(Press-News.org) Taking biofabrication to the next level: innovations in volumetric bioprinting
UMC Utrecht researchers propose solutions for bioprinting living tissue
Bioprinting is the printing of living cells and tissues. It's a promising technique that hopefully, one day, can solve the organ donor shortage by growing organs from patients' own cells. However, printing living tissues and cells is extremely complicated, and many hurdles need to be overcome to be able to get there. In this article, three recent innovations by UMC Utrecht are highlighted that will help to make bioprinting more clinically relevant.
The rise of volumetric bioprinting
The first association with 3D bioprinting is ‘classic’ 3D printing or extrusion printing with plastic filament. This has become quite famous in the past 15 years or so, with even over-the-counter printers available for the home. In principle, it should be possible to replace the plastic and print pieces of biologically functional tissue, with different kinds of cells present. But to achieve this, highly detailed and differentiated tissues will have to be made: even a cubic millimeter of organ tissue will need blood capillaries in it as well, so the bar is set very high for printers if we want to create functional tissue that we can implant on a clinically relevant scale.
With the development of bioinks, 3D extrusion bioprinting has become possible. New nozzles, nutritious inks and pre-made scaffolds make it easier for the cells to survive this process. And by using various inks at the same time, different kinds of cells could be deposited and in doing so create tissues. However, layer-by-layer printing still takes a long time; many hours for a multi-cubic centimeter object. Cells are likely to die during this process. Additionally, extrusion prints need to be able to withstand gravity, so the inks need to be sturdy, which means they are not very cell-friendly.
To overcome this slow and gravity-dependent process, volumetric printing has been adopted for bioprinting as well. In this process, a spinning vial with special gel is exposed to laser light. Where the laser light hits, the photosensitive gel will solidify quickly. This means that with a laser 3D light reconstruction, intricate shapes of multiple centimeters cubed can be created in a matter of seconds. Now, while this solves the issue of speed and gravity, it comes with its own drawbacks. These photosensitive gels can, in this way, only contain cells in suspension, so controlling which kind of cell ends up where – and how many of them – is hard to control. And because the gel is hard, it’s difficult for the cells to move, extend and communicate with each other, which is essential for the formation or even functioning of the tissue.
At the Regenerative Medicine Center Utrecht, researchers are continuously working to overcome these challenges, and the three papers that are discussed below have each solved part of the challenges described above.
Innovation 1: Creating biologically functional regions in a print
Volumetric bioprinting, with which an object a few centimeters in size can be printed in mere seconds, offers many possibilities for the printing of cells. The speed of the process combined with the cell-friendliness of the gel are great advantages. However, when the print is finished, the cells may not be placed exactly where they are needed, nor is it possible to alter the gel much to aid the development, growth or specialization of cells to create functional tissues. Overcoming this hurdle, then, is important, because in our body cells know where to go and where to stay following signals that they sense in specific regions or tissues.
Adding functionality to the printed gel
To make it possible to make chemical changes to the print after the initial printing process, the researchers played with the porosity of the gel, as well as the compounds in it that bind with other molecules in the gel. “With this technique it is possible to engraft biomolecules to our printed constructs within minutes in a high spatial resolution,” first author Marc Falandt explains. “First we printed our gelatin-based constructs with the volumetric printer, then by infusing these constructs with biomolecules and photoinitiator, we could create complex 3D motives inside the gelatin structures. This method gives us three-dimensional control of the location where you want your biomolecules to be trapped. Something that was not possible before.”
Helping cells find their way by giving them a chemical map
With this innovation, it is now possible to create volumetric prints that can have growth factors or bioactive proteins “painted” into them in any desired 3D shape. For example, signal molecules that guide the direction and formation of blood vessels can be placed in such a way that they create a trail that attracts new vessels only where and when needed inside the 3D printed object.
These signals could then attract the right cells, or help stem cells to fulfill their regenerative potential. Falandt: “This work really takes the first steps into the development and characterization of smart materials that allow biochemical editing in 3D. In combination with the fast volumetric bioprinting technique, this approach is extremely promising for the creation of a biofabricated scaffolds that could guide cell behavior and development. It could allow us to closely mimic the complex biochemical environment of native tissues and organs with our 3D bioprints.
Innovation 2: granular gels mean the best of both worlds for printed cells
For a successful fabricated tissue, the printed cells need to be pampered in order to survive and thrive in the finished product. And if they are to form a functional tissue, they need to be able to grow, move, and communicate with each other.
Various printing strategies have been tried to solve this, and they all have their pros and cons. In 3D extrusion printing, cells can be deposited in a variety of types and with high numbers, but this process takes very long, causes mechanical stress to the cells and is gravity-dependent – all detrimental to the cells’ survival and functioning. With fast volumetric bioprinting, speed and gravity may have been solved, but here the challenge is that cells are distributed randomly in the resin and in lower numbers, and because the final print consists of solid resin, the cells are unable to function and communicate properly.
Creating a granular microworld
To solve this issue, the materials used for bioprinting must provide an environment that allows for the self-organization and communication of cells. While this is generally possible with soft hydrogels, ensuring high printing resolution and shape fidelity of these materials remains a key bottleneck, especially when using conventional layer-by-layer fabrication techniques.
First author Davide Ribezzi explored the use of granular resins to overcome these challenges. ‘Granular gels are basically gel microparticles packed tightly together,’ Ribezzi says. ’While each microparticle possesses comparable properties to its bulk hydrogel counterpart, packed microgel particles can be designed and customized to display a broad array of added useful properties.’ Leveraging on particulate biomaterials is therefore a promising strategy to face drawbacks related to bulk cell encapsulation and material processability in the printing processes.
Combining different printing strategies
The granulated resins indeed allowed the researchers to combine extrusion and volumetric printing. Using extrusion printing, certain cells or other chemicals can be specifically deposited in the resin. This approach optimizes the balance between the speed of volumetric printing with the accuracy of extrusion printing. The gel moves around the printing nozzle like custard around an intrusive finger, so the cells can be placed in multiple layers quickly, without having to worry about the strength of the structure. Then, volumetric printing can finish the process by creating and finessing the shapes around the extruded cells.
This process wasn’t without its challenges. Ribezzi: 'Processing biological materials always requires lots of attention and meticulous planning of the experiments. But in our research we exploit the thermal properties of the microgel, which allows for a precise tuning of the mechanical and optical properties. This translated into tunable stimuli sensed by the embedded cells. However, this higher degree of tuning needed an even higher degree of attention and precision during the printing process.’
More biological activity; the proof is in the granular pudding
Experiments with cells confirm that the granulated resins allow for much more biological activity after printing, vastly outperforming the solid gels. Within eight days of being printed into the resin, stem cells were able to spread out more, epithelial cells created more junctions and neuron-like cells made more connections to each other.
Ribezzi: ‘For future studies, we envision the mixing and even local patterning of microgels obtained from different materials. It would allow us to create composite constructs with unique properties, or with bioactive pockets releasing for example drugs. These tools will boost tissue functionality, open up additional opportunities for tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, and the emerging area of engineered living materials.’
Innovation 3: Combining bioprinting techniques to pursue functional blood vessels
Volumetric bioprinting is a fast technique, which allows cells to survive the printing process. However, because this type of printing is done in cell-friendly gels, the resulting prints are structurally not very sound. This is a problem for printed blood vessels, which have to be able to withstand high pressures and bending. For this reason, a merger of volumetric bioprinting and melt electrowriting was pursued.
Melt electrowriting is a highly accurate type of 3D printing that works by directing a narrow filament of molten (biodegradable) plastic. It’s able to produce intricate scaffolds that are mechanically strong and able to deal with force. The downside here is that they can’t be printed with cells in there directly, because of the high temperatures involved. Therefore, volumetric bioprinting was used here to solidify cell-laden gels onto the scaffolds.
How to merge electrowriting with volumetric printing
The process starts with the creation of a tubular scaffold using melt electrowriting. This is then submerged into a vial with photoactive gel and placed in the volumetric bioprinter. In principle, the laser of the printer can selectively solidify the gel that sits in, on and/or around the scaffold. “In order to get this right, we had to place the scaffold exactly center in the vial,” first author Gabriël Größbacher says. “Any deviation from the center would mean that the volumetric print would be off-set. But we managed to center it perfectly by printing the scaffold on a mandril that we fitted to the vial.”
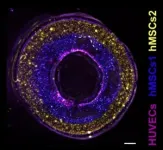
In this study, Größbacher and colleagues tested various thicknesses of the scaffold, which resulted in more or less strong tubes. Finally, they also tested various placements of the bioprinted gels. These could either be placed on the inner side of the scaffold, inside the scaffold itself or on the outside of it. By using two differently labeled stem cells, the team was able to print a proof of principle blood vessel with two layers of stem cells, and seeded epithelial cells in the center to cover the lumen of the vessel.
From tubes to functional vessels
The design could also allow for holes in the side of the print, giving the possibility for controlled permeability of the vessel for the blood to do its function. Finally, the researchers also created more complex structures like forked vessels, and even vessels with venous valves that were functional in maintaining a unidirectional flow.
Größbacher: “This was a proof of principle study. What we now need to do is replace the stem cells with functional cells that are part of a real blood vessel. That means adding muscle cells and fibrous tissue around the epithelial cells. Our goal now is to print a functional blood vessel.”
Outlook: the way forward to is to combine and expand these techniques
While these innovations provide interesting options to bring bioprinting forward, it will work best if they can be combined and expanded. Group leader Riccardo Levato states: 'Being able to print biologically active molecules into a print that uses granular gel means that the cells can use the molecular information better, as well as grow and develop into a tissue, together with their neighboring cells.'
END
Taking biofabrication to the next level: innovations in volumetric bioprinting
UMC Utrecht researchers propose solutions for bioprinting living tissue
2023-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Insights into redox-independent cellular stress response
2023-06-12
Cellular stress, or oxidative stress, occurs when there is a buildup of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which interferes with cellular mechanisms and can even cause damage to proteins, lipids, and DNA. Owing to their destructive nature, all cells have robust mechanisms in place to remove ROS and reduce oxidative stress. One such mechanism is the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2)-mediated stress response, where NRF2 is a master transcription factor that aids in reducing oxidative stress.
Much is known about the redox-dependent activation of NRF2 and its subsequent role in stress response. In this pathway, ...
Chronic exposure to lead, cadmium and arsenic increases risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-06-12
Statement Highlights:
Around the world, most people are regularly exposed to low or moderate levels of lead, cadmium and arsenic in the environment, increasing risk of coronary artery disease, stroke and peripheral artery disease, according to a new American Heart Association statement.
These metals, considered contaminant metals, have no function in the human body. They are found in groundwater, water pipes, paint, tobacco products, fertilizer, plastic, electronics, gasoline, batteries, some foods and other commonly used items.
Lead, ...
Which women should receive more than mammograms to screen for breast cancer?
2023-06-12
Study’s findings point to the importance of considering other risk factors beyond breast density.
Dense breast tissue, which contains a higher proportion of fibrous tissue than fat, is a risk factor for breast cancer and also makes it more difficult to identify cancer on a mammogram. Many states have enacted laws that require women with dense breasts to be notified after a mammogram, so that they can choose to undergo supplemental ultrasound screening to improve cancer detection. A recent study published ...
Twenty species of sea lettuce found along the Baltic and Scandinavian coasts
2023-06-12
The number of species of the green alga sea lettuce in the Baltic Sea region and Skagerak and is much larger than what was previously known. Researchers at the University of Gothenburg have surveyed 10,000 kilometres of coast and found twenty species of sea lettuce.
Green macroalgae of the genus Ulva, also known as sea lettuce, are almost ubiquitous in the wider Baltic Sea region and and can be found from the Atlantic waters all the way up to the Bay of Bothnia in the Baltic Sea. Sea lettuce reproduce easily and grow ...
Cancer diagnoses dropped sharply in Alberta during COVID-19 response
2023-06-12
Pandemic restrictions corresponded with a significant drop in diagnoses of breast, colorectal and prostate cancers as well as melanoma, according to a new Alberta study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221512.
"The sweeping and unprecedented measures enacted at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in Alberta had an inevitable impact on cancer care," writes Dr. Darren Brenner, an epidemiologist in Calgary, Alberta, and associate professor at the University of Calgary's Cumming School of Medicine, with coauthors. "Even though treatment and urgent surgeries for cancers were prioritized ...
Canada’s carbon pricing poses a $256 billion financial risk for borrowers and banks
2023-06-12
By putting a price on the cost of carbon, the Government of Canada aims to curtail greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, but it comes with an increased risk for financial lenders and borrowers with high carbon emissions.
In a first-of-its-kind study, University of Waterloo researchers analyzed the effects of Canada’s carbon price regime on the economy. The results indicate that as carbon costs rise, high-emitting carbon industries such as mining and energy are at the greatest risk of default, with total assets of $256 billion at risk of being lost and almost a quarter ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers uncover new insights into why individuals are affected differently by COVID-19 infection
2023-06-12
Abu Dhabi, UAE (June 12): A team of researchers at NYU Abu Dhabi, led by Associate Professor of Biology Youssef Idaghdour and working in collaboration with clinicians at several Abu Dhabi hospitals, investigated the association between microRNAs, a class of small RNA molecules that regulate genes, and COVID-19 severity among 259 unvaccinated COVID-19 patients living in Abu Dhabi. The team identified microRNAs that are associated with a weakened immune response and admission to ICU.
During this process, ...
Vaccine against deadly chytrid fungus primes frog microbiome for future exposure
2023-06-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A human or animal’s microbiome — the collection of often beneficial microorganisms, including as bacteria and fungi, that live on or within a host organism — can play an important role in the host’s overall immune response, but it is unclear how vaccines against harmful pathogens impact the microbiome. A new study led by researchers at Penn State found that a new vaccine against the deadly chytrid fungus in frogs can shift the composition of the microbiome, making frogs more resilient to future exposure to the ...
Should robots be given a human conscience?
2023-06-12
Modern-day society relies intrinsically on automated systems and artificial intelligence. It is embedded into our daily routines and shows no signs of slowing, in fact use of robotic and automated assistance is ever-increasing.
Such pervasive use of AI presents technologists and developers with two ethical dilemmas – how do we build robots that behave in line with our values and how to we stop them going rogue?
One author suggests that one option which is not explored enough is to code more humanity into robots, gifting robots with traits such as empathy and compassion.
Is ...
Research brings hope for early treatment of brain degeneration in ‘children of the night’
2023-06-12
Glasgow, UK: Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) is a rare and devastating genetic disorder characterised by an inability to repair skin damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) light. As a result, patients with XP develop skin cancers, usually in childhood. Once diagnosed, they can be protected by avoiding sunlight (hence sometimes being called ‘children of the night’), wearing special clothing and sunglasses, and using sunscreen. But some will also develop neurodegenerative conditions such as hearing loss, loss of intellectual function, poor co-ordination and seizures. Finding out why this is, and which ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Natural compound from pomegranate leaves disrupts disease-causing amyloid
A depression treatment that once took eight weeks may work just as well in one
New study calls for personalized, tiered approach to postpartum care
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
Signs on Stone Age objects: Precursor to written language dates back 40,000 years
MIT study reveals climatic fingerprints of wildfires and volcanic eruptions
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
The hidden infections that refuse to go away: how household practices can stop deadly diseases
Ochsner MD Anderson uses groundbreaking TIL therapy to treat advanced melanoma in adults
A heatshield for ‘never-wet’ surfaces: Rice engineering team repels even near-boiling water with low-cost, scalable coating
Skills from being a birder may change—and benefit—your brain
Waterloo researchers turning plastic waste into vinegar
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
Exposure to alcohol-related social media content and desire to drink among young adults
Access to dialysis facilities in socioeconomically advantaged and disadvantaged communities
Dietary patterns and indicators of cognitive function
New study shows dry powder inhalers can improve patient outcomes and lower environmental impact
Plant hormone therapy could improve global food security
[Press-News.org] Taking biofabrication to the next level: innovations in volumetric bioprintingUMC Utrecht researchers propose solutions for bioprinting living tissue