
The study does have some limitations, the researchers write, primarily the fact that they focused on elderly Medicare beneficiaries who were hospitalized with medical conditions, so the results may not apply to other population groups. In addition, they limited outcomes to specific measures of care quality and resource use, so these findings may not generalize to other outcomes.
But the findings “should be reassuring for policymakers, medical educators, and patients because they suggest that any differences between allopathic and osteopathic medical schools, either in terms of educational approach or students who enroll, are not associated with differences in quality or costs of care, at least in the inpatient setting,” the researchers write.
Additional study authors are Dr. Atsushi Miyawaki of UCLA and the University of Tokyo; Dr. Anupam Jena of Harvard University, Massachusetts General Hospital and the National Bureau of Economic Research; and Dr. Nate Gross of Doximity.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute on Aging (R01AG068633) and the Social Science Research Council.
END
UCLA-led research suggests no difference in health outcomes, care costs for patients treated by traditional MDs or osteopaths
2023-05-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Low-flavanol diet drives age-related memory loss, large study finds
2023-05-29
May 29, 2023--A large-scale study led by researchers at Columbia and Brigham and Women’s Hospital/Harvard is the first to establish that a diet low in flavanols—nutrients found in certain fruits and vegetables—drives age-related memory loss.
The study found that flavanol intake among older adults tracks with scores on tests designed to detect memory loss due to normal aging and that replenishing these bioactive dietary components in mildly flavanol-deficient adults over age 60 improves performance on these tests.
“The improvement among study participants with low-flavanol diets was substantial and ...
Vehicle stop study illuminates importance of officer's first words
2023-05-29
Eugenia Rho believes in the importance of first impressions, especially during vehicle stops.
An assistant professor in the Department of Computer Science, Rho is the lead author of a new research paper that illustrates how a law enforcement officer’s first 45 words during a vehicle stop with a Black driver can often indicate how the stop will end.
“We found that there’s a key difference in how officers talk to Black drivers during the first moments of stops that end in an arrest, handcuffing, or search versus those that don’t end in such outcomes,” said Rho, who leads the Society, AI, and Language (SAIL) ...
Eliminating gene SRC-3 in immune cells triggers effective long-lasting anti-cancer response
2023-05-29
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have discovered a crucial regulator of the anti-cancer immune response that could change the game in the fight against cancer. Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the study shows that in animal models of breast and prostate cancer, eliminating the gene SRC-3, specifically in a type of immune cell called regulatory T cells (Tregs), triggered a lifelong anti-cancer response that eradicated the tumor without the typical side effects observed with other therapies.
Furthermore, transferring Tregs without SRC-3 to animals carrying breast cancer ...
Even lawyers don’t like legalese
2023-05-29
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- It’s no secret that legal documents are notoriously difficult to understand, causing headaches for anyone who has had to apply for a mortgage or review any other kind of contract. A new MIT study reveals that the lawyers who produce these documents don’t like them very much either.
The researchers found that while lawyers can interpret and recall information from legal documents better than nonlawyers, it’s still easier for them to understand the same documents when translated into “plain English.” Lawyers also rated plain ...
One-third of galaxy’s most common planets could be in habitable zone
2023-05-29
Our familiar, warm, yellow sun is a relative rarity in the Milky Way. By far the most common stars are considerably smaller and cooler, sporting just half the mass of our sun at most. Billions of planets orbit these common dwarf stars in our galaxy.
To capture enough warmth to be habitable, these planets would need to huddle very close to their small stars, which leaves them susceptible to extreme tidal forces.
In a new analysis based on the latest telescope data, University of Florida astronomers have discovered ...
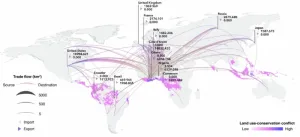
Mapping the conflict between farming and biodiversity
2023-05-29
It’s well known that producing foods such as beef can have an outsized footprint when it comes to carbon emissions. But a new study shows that some of these same staples can have an equally huge effect when it comes to biodiversity losses.
One of the main problems, the study found, results when food production overlaps with areas that have been identified as having the highest conservation priority.
Food production remains the main cause of biodiversity loss.
“Food production remains the main cause of biodiversity loss,” said Keiichiro Kanemoto, an associate professor at the Research Institute for Humanity ...
COVID-19 vaccine builds powerful immune response in First Nations peoples, study finds
2023-05-29
Published in Nature Immunology and Nature Briefing, the research is the first of its kind to decisively map immune responses produced by a COVID-19 vaccination in any First Nations populations.
In partnership with Menzies School of Health Research, researchers at the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute) evaluated immune responses in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples and non-Indigenous individuals after receiving the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.
Lead author of the study and PhD candidate at the Doherty ...
X-ray emissions from black hole jets vary unexpectedly, challenging leading model of particle acceleration
2023-05-29
Researchers discovered only relatively recently that black hole jets emit x-rays, and how the jets accelerate particles to this high-energy state is still a mystery. Surprising new findings in Nature Astronomy appear to rule out one leading theory, opening the door to reimagining how particle acceleration works in the jets—and possibly also elsewhere in the universe.
One leading model of how jets generate x-rays expects the jets’ x-ray emissions to remain stable over long time scales (millions of years). However, the new paper found that the x-ray emissions of a statistically significant number of jets varied over just a few years.
“One ...
New blood biomarker can predict if cognitively healthy elderly will develop Alzheimer’s disease
2023-05-29
PITTSBURGH, May 29, 2023 – Why do some people develop Alzheimer’s disease while others don’t? And, even more puzzlingly, why do many individuals whose brains are chock-full of toxic amyloid aggregates—a telltale sign of Alzheimer’s brain pathology—never go on to develop Alzheimer’s-associated dementias?
University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers appear to have found the answer. Star-shaped brain cells called astrocytes are key to swaying the pendulum in Alzheimer’s disease progression, shows new game-changing research published today in Nature Medicine.
By testing the blood of more ...
A novel blood serum assay to diagnose neurodegenerative diseases
2023-05-29
Synucleinopathies are a group of neurodegenerative diseases caused by the abnormal accumulation α-synuclein, a protein normally found in the brain and neurons. Incorrect folding of α-synuclein leads to formation of ‘seeds’, which attract more α-synuclein proteins to form larger clumps. Although, α-synuclein seeds have been found in various tissues and blood of patients with synucleinopathies, its potential as a biomarker is ambiguous.
Recently, in a study published in Nature Medicine, Associate Professor Ayami Okuzumi along with Senior Associate Professor Taku Hatano, both ...