New push will digitize records of African plants held in herbaria and museums across the US
2023-06-06
(Press-News.org)
LAWRENCE — Over the past few decades, herbaria and museums worldwide have created digital data records documenting millions of specimens in their holdings. The benefits of digitizing the contents of natural history museums and research institutions flow to the public and researchers worldwide.
Now, through a group of related grants from the National Science Foundation, researchers are systemically digitizing more than a million specimens of plants from across tropical Africa held at 20 institutions throughout the United States. The tropical African plant specimens — documenting some of the richest elements of biodiversity in the world — will be digitally imaged, while associated data are captured and data records are georeferenced.
Some of the job of assembling and performing quality control on the related datasets is taking place at the University of Kansas Biodiversity Institute, with $1 million of National Science Foundation funds supporting data cleaning and improvement work led by Town Peterson, University Distinguished Professor of Ecology & Evolutionary Biology and senior curator with the KU Natural History Museum and Biodiversity Institute. Peterson also directs the overall projects, which includes the U.S. herbaria and four African partner institutions.
“Herbaria tend to have large-scale collections, so this is a big initiative,” Peterson said. “The herbarium community in the U.S. has made really good progress on U.S. data thanks to some big initiatives at NSF, so now you can access a lot of the herbarium data on U.S. plants online easily. Still, there's a lot of herbarium specimens from other parts of the world that nobody's gotten to yet. Tropical Africa is one of those places.”
Building on previous digitization collaborations with Alex Asase, professor at the University of Ghana, Peterson was involved in assembling the network of American herbaria to apply for the new NSF funds. Previously, Peterson and Asase partnered to organize digitization of more than 250,000 herbarium records for specimens from West Africa in work funded by the JRS Biodiversity Foundation. This new grant aims to move much of the specimen digitization enterprise to a new model, in which the people wanting and needing to use the data are major factors in capturing, improving and sharing the data.
“Alex is in charge of one of the larger herbaria in in West Africa,” Peterson said. “So, he digitized those data and got them online for the scientific community. Alex’s work has helped other herbaria in Benin, Togo, Liberia, Nigeria and Cameroon. But the biggest collections are held in herbaria and museums in Europe… you can't really have any control over collections priorities in those institutions. So how do you speed that up? Alex asked, ‘What if we were to find a solution where the people who need the data promote and essentially make the capture of the data happen?’”
The new NSF-funded project is larger in scope, involving essentially all U.S. institutions with important holdings from the region. Among the partners are the University of California-Berkeley, California Botanic Garden (formerly Rancho Santa Ana Botanic Garden), Missouri Botanical Garden, Harvard University and the New York Botanical Garden.
“The idea is that NSF funds U.S. herbaria to scan and capture data from all of their plant specimens from tropical Africa,” Peterson said. “The data are then improved via data-quality checking here at the University of Kansas and georeferenced by African partner teams located in Ghana, Rwanda, Malawi and Gabon. That is, a major part of the process of making these data come alive will be done by African scientists and students who are eager to access such a rich store of information.”
Peterson, an ornithologist by training, also is a leader in working with data generated by digitization projects. The KU Biodiversity Institute was an early pioneer in the field. In this capacity, his team at KU (including KU graduate students) will work with the huge datasets that the herbaria and African georeferencing teams will generate.
“The data come back here to KU, and my group will do a lot of the quality control,” Peterson said. “We’ll pick out possible problems. Then this big data pool — about 1.3 million new data records for tropical Africa — will be at the disposition of not just the network of herbaria, but the whole world community. The data will be there for scientific analyses to be done.”
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-06
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists found that a small tweak created big performance improvements in a type of solid-state battery, a technology considered vital to broader electric vehicle adoption.
These batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of a potentially flammable liquid. When the battery charges or operates, ions move between electrodes through the electrolyte between them. A new method for pressing the solid electrolyte practically eliminates tiny air pockets that block ion flow, so the battery charges twice as fast.
ORNL lead researcher Marm Dixit said the approach involved heating the press after spreading ...
2023-06-06
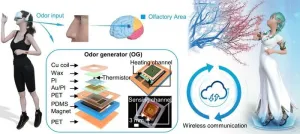
A research team co-led by researchers from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently invented a novel, wireless, skin-interfaced olfactory feedback system that can release various odours with miniaturised odour generators (OGs). The new technology integrates odours into virtual reality (VR)/augmented reality (AR) to provide a more immersive experience, with broad applications ranging from 4D movie watching and medical treatment to online teaching.
“Recent human machine interfaces highlight the importance of human sensation feedback, including vision, audio and haptics, associated with wide applications in entertainment, medical treatment and VR/AR. Olfaction also plays a significant ...
2023-06-06
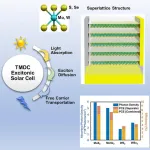
When it comes to supplying energy for space exploration and settlements, commonly available solar cells made of silicon or gallium arsenide are still too heavy to be feasibly transported by rocket. To address this challenge, a wide variety of lightweight alternatives are being explored, including solar cells made of a thin layer of molybdenum selenide, which fall into the broader category of 2D transition metal dichalcogenide (2D TMDC) solar cells. Publishing June 6 in the inaugural issue of the journal Device, researchers propose a device design that can take the efficiencies of 2D TMDC ...
2023-06-06
About The Study: In this survey of clinician-researchers who received career development grants from the National Institutes of Health, there were concerning rates of sexual harassment, cyber incivility, and negative perceptions of climate, disproportionately affecting minoritized groups and affecting mental health. Ongoing efforts to transform culture are necessary.
Authors: Reshma Jagsi, M.D., D.Phil., of Emory University in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
2023-06-06
BOSTON—Currently there are no contraceptives capable of producing permanent sterilization in companion animals. Spaying, the surgical removal of the ovaries and uterus, is the most widely used strategy to control unwanted reproduction in female cats.
For the first time, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), and their collaborators have demonstrated that a single dose of anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) gene therapy can induce long-term contraception in the domestic cat, potentially providing a safe and effective alternative to surgical spaying. The research ...
2023-06-06
About The Study: In this network meta-analysis of 10 observational studies including 3,083 patients with breast cancer who received surgical treatment, expert panel–based and computer-based aesthetic outcome evaluation consistently scored lower than patient-perceived outcomes. Standardization and supplementation of expert panel and software aesthetic outcome tools with racially, ethnically, and culturally inclusive patient-reported outcome measures is needed to improve clinical evaluation of the journey of patients with breast cancer and to prioritize components ...
2023-06-06
About The Study: This randomized clinical trial found that, although the peer health coaching program did not significantly decrease systolic blood pressure, participants who received the intervention reported better mental health-related quality of life compared with the control group. The results suggest that a peer-support model that is integrated into primary care can create opportunities for well-being improvements beyond blood pressure control.
Authors: Karin M. Nelson, M.D., M.S.H.S., of the Veterans Affairs Puget Sound Health Care System in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
2023-06-06
College Park, Md. — Air conditioning, refrigeration, and other cooling technologies account for more than 20 percent of today’s global energy consumption, while the refrigerants they use have a global warming potential thousands of times greater than carbon dioxide. In a recent study in the journal Science, a team led by Maryland Engineering Professors Ichiro Takeuchi, Reinhard Radermacher, and Yunho Hwang introduced a high-performance elastocaloric cooling system that could represent the next generation of cooling devices.
Takeuchi calls ...
2023-06-06
Patients would be more willing to enter medication-assisted treatment for opioid use disorder if existing stigmas were reduced and more accessible payment support was readily available, a West Virginia University study finds.
Adam Baus, director of the Office of Health Services Research, and his team gained insight from patients on what helped or hindered medication-assisted treatment, or MAT, to support recovery.
“Little research attention has been given to learning directly from those in medication-assisted treatment for opioid use disorder,” said Baus, also a research assistant professor with the WVU School of Public Health ...
2023-06-06
Researchers at Kyoto University, Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST), and Photron Limited in Japan have developed the world’s fastest camera capable of detecting fluorescence from single molecules. They describe the technology and examples of its power in two articles published in the same issue of the Journal of Cell Biology.
“Our work with this camera will help scientists understand how cancer spreads and help develop new drugs for treating cancer,” says bio-imaging expert Takahiro Fujiwara, who led the research at the Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS).
Single fluorescent-molecule ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New push will digitize records of African plants held in herbaria and museums across the US