(Press-News.org) Staffing levels likely drive the differences in hospitalizations and emergency department visits among nursing homes, the researchers report in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
Studies show that nursing homes serving high proportions of Black residents may experience poor healthcare outcomes. To better understand the environmental and structural characteristics of nursing homes that may lead to these outcomes, the researchers examined data from 14,121 U.S. nursing homes using multiple national datasets from 2019.
They found that, compared to nursing homes with no Black residents, nursing homes with at least 50% Black residents had lower ratios of registered nurse (RN) and certified nursing assistant (CNA) hours per resident per day and greater ratios of licensed practical nurse (LPN) hours per resident per day. In general, as the proportion of Black residents in a nursing home increased, hospitalizations and emergency department visits also increased.
Nursing homes serving Black residents were also more likely to be located in urban settings, for-profit, located in the South, and have more Medicaid-funded residents.
“As lower use of RNs has generally been associated with increased emergency department visits and hospitalizations of nursing home residents, it is likely that the relative scarcity of skilled workers largely drove the differences in hospitalizations and emergency department visits in nursing homes with greater proportions of Black residents,” said Jasmine Travers, PhD, RN, assistant professor at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and the study’s lead author.
“Staffing is a modifiable area in which federal and state agencies should take action to eliminate disparities in quality of care among nursing homes,” added Travers.
Additional study authors include Nicholas Castle of West Virginia University, Susan H. Weaver of New Jersey Collaborating Center for Nursing, Uduwanage G. Perera of Columbia University School of Nursing, Bei Wu of NYU Meyers, Andrew W. Dick of Rand Corporation, and Patricia W. Stone of Columbia University School of Nursing. The research was funded by the National Institute of Nursing Research (R01 NR013687), National Institute on Aging (K76 AG074922), and Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (77872).
END
Nursing homes serving Black residents have greater hospitalizations, emergency department visits
2023-06-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
When materials discovery glitters
2023-06-14
By Rebekah Orton
Thomas Edison famously tried hundreds of materials and failed thousands of times before discovering that carbonized cotton thread burned long and bright in an incandescent light bulb. Experiments are often time consuming (Edison’s team spent 14 months) and expensive (the winning combination cost about $850,000 in today’s money).
Expenses and time increase exponentially when developing the quantum materials that will revolutionize modern electronics and computing.
To make quantum material discovery possible, researchers turn to detailed databases as their virtual laboratory. A new database of understudied quantum materials ...
Just add sugar: Research shows common antioxidant can be more beneficial through glycosylation
2023-06-14
New research shows that polyphenolic compounds, which are commonly found in fruits and vegetables, can be combined with sugar molecules to create potential life-saving drugs.
Polyphenols are a class of compounds found in many plant-based foods. Polyphenols help prevent cellular damage in the body and can help to prevent diseases such as cancer or heart disease. However, many of them do not dissolve in water, making it difficult to fully take advantage of their health benefits.
Biological Engineering Professor Jixun Zhan and his graduate students Jie Ren and Caleb Barton recently published a comprehensive ...
Dietary supplementation shown to improve nutrition biomarkers in study of older men
2023-06-14
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A six-month study of healthy older men demonstrated that daily multivitamin/multimineral supplementation had a positive effect on key nutrition biomarkers.
The research led by Oregon State University’s Tory Hagen and Alexander Michels also showed that the changes in nutrition status could have direct connections to cellular function, measured by the oxygen consumption of the study participants’ blood cells.
The findings, published in the journal Nutrients, suggest that supplementation may be a key tool to help people stay healthier as they age.
“Many older adults take ...
Remains at Crenshaw site are local, ancestors of Caddo, study finds
2023-06-14
Hundreds of human skulls and mandibles recovered from the Crenshaw site in southwest Arkansas are the remains of ancestors of the Caddo Nation and not foreign enemies, according to a new study published in the Journal of Archaeological Science.
Collaborating with the Caddo Nation in Oklahoma, researchers at the University of Arkansas and Arkansas Archeological Survey tested lead and strontium isotopes in the teeth of human remains and compared them to ancient animal teeth from several surrounding regions to determine that the 700-year-old human remains were local ...
The Viking disease can be due to gene variants inherited from Neanderthals
2023-06-14
Many men in northern Europe over the age of 60 suffer from the so-called Viking disease, which means that the fingers lock in a bent position. Now researchers at Karolinska Institutet, together with colleagues, have used data from over 7,000 affected individuals to look for genetic risk factors for the disease. The findings, which have been published in Molecular Biology and Evolution, show that three of the strongest risk factors are inherited from Neanderthals.
Up to 30 percent of men in northern Europe over 60 suffer from ...
Further hope for base-edited T-cell therapy to treat resistant leukaemia
2023-06-14
Three young patients with relapsed T-cell leukaemia have now been treated with base-edited T-cells, as part of a ‘bench-to-bedside’ collaboration between UCL and Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children (GOSH).
The data from the NHS clinical trial, published in The New England Journal of Medicine and funded by the MRC, shows how donor CAR T cells were engineered using cutting edge gene editing technology to change single letters of their DNA code so they could fight leukaemia.
The experience of using the cells in three patients is shared, and includes 13-year-old Alyssa from Leicester, who last year was the first person in the world to ...
A new way to visualize force-sensing neurons
2023-06-14
A recent study by researchers at Texas Children’s Hospital, Baylor College of Medicine, and Scripps Research Institute has discovered fluorescent dye FM 1-43 as an effective and versatile tool to visualize PIEZO2 ion channel activity in mechanosensory neurons. The study, published in Neuron, was led by Dr. Kara Marshall, assistant professor at Baylor College of Medicine and investigator at the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children’s Hospital, with Dr. Ardem Patapoutian, Nobel Laureate and professor at Scripps Research Institute.
Mechanosensation is the ability ...
Study finds that proven medications for alcohol use disorder are rarely given to adolescents and young adults on public insurance
2023-06-14
BOSTON – Heavy drinking commonly begins in adolescence and is a known risk factor for the development of alcohol use disorder (AUD). Data from adult clinical trials suggest offering evidence-based medications for AUD to younger adults could promote their engagement in treatment and improve clinical outcomes.
But are those medications being used when and where they are needed? In a review of claims data for youths insured by Medicated in 15 U.S. states, a team of researchers found that most youths with a diagnosis of AUD do not receive medications as part of their therapy, despite ...
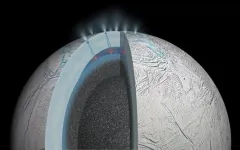
Phosphate, a key building block of life, found on Saturn’s moon Enceladus
2023-06-14
An international team including a University of Washington scientist has found that the water on one of Saturn’s moons harbors phosphates, a key building block of life. The team led by the Freie Universität Berlin used data from NASA’s Cassini space mission to detect phosphates in particles ejected from the ice-covered global ocean of Saturn’s moon Enceladus.
Phosphorus, in the form of phosphates, is vital for all life on Earth. It forms the backbone of DNA and is part of cell membranes and bones. The new study, published June 14 in ...
Conflict in marriage less harmful for kids when dad keeps it constructive
2023-06-14
URBANA, Ill. — Conflict is unavoidable in all marriages. When it erupts in families with children, stressed or angry parents may take their pain out on the kids, projecting their anger or withdrawing emotionally or physically. In the worst cases, children’s socioemotional development can suffer. But the way parents, especially fathers, deal with marital conflict can make a difference to kids, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.
“In the past, marital conflict ...