A new player unveiled for lipid oxidation
2023-05-31
(Press-News.org)
Overweight and obesity pose significant health risks, including an increased likelihood of developing diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Researchers are seeking practical ways to promote the oxidation of lipids, which could help balance energy storage and consumption. A recent study has identified opioid growth factor receptor (Ogfr) gene as a promising new target for this process.
Rodents possess thermogenic fat that includes brown and beige adipocytes, which have a high capacity to uptake and utilize glucose and lipids. This promotes lipid oxidation and assists them in surviving environmental challenges such as food scarcity and cold temperatures. Studies conducted on human subjects also demonstrate that adipose tissue activities are responsive to environmental changes or diet, which suggests that they may serve as promising therapeutic targets.
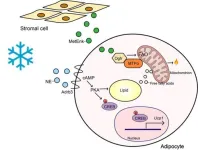
The researchers found that OGFr boosts lipid oxidation and promotes heat production in fat tissues (Figure 1). Ogfr is highly expressed in adipocytes, and it is difficult to maintain core body temperature during exposure to cold challenges in mice with genetic Ogfr deletion in adipocytes. Furthermore, when Ogfr was ablated in adipocytes, fatty acid oxidation was reduced, glucose tolerance impaired, and tissue inflammation increased in mice with diet-induced obesity. Human adipocytes also express OGFr highly, indicating a shared mechanism.
The identification of OGFr as a crucial player for enhancing lipid oxidation provides a new avenue for addressing obesity and related afflictions. Further research on the OGFr-mediated lipid oxidation mechanism could prove helpful in developing novel therapeutic strategies for obesity and metabolic disorders. Additionally, the related functioning of OGFr in human adipocytes opens the possibility of translating these findings to clinical settings, where OGFr-based pharmacological interventions could enhance fat activities and improve metabolic health.
###
Reference: Shan Zhang et al. (2023) Opioid growth factor receptor promotes adipose tissue thermogenesis via enhancing lipid oxidation. Life Metabolism. https://academic.oup.com/lifemeta/advance-article/doi/10.1093/lifemeta/load018/7151537
About Higher Education Press
Founded in May 1954, Higher Education Press Limited Company (HEP), affiliated with the Ministry of Education, is one of the earliest institutions committed to educational publishing after the establishment of P. R. China in 1949. After striving for six decades, HEP has developed into a major comprehensive publisher, with products in various forms and at different levels. Both for import and export, HEP has been striving to fill in the gap of domestic and foreign markets and meet the demand of global customers by collaborating with more than 200 partners throughout the world and selling products and services in 32 languages globally. Now, HEP ranks among China’s top publishers in terms of copyright export volume and the world’s top 50 largest publishing enterprises in terms of comprehensive strength.
About Life Metabolism
Life Metabolism is a fully open access, peer-reviewed journal that publishes one volume per year online, providing a platform for the publication of works of high significance and broad interest in all areas of metabolism. Life Metabolism welcomes several different article types, including original article, review article, research highlight, letter, editorial, perspective, and so on. Once a paper is accepted, Life Metabolism can publish a precopyedited, preproofed version of the paper online within 48 hours of receiving a signed licence, and this will be replaced by a copyedited, proofed version of the paper as soon as it is ready. The Editors-in-Chief are professors Peng Li at Tsinghua University and John R Speakman at University of Aberdeen, UK. In the first three years, there will be no publication costs for publishing in Life Metabolism, and Open Access fees will be waived.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-05-31
More than 80% of New Yorkers who inject drugs test positive for the opioid fentanyl, despite only 18% reporting using it intentionally, according to a new study by researchers at the NYU School of Global Public Health.
The findings, published in the International Journal of Drug Policy, suggest that many people who inject drugs are unknowingly using fentanyl, which may increase their risk for overdose and potentially their tolerance to fentanyl if it is used over time.
In 2021, more than 100,000 people died of a drug overdose in the United States, with 66% of these deaths involving illicit fentanyl—a synthetic opioid that is 50 to 100 times more potent than morphine.
In ...
2023-05-31
Washington, DC – Cats can play a role in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and their contaminated environment (pens in this study) can be infectious, according to new research. The study was published in Microbiology Spectrum, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
“In practice, after introduction of SARS-CoV-2 in our household, we should see our cat as part of the family regarding virus transmission,” said study coauthor Wim van der Poel DVM, Ph.D., Professor of Emerging and Zoonotic Viruses, Wageningen University and Research, in the Netherlands.
Van der Poel and colleagues conducted the study to gain better insight ...
2023-05-31
Researchers from University of Connecticut, Texas A&M University, University of Colorado at Boulder, and University of Florida published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines whether price promotions on some products differentially impact demand for other products depending on their relative locations within a display.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “The Negative and Positive Consequences of Placing Products Next to Promoted Products” and ...
2023-05-31
Some foods and medicines, such as many COVID-19 vaccines, must be kept cold. As a step toward a robust, stable technique that could indicate when these products exceed safe limits, researchers in ACS Nano report a class of brilliantly colored microcrystals in materials that become colorless over a wide range of temperatures and response times. As a proof of concept, the team packaged the color-changing materials into a vial lid and QR code.
Walk-in freezers and refrigerated trucks generally maintain their set temperatures, but ...
2023-05-31
As more and more electric cars are travelling on the roads of Europe, this is leading to an increase in the use of the critical metals required for components such as electric motors and electronics. With the current raw material production levels there will not be enough of these metals in future – not even if recycling increases. This is revealed by the findings of a major survey led by Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, on behalf of the European Commission.
Electrification and digitalisation are leading to a steady increase in the need for critical metals* in the EU’s vehicle fleet. Moreover, only a small proportion of the metals are ...
2023-05-31
Analysis of a British spinosaur tooth by palaeontologists at the EvoPalaeoLab of the University of Southampton shows that several distinct spinosaur groups inhabited Cretaceous Britain.
Stored within the collections of the Hastings Museum and Art Gallery in East Sussex, the fossil that forms the basis of the new study was gifted to the museum in 1889. It was collected from the local Lower Cretaceous rocks of the Wealden Supergroup, a thick, complicated rock sequence deposited across south-eastern England between 140 and 125 million years ago.
The ...
2023-05-31
IMDEA Software and IMDEA Networks Institutes participate together with six other partners (Instituto Nacional de Técnica Aeroespacial, Centro Español de Metrología, Fundación Vithas, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid and Universidad Complutense de Madrid) in the MADQuantum-CM project, funded by the Community of Madrid, the Spanish State through the Plan for Recovery, Transformation and Resilience, and the European Union through the NextGeneration EU funds. The objective ...
2023-05-31
Research Highlights:
One-third of adults in the U.S. with Type 2 diabetes may have symptomless or undetected cardiovascular disease.
Adults with Type 2 diabetes who do not have any signs or symptoms of cardiovascular disease are more likely to have elevated levels of two proteins linked to heart disease than peers without Type 2 diabetes. These cardiac biomarkers are associated with an increased risk of death from cardiovascular disease and any cause.
The findings suggest that routine screening for these two cardiac biomarkers and more tailored interventions may help to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease ...
2023-05-31
Statement Highlights:
In its first scientific statement addressing cardiovascular health in American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) women of childbearing age, the American Heart Association reports that more than 60% of AI/AN women already have suboptimal heart health when they enter pregnancy, which is strongly related to the development of heart disease later in life.
In addition, more than 4 in 5 AI/AN women reported they have experienced violence, and they are disproportionately likely to have also experienced a high number of adverse childhood experiences, which contribute to higher heart disease risk.
Type 2 diabetes is the predominant, traditional cardiovascular ...
2023-05-31
The term ‘well-being’ entered popular vocabulary during the Covid-19 pandemic soon after ‘lockdown’ and ‘quarantine’. We quickly discovered that without the ability to take walks, socialize, and work, our well-being suffered. Health was suddenly more than just the state of our bodies – it also depended on our ability to engage in activities that matter to us.
Though this was a revelation to many, the World Health Organization (WHO) had already begun this rethinking of health. It created a new concept and assessment ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A new player unveiled for lipid oxidation