(Press-News.org) Staying up late at night has little impact on how long ‘night owls’ live, according to new research published in the peer-reviewed journal Chronobiology International.
Data based on nearly 23,000 twins, however shows that evening types have a slightly increased risk of dying than morning types, but this is largely linked to smoking and drinking.
The study which tracked people over the course of more than 37 years in Finland suggests that lifestyle should be considered.
This is when analyzing the impact on health of chronotype – the body’s natural inclination to sleep at a certain time.
“Our findings suggest that there is little or no independent contribution of chronotype to mortality,” says author Dr Christer Hublin, from the Finnish Institute of Occupational Health in Helsinki.
“In addition, the increased risk of mortality associated with being a clearly ‘evening’ person appears to be mainly accounted for by a larger consumption of tobacco and alcohol. This is compared to those who are clearly ‘morning’ persons.”
There is increasing evidence that sleep duration and quality, and night shift work affect health. Earlier studies have linked night owls with a higher risk of disease especially heart problems.
Data published in 2018 from the UK Biobank, looking at people over the course of 6.5 years, found evening types have a small increased risk of death from any cause including disease, and from heart condition.
It was this previous research which inspired today’s new study, as authors wanted to analyze some things which were not measured – alcohol consumption and the amount people smoked, rather than just status.
This new research, which was co-led by Dr Jaakko Kaprio, from the Finnish Twin Cohort study at the University of Helsinki, followed 22,976 men and women aged 24 years and from 1981 to 2018.
At the start of the study, the twins were asked to pick from four possible responses: ‘I am clearly a morning person’; ‘I am to some extent a morning person’; ‘I am clearly an evening person’; ‘I am to some extent an evening person’.
The researchers followed-up the participants in 2018 to establish if any had died. They based this on data provided by nationwide registers.
The authors took into account education, daily alcohol consumption, smoking status and quantity, BMI, and sleep duration.
Results showed that 7,591 of the twins identified as ‘to some extent’ and 2,262 as ‘definite’ evening types. The figures for morning types were 6,354 and 6,769, respectively.
Compared to morning types, night owls were younger and drank/smoked more. Definite evening types were also less likely to report getting 8 hours sleep.
Of the total participants, 8,728 had died by 2018 and the chance of dying from any cause was 9% higher among definite night owls compared to early birds.
However, the study found that smoking and alcohol largely caused these deaths, not chronotype. This finding was highlighted by the fact non-smokers were at no increased risk of dying.
The causes of deaths from alcohol included related disease as well as from accidental alcohol poisoning.
Dr Kaprio notes that they were more able to relate their findings to society as a whole. Their participants’ health was no different than the general population whereas the UK Biobank’s were healthier than average.
They highlight the access to comprehensive data on lifestyle factors as a strength of their research. However, the findings were based on self-reported data from asking one question.
END
Alcohol and smoking to blame for premature deaths among night owls, 37-year study suggests
2023-06-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Removing barriers to commercialization of magnesium secondary batteries
2023-06-16
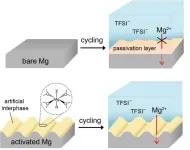
A research team led by Dr. Minah Lee of the Energy Storage Research Center at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology(KIST) has developed a chemical activation strategy of magnesium metal that enables efficient operation of magnesium batteries in common electrolytes that are free of corrosive additives and can be mass-produced.
While the demand for lithium-ion batteries is exploding due to the rapid growth of the electric vehicle and energy storage system(ESS) markets, the supply and demand of their raw materials such as lithium and cobalt ...
Fathers key to supporting breastfeeding and safe infant sleep
2023-06-16
Fathers can make a huge difference in whether an infant is breastfed and placed to sleep safely, according to a recent survey of new fathers via the Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS) for Dads. This new tool is modeled on the annual surveillance system that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and public health departments have used for more than 35 years to survey new mothers. By utilizing PRAMS for Dads, this article is the first to describe father-reported rates of infant breastfeeding and sleep practices in a state-representative sample. Findings are published in the journal Pediatrics.
Among fathers who wanted their infant’s ...
A facile strategy for comprehensive proteome analysis of urine
2023-06-16
Urine is one of the attractive sources for early and sensitive biomarker discovery since it can accumulate and reflect changes in the human body while being collected non-invasively. However, analysis of the urine proteome presents challenges due to its wide dynamic range, spanning approximately 10 orders of magnitude in protein concentrations. The presence of high-abundance proteins in urine can overshadow potential disease biomarkers, making their identification difficult. Fractionation and depletion ...
Exposure to dioxins can worsen thyroid function
2023-06-16
CHICAGO—Exposure to dioxins can negatively impact thyroid function, according to a study presented Thursday at ENDO 2023, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Chicago, Ill.
Dioxins are highly toxic compounds that are primarily produced by industrial processes, and their persistence in the environment makes them a significant public health concern. They are produced through a variety of incineration processes, including improper municipal waste incineration and burning of trash. They can be released into the air during natural processes, such as forest fires and volcanoes. ...
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals may raise risk of cognitive disorders in future generations, animal study finds
2023-06-16
Adverse cognitive effects linked to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) exposure, a type of endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC), have the potential to be passed down through generations, according to an animal study being presented Thursday at ENDO 2023, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Chicago, Ill.
PCBs can mimic the effect of the hormone estrogen on the body, contributing to a variety of neuroendocrine, metabolic and reproductive problems.
“Endocrine-disrupting chemicals present in our food, air, water and personal products may cause cognitive-behavioral disorders like attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder or overeating in future generations,” ...
IIASA analysis underpins new 2040 climate targets by EU Advisors
2023-06-16
In two new reports, IIASA researchers, with support from colleagues at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), examined the feasibility and fairness of emissions targets and considerations for the European Climate Law. Keywan Riahi, a member of the 15-strong EU Advisory Board and IIASA Energy, Climate, and Environment Program Director, took the lead in conducting the analyses.
The European Scientific Advisory Board on Climate Change is an independent board entrusted with the crucial responsibility of providing transparent and scientific guidance to the EU on setting a new emissions reduction target to be achieved by 2040, as well as budgets for greenhouse ...
A newly identified protein confers drought tolerance to plants
2023-06-16
CRAG researchers have discovered that AtMC3 protein is exclusively located in a specific part of the plant vascular system.
Increased levels of AtMC3 are able to confer enhanced tolerance to severe water scarcity conditions, without affecting plant yield.
This knowledge will contribute to find tools to cope with increasing drought phenomena due to climate crisis.
Bellaterra (Barcelona), 16 June 2023
Researchers led by Núria Sánchez-Coll, CSIC researcher at the Centre ...
Pregnancy hormone repairs myelin damage in MS mouse model
2023-06-15
SUMMARY
Treating a mouse model of multiple sclerosis with the pregnancy hormone estriol reversed the breakdown of myelin in the brain’s cortex, a key region affected in multiple sclerosis, according to a new UCLA Health study.
BACKGROUND
In multiple sclerosis, inflammation spurs the immune system to strip away the protective myelin coating around nerve fibers in the brain’s cortex, hampering electrical signals sent and received by the brain. Atrophy of the cortex in MS patients is associated with permanent worsening of disability, such as cognitive decline, visual impairment, weakness and sensory loss.
No currently available treatments ...
$11.7M from Department of Defense to fund research on common complication to traumatic brain injury
2023-06-15
INDIANAPOLIS — Researchers at the School of Science at IUPUI will lead two grants totaling $11.7 million from the U.S. Department of Defense to fund research on discovering a drug treatment for hydrocephalus, a condition commonly associated with complications from traumatic brain injury that causes cerebrospinal fluid to accumulate in the brain.
Using funds from a $7.8 million Department of Defense Focused Program grant, Bonnie Blazer-Yost and Teri Belecky-Adams, both professors in the Department of Biology, will team up with scientists from Johns Hopkins University to test the effectiveness of treatments for three types of hydrocephalus — genetic, ...
Ochsner Health announces Tiffany Murdock as incoming system vice president and chief nursing officer
2023-06-15
NEW ORLEANS – Ochsner Health is pleased to announce Tiffany Murdock as the organization’s next system vice president and chief nursing officer (CNO), effective later this summer. In this leadership role, Murdock will set the strategy and vision for the organization’s nursing practice and lead the organization’s more than 9,000 nurses. Murdock joins Ochsner’s leadership team after eight years at Singing River Health System, where she has served since 2022 as Singing River’s first female chief executive officer (CEO).
Murdock ...