(Press-News.org) SDE BOKER, Israel, June 14, 2023 – Photovoltaic technology is indispensable for our ability to mitigate climate change. Nonetheless, more than 70% of the energy made available to us by the sun is wasted in conventional photovoltaic cells. There is little hope for sustainable technological advancement without addressing this issue.
The operational temperature is a critical factor in a solar cell's ability to convert sunlight to free energy. Accordingly, much research has been directed toward understanding the temperature effects in the efficiency of photovoltaic solar cells. Surprisingly, however, little is known about what this temperature would end up being.
In a paper, "Effect of maintaining a fixed ambient temperature on the evaluation of photovoltaic device performance," published in Phys. Rev. Appl. last week, researchers from the Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Solar Energy Research Center, answer this question by balancing the photon and energy rates of the photovoltaic effect.
Their new approach theorizes a fluctuation in temperature in response to the heat produced from light absorptance and the connection to a fixed temperature environment, whereas present analyses are based on the premise that the cell temperature would remain fixed regardless of its operational conditions.
"This article's solid theoretical grasp is a prerequisite for significant technological advancement. Therefore, illuminating the hidden aspects of the photovoltaic effect contributes to realizing disruptive concepts, such as thermoradiative and thermophotonic cells," says lead author Dr. Avi Niv.
Thermoradiative and thermophotonic cells are advanced conceptions of photovoltaic energy conversion that enable industrial processes’s waste heat recovery (thermoradiative) or are more efficient in converting the sun’s radiative energy flux to electricity (thermophotonic).
END
Solar cells can, finally, stand the heat
2023-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
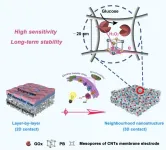
Scientists develop novel biosensing-membrane for glucose detection and monitoring
2023-06-14
Glucose oxidase (GOx)-based biosensors have attracted much attention for their potential in rapid glucose detection and continuous monitoring, which are crucial for disease diagnosis and prevention, as well as for controllable production in sugar-making and fermentation processes.
The glucose oxidase/electrocatalysts/electrode (GOx/ECs/electrode) cascade system serves as the core part of most glucose biosensing devices (both invasive and non-invasive). However, patterned assembly of these cascade sensing units remains challenging, thus limiting the ...
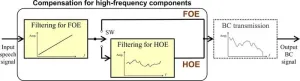
Improving word intelligibility of bone-conducted speech using bone-conduction headphones
2023-06-14
Ishikawa, Japan -- Bone-conduction (BC) headphones enhance hearing capability by generating vibrations in bone or skin close to the ear, including the regio temporalis. They simultaneously leave the ear canal open to allow the surrounding air-conducted (AC) sounds for normal hearing. However, word intelligibility – recognition ability – is often poor during bone-conducted speech perceived using BC headphones due to the attenuation of its high-frequency components, especially under noisy conditions. While inserting ear plugs in the ear canal help improve ...
Study shines new light on old drug for trauma care
2023-06-14
A new study from Australia, New Zealand and Germany published in the New England Journal of Medicine raises important questions about the success or otherwise of emergency medicine.
The study examined the drug tranexamic acid, which is commonly used to limit bleeding during surgery. However, its usefulness in emergency settings as a pre-emptive strike in life-threatening bleeding has been controversial, and recent studies have provided contradictory results about whether or not it saves lives or causes dangerous blood clotting.
The Pre-hospital ...
Cutting back on social media reduces anxiety, depression, loneliness
2023-06-14
AMES, IA — Last month, the American Psychological Association and the U.S. Surgeon General both issued health advisories. Their concerns and recommendations for teens, parents and policymakers addressed a mounting body of research that shows two trends are intertwined.
Young people are using social media more, and their mental health is suffering.
Researchers at Iowa State University found a simple intervention could help. During a two-week experiment with 230 college students, half were asked to limit their ...
DESI data sheds more light on 3D map of cosmos, study of universe
2023-06-14
Dr. Mustapha Ishak-Boushaki, a theoretical astrophysicist at The University of Texas at Dallas, has spent his career seeking answers to some of the universe’s greatest mysteries, including why the expansion of the universe seems to be accelerating and whether gravity behaves differently beyond our closest cosmic neighbors.
To study these and other questions, a large collaboration of scientists, including Ishak-Boushaki and UTD physics doctoral students Cristhian Garcia Quintero, Leonel Medina Varela and Yunan Xie, are using data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic ...
Under the weather: Scientists should spend more time in the rain
2023-06-14
Scientists need to get out of the lab and into the rain, say an interdisciplinary group of researchers led by John T. Van Stan of Cleveland State University. Writing in the journal BioScience, the authors make the case that human observation of storm events (be it rain, snow, or occult deposition) is key to understanding wet weather and its myriad effects on the natural world.
Recently, Van Stan and colleagues noted a trend in the scientific community towards relying on remote ...
Gene provides clues for preventing common diabetes side effect of corticosteroid treatment
2023-06-14
A study led by researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research shows for the first time how a gene called RELA, known to regulate inflammation, also plays an essential role in maintaining normal blood-sugar levels.
The findings, published in Diabetologia, have implications for the prevention of steroid-induced diabetes, a temporary form of diabetes that affects up to half of hospital patients treated with high-dose steroids.
“Our discovery sheds new light on a complex network of factors governing glucose metabolism and how it can go awry in diabetes,” says Professor ...
How prescribed burns could limit megafires in California, Oregon, and Washington
2023-06-14
Wildfire smoke is a threat to air quality, public health, and ecosystems throughout the U.S. Notwithstanding the impact of this year’s Canadian wildfires, the West typically sees much higher exposure to wildfire smoke than other regions of the country. New research from Harvard University, the U.S. Forest Service, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration indicates that controlled burns – particularly in coastal areas of northern California and the Pacific Northwest – could dramatically reduce the overall amount of wildfire smoke exposure in vulnerable rural communities and dense ...
Specialty drugs accounted for most new product launches in the past decade. Why do we know so little about how clinical studies influence their diffusion?
2023-06-14
Researchers from McGill University and Ontario Tech University published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines the drivers of specialty drug diffusion.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Scientific Evidence Production and Specialty Drug Diffusion” and is authored by Demetrios Vakratsas and Wei-Lin Wang.
A notable trend in the pharmaceutical industry is the development of specialty drugs to treat complex, severe diseases, often with a limited number of patients. Of the 219 new drugs (or new active substances, NASs) that were launched in the U.S. between 2014 and 2018, 136 ...
NCCN debuts roadmap for improving thyroid cancer care in low- and middle-income countries on world stage
2023-06-14
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA and LONDON, UK [June 14, 2023] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) is introducing a new global resource to improve thyroid cancer care in low- and middle-income countries at the upcoming World Congress on Thyroid Cancer, in London. During the event, NCCN Senior Vice President and Chief Medical Officer, Wui-Jin Koh, MD, will present on NCCN’s ongoing global work to define and advance high-quality, high-value, patient-centered cancer care. As part of ...