(Press-News.org) EL PASO, Texas (June 8, 2023) – Researchers from The University of Texas at El Paso’s School of Pharmacy will explore the viability of a new treatment for vascular dementia, thanks to a $2.2 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). The grant builds on work that’s previously been done by the team and their collaborators.
Vascular dementia — the second most common type of dementia worldwide — is caused by reduced or blocked blood flow in the brain. Similar to Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia causes memory loss and cognitive problems such as confusion, slowed thinking, and difficulty with problem solving and speaking.
Mohammad Iqbal Bhuiyan, Ph.D., assistant professor in the UTEP School of Pharmacy, is the project’s principal investigator. His NINDS-funded research will focus on better understanding the biological triggers behind vascular dementia and investigating a new candidate drug, known as “ZT-1a,” to counteract the condition.
"The opportunity to work with my UTEP colleagues and the NINDS to develop an innovative therapeutic strategy excites me the most," Bhuiyan said. "Our study will ideally demonstrate that this candidate drug is effective and can prevent cognitive impairments in dementia patients."
Before joining UTEP, Bhuiyan served as PI and Co-I on several NIH and Veterans Affairs grants, studying ischemic strokes, which occur when a vessel supplying blood to the brain is obstructed.
In a study published earlier this year, Bhuiyan and former colleagues at the University of Pittsburgh discovered that ZT-1a, a compound that belongs to a category of drugs called SPAK inhibitors, is neuroprotective and can suppress the detrimental effects of ischemic stroke.
According to Bhuiyan, the findings suggest that ZT-1a has therapeutic potential against vascular dementia as a brain white matter protectant. Using the NINDS grant, the UTEP team will now test that hypothesis over the next several years.
"The Centers for Disease Control estimate that nearly 14 million adults will live with dementia by 2060,” said José O. Rivera, Pharm.D., dean of the UTEP School of Pharmacy. “That is why Dr. Bhuiyan’s research has such potential for impact. I congratulate him and his colleagues here at UTEP on receiving this highly competitive grant from the NIH, and I look forward to the insights they will uncover.”
Additional UTEP contributors will include postdoctoral researchers M. Tipu Sultan, Ph.D., and M. Khadija Habib, Ph.D.; graduate student M. Shamim Rahman; and research technician Israt Jahan.
The University of Pittsburg and the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia will also contribute to the project.
About The University of Texas at El Paso
The University of Texas at El Paso is America’s leading Hispanic-serving University. Located at the westernmost tip of Texas, where three states and two countries converge along the Rio Grande, 84% of our 24,000 students are Hispanic, and half are the first in their families to go to college. UTEP offers 169 bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degree programs at the only open-access, top-tier research university in America.
END
Researchers to explore potential of new treatment against vascular dementia
Research explores how suppressed blood flow in the brain causes dementia
2023-06-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ancient herbivore’s diet weakened teeth leading to eventual starvation, study suggests
2023-06-09
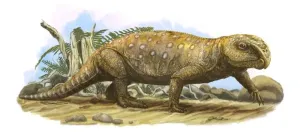
A team of researchers from the University of Bristol have shed light on the life of the ancient reptile Rhynchosaur, which walked the earth between 250-225 million years ago, before being replaced by the dinosaurs.
Rhynchosaurs are a little-understood group of roughly sheep-sized ancient reptiles that thrived during the Triassic Period, a time of generally warm climates and tough vegetation.
In the new study, the researchers studied specimens found in Devon and used CT scanning to see how the teeth wore down ...
Personalized vaccines may revolutionize cancer treatment
2023-06-09
Researchers from Edith Cowan University (ECU) are leading ground-breaking global trials which could save lives by changing how we treat cancer in the near future.
ECU Centre for Precision Health Clinical Professor Adnan Khattak presented the trial’s latest results at the 2023 American Society of Oncology (ASCO) congress in Chicago this week, the biggest cancer treatment conference in the world with more than 45,000 attendees.
Professor Khattak outlined how survival and disease recurrence rates among people who’d had high-risk skin cancers (melanomas) removed improved significantly when an mRNA vaccine ...
THE LANCET INFECTIOUS DISEASES: Taking a common diabetes medication after testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 reduces risk of developing long COVID by 40%, study finds
2023-06-09
Peer-reviewed / Randomised Controlled Trial / People
Peer-reviewed / Randomised Controlled Trial / People
The Lancet Infectious Diseases: Taking a common diabetes medication after testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 reduces risk of developing long COVID by 40%, study finds
US study of 1,126 overweight and obese people finds 6.3% of participants who took metformin, a medication commonly used to control blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes, within three days of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 reported a long COVID diagnosis within 10 months, compared to 10.4% of those who received a placebo.
This is the first published randomised ...
Confidence in vaccines has plummeted in Africa since the pandemic – Study across eight countries shows
2023-06-09
Public confidence in vaccines has plunged across sub-Saharan Africa since the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a study of 17,000 people, across eight countries, published today in the peer-reviewed journal Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.
The findings come as the World Health Organization and UNICEF have reported the largest sustained fall in uptake of routine childhood immunizations in three decades.
Six million fewer children in Africa received routine shots for diseases including tetanus, polio, diphtheria and measles over the past ...
LGB adults at higher risk of suicidal thoughts and self-harm
2023-06-09
Lesbian, gay and bisexual (LGB) people are more than twice as likely than their straight peers to experience suicidal thoughts or self-harming behaviours, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The study, published in Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, is the first ever to analyse nationally representative data on sexual orientation and suicidality in England whilst being able to compare individual sexual minority groups. The researchers analysed data combined from two household surveys of 10,443 English adults (aged 16 and over), representative of the population, sampled in 2007 and 2014.
As ...
University of Arizona launching computer science and engineering B.S.
2023-06-08
Right now, United States employers are unable to fill around 1 million computer science-related jobs because of a lack of qualified candidates, as estimated by the Bureau of Labor Statistics. And the demand isn’t going away – the bureau projects employment in the field to grow much faster than average through 2031, while the number of graduates will continue to lag behind job openings.
This workforce need is the primary reason the College of Engineering will soon offer a bachelor's degree in computer science and engineering, said Michael Wu, head of the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, which houses the ...
Children in Chile saw 73% fewer TV ads for unhealthy foods and drinks following trailblazing marketing restrictions
2023-06-08
Chilean policies aimed at reining in unhealthy food marketing are succeeding in protecting children from the onslaught of television advertisements (TV ads) for these products, according to new research. The country’s multi-phased regulations, which began in 2016, have led to a 73% drop in children’s exposure to TV ads for regulated foods and drinks (those that exceed legal thresholds for calories, sugar, salt or saturated fat) by 2019. During this time, the number of ads for unhealthy foods dropped 64% on all TV programs ...
Incomplete imaging for transient ischemic attack emergencies increases stroke risk
2023-06-08
Leesburg, VA, June 8, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), transient ischemic attack (TIA) emergency department (ED) encounters with incomplete neurovascular imaging were associated with higher odds of subsequent stroke within 90 days.
“Increased access to urgent neurovascular imaging in patients with TIA may represent a target that could facilitate detection and treatment of modifiable stroke risk factors,” wrote first author Vincent M. Timpone, MD, from the department of radiology at the University of Colorado Hospital in Aurora.
Timpone et al. ...
Researchers create engineered human tissue to study mosquito bites, disease
2023-06-08
Researchers Create Engineered Human Tissue to Study Mosquito Bites, Disease
Scientists hope to use this new platform to study how pathogens that mosquitoes carry impact and infect human cells and tissues.
By Eric Eraso | June 8, 2023
A UCF research team has engineered tissue with human cells that mosquitoes love to bite and feed upon — with the goal of helping fight deadly diseases transmitted by the biting insects.
A multidisciplinary team led by College of Medicine biomedical researcher Bradley Jay Willenberg with Mollie Jewett (UCF Burnett School of Biomedical Sciences) and Andrew Dickerson (University of Tennessee) ...
Mass General Cancer Center researchers share Insights on the evolution of proton radiotherapy
2023-06-08
As one of the first hospitals in the world to establish a proton radiotherapy program to treat cancer, Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and the Mass General Cancer Center have been pioneers in using and improving proton therapy for treating both benign and malignant tumors effectively while delivering a lower dose of radiation to tissue surrounding the target site. Researchers at MGH have led and continue to lead studies that are defining the best use of proton therapy, which is now being offered at 106 centers worldwide.
In a Review article published in The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Researchers to explore potential of new treatment against vascular dementiaResearch explores how suppressed blood flow in the brain causes dementia