(Press-News.org) A treatment for a rare cancer-like lung disease found in women of childbearing age may have been discovered by University of Cincinnati researchers.
The rare lung disease is called lymphangioleiomyomatosis or LAM, and the cause of it is unknown with no cure established. New UC research, funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, discovered that two existing drugs show signs of being effective in treating LAM and could lead to the development of a cure.
The study was published in Science Advances,
“The exact number of women with LAM is unknown but it is estimated that for every 1 million women in the world, three to seven women have LAM,” says Tasnim Olatoke, third-year graduate student in the UC College of Medicine and lead author on the study. “This life-threatening disease is caused by slow infiltration of abnormal cells into the lungs, which form tumors that damage the lungs and lead to difficulty in breathing.”
Olatoke says sirolimus, the only Food and Drug Administration-approved drug and current medication of choice for treating LAM, is not optimally efficient and does not cure LAM. The biggest questions facing scientists studying LAM include where these cells come from and why they have such strong affinity for the lungs. The greatest challenge to finding a cure for LAM is that its underlying mechanism is not completely understood.
“We identified a novel pathway that is dysregulated in LAM,” Olatoke says. “We found two drugs that target this pathway. We are examining both of those drugs to see how we can use them to reduce the progression of LAM.”
Olatoke says once they confirmed that the pathway was dysregulated, they treated cells from those patients with the drug and discovered that, by treating the cell, they were able to kill those tumor cells. The researchers also tried an animal model where they injected the cells that come from patients into them and by treating them with the drug, they were able to limit the survival of the tumor cells and reduce their progression in the lungs as well as limiting tumor development.
“This is an entirely new direction because it has not been explored at all,” Olatoke says. “We do not know where the cells that enter and destroy the lungs come from, but through our findings, we think that the cells come from the uterus. We think that this pathway is originally dysregulated in the uterus, and the cells move from the uterus to the lungs. Nobody has shown that, nobody knows where the cells come from, so this is the first evidence-backed proof in the field showing that maybe the cells come from the uterus.”
Olatoke says one of the more satisfying aspects of this research is working with LAM patients, and notes that June is Worldwide LAM Awareness Month.
“They are the nicest, kindest people ever,” she says. “They are going through so much, but they show empathy, they support our research. This study was partly sponsored by them.
“They are just warm and genuine people who really want a cure. They support our research by taking part in clinical trials and being active. Everything we request for our research, they are always ready to help. It’s a beautiful community,” Olatoke says.
“Another rewarding part, especially with this paper, was working with multiple investigators across different institutions,” she says. “The paper is a brainchild of multiple talented investigators across UC, [Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center] and Texas Tech — a beautiful testament to how collaboration positively drives science.”
According to Olatoke, the findings provide the first proof-of-concept for the potential therapeutic benefit of targeting the pathway signaling in LAM as well as diseases related to tuberous sclerosis complex, a rare genetic disorder that causes benign tumors and lesions. The possibility of what this research could lead to is what excites her about this study.
“It’s the hope that we can find therapeutic strategies to cure LAM,” Olatoke says. “What inspires me every day to continue doing this research is that hopefully we can find something that can be useful to LAM patients.”
END
University of Cincinnati research finds potential therapy for rare but devastating lung disease
Findings could lead to a cure for LAM
2023-06-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Insilico Medicine’s transformer-based aging clock provides insights into aging, disease, and new therapeutic targets
2023-06-15
Clinical stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”) has announced a new multimodal transformer-based aging clock that is capable of processing diverse data sets and providing insights into biomarkers for aging, mapping them to genes relevant to both aging and disease, and discovering new therapeutic targets designed to slow or reverse both aging and aging-related diseases. The company calls the aging clock Precious1GPT, in a nod to the powerful “One Ring” in Lord of the Rings. The findings were published in the June 13 issue of the journal Aging.
Insilico has been ...
Hip fracture burden to nearly double worldwide by 2050
2023-06-15
An international group of researchers led by the Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, LKS Faculty of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong (HKUMed), and including Douglas P Kiel, MD, MPH, Director Musculoskeletal Research Center, Marcus Institute for Aging Research, Hebrew SeniorLife, and Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, evaluated the secular trends in hip fracture incidence, treatment patterns following a hip fracture, and all-cause mortality in 19 countries and regions from 2005 to 2018. While the age- and sex-standardised hip fracture incidence rates decreased ...
Research findings „Study on Adult Learning and Education“
2023-06-15
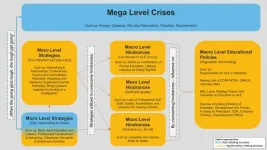
From August 2022 until October 2022, interviews with 25 experts from the selected countries were conducted and then analyzed trough a Ground Theory approach. From this, a model emerged, showing how factors and actors at different societal levels - mega, macro, meso and micro - interact to shape adult learning and education in different contexts.
Mega level comparisons show that overarching issues such as war and conflict, historical and systemic discrimination, disease and extreme poverty as well as political authoritarianism act both as an impetus and as barriers to ALE activities.
Comparative analysis shows that at the macro level, with ...
New tool uncovers COVID-19 susceptibility mechanism
2023-06-15
Researchers have discovered a mechanism for COVID-19 susceptibility using a newly created tool. The tool, GASPACHO, captures dynamic changes in gene expression along the innate immune response, allowing researchers to identify genes and molecular pathways associated with disease risk that have previously been too complex to detect or interpret.
Using GASPACHO (GAuSsian Processes for Association mapping leveraging Cell HeterOgeneity), researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the National Center for Child Health and Development in Japan, Tel Aviv University and their collaborators have identified a gene variant that affects COVID-19 susceptibility. ...
Jefferson Lab oversight roles filled by DOE
2023-06-15
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – The U.S. Department of Energy has selected Craig Ferguson to lead the Thomas Jefferson Site Office (TJSO) at the Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility in Newport News, Va. As TJSO manager, Ferguson will lead in the oversight and contract management of Jefferson Lab. Additionally, Donté Davis has been confirmed as TJSO deputy manager, a role he first stepped into earlier this year.
Ferguson is familiar with Jefferson Lab and its mission, having already served in a leadership role at the lab. In 2005-2008, he was the lab’s associate director for environment, safety, health & quality.
“I am excited to return ...
High-quality child care contributes to later success in science, math
2023-06-15
Children who receive high-quality child care as babies, toddlers and preschoolers do better in science, technology, engineering and math through high school, and that link is stronger among children from low-income backgrounds, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“Our results suggest that caregiving quality in early childhood can build a strong foundation for a trajectory of STEM success,” said study author Andres S. Bustamante, PhD, of the University of California Irvine. “Investing in quality child care and early childhood education could help ...
Study finds that a small number of teachers effectively double the racial gaps among students referred for disciplinary action
2023-06-15
Washington, June 15, 2023—The top 5 percent of teachers most likely to refer students to the principal’s office for disciplinary action do so at such an outsized rate that they effectively double the racial gaps in such referrals, according to new research released today. These gaps are mainly driven by higher numbers of office discipline referrals (ODRs) issued for Black and Hispanic students, compared to White students. The study, published in Educational Researcher, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research ...
Previously overlooked algae toxin widespread in southern Indian River Lagoon
2023-06-15
Spanning about one-third of Florida’s East coast, the Indian River Lagoon has faced frequent harmful algal blooms in recent years. Among them, Pseudo-nitzschia spp., algae that produces the neurotoxin domoic acid.
Domoic acid can bioaccumulate within food webs, causing sickness and death in higher trophic level organisms such as marine mammals and birds, and have been documented in sea turtles in Florida coastal waters and in bull sharks within the Indian River Lagoon system. In humans, consumption of shellfish contaminated with domoic acid can cause harmful symptoms.
Unlike other harmful algal blooms, Pseudo-nitzschia are not bioluminescent and do not cause water discoloration ...
Amsterdam UMC to lead global hunt for new interventions in the battle against unhealthy behavior
2023-06-15
Chronic diseases (NCDs) are a global health epidemic and almost 80% of them occur in low- and middle-income countries. While the WHO have developed policies to combat chronic diseases, research shows that, in certain regions, they are not having the desired effect, leaving fragile health systems increasingly overwhelmed. In order to combat this, thanks to a Horizon Europe grant, Amsterdam UMC is set to lead a global consortium with the aim of developing interventions that work in practice.
Consortium leader and Professor of Global Migration, Ethnicity and Health at Amsterdam UMC, Charles Agyemang notes that, ...
A ‘pinch’ of mineral salts helps the noncaloric sweeteners go down
2023-06-15
Perfect noncaloric replacements for sugar and high fructose corn syrup just don’t exist yet. For example, some alternatives have a lingering sweet aftertaste and lack a sugar-like mouthfeel, leaving consumers unsatisfied. Now, researchers in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry propose adding blends of nutritionally important mineral salts to make noncaloric sweeteners seem more like the real thing. Taste-testers indicated that these blends gave zero- and low-calorie drinks a better ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] University of Cincinnati research finds potential therapy for rare but devastating lung diseaseFindings could lead to a cure for LAM