(Press-News.org) People who owned black-and-white television sets until the 1980s didn’t know what they were missing until they got a color TV. A similar switch could happen in the world of genomics as researchers at the Berlin Institute of Medical Systems Biology of the Max Delbrück Center (MDC-BIMSB) have developed a technique called Genome Architecture Mapping (“GAM”) to peer into the genome and see it in glorious technicolor. GAM reveals information about the genome’s spatial architecture that is invisible to scientists using solely Hi-C, a workhorse tool developed in 2009 to study DNA interactions, reports a new study in Nature Methods by the Pombo lab.
“With a black-and-white TV, you can see the shapes but everything looks grey,” says Professor Ana Pombo, a molecular biologist and head of the Epigenetic Regulation and Chromatin Architecture lab. “But if you have a color TV and look at flowers, you realize that they are red, yellow and white and we were unaware of it. Similarly, there’s also information in the way the genome is folded in three-dimensions that we have not been aware of.”
Understanding DNA organization can reveal the basis of health and disease. Our cells pack a 2-meter-long genome into a roughly 10 micrometer-diameter nucleus. The packaging is done precisely so that regulatory DNA comes in contact with the right genes at the right times and turns them on and off. Changes to the three-dimensional configuration can disrupt this process and cause disease.
“We’ve known for a long time that diseases run in families,” says Dr Robert Beagrie, co-first author of the study and a molecular biologist at the University of Oxford, formerly at the Pombo lab. “More recently, we’ve come to understand that a great deal of this predisposition is because we inherit DNA sequence variants from our parents that affect how our genes are switched on and off.”
GAM provides more complex information
Techniques such as Hi-C and GAM allow scientists to freeze and study the interactions between regulatory sequences and genes. In Hi-C, chromatin is cut into pieces using enzymes and then glued together again in such a way that two-way DNA interactions are revealed upon sequencing. In GAM, first described by the Pombo team in “Nature” in 2017, scientists take hundreds of thin slices of nuclei, each from individual cells, and extract DNA from them. They sequence the DNA and statistically analyze the data to learn which regions interact.
Using this technique, the team created a map of the three-dimensional interactions. When they compared this with existing 3D maps of the genome created using Hi-C, they found many novel interactions. This puzzled them until they realized they were seeing more complex interactions using GAM, with multiple regions of DNA coming together at the same time. “These more complex contacts contain active genes, regulatory regions, and super enhancers, which regulate important genes that determine cell identity,” says Dr. Christoph Thieme, co-first author of the study and a senior postdoctoral fellow in the Pombo lab.
In comparison, Hi-C captured mostly two-way interactions. Both techniques are complementary as two in three contacts detected by GAM were not visible using Hi-C — and vice-versa.
“I was super excited to see that we had uncovered a really strong effect,” Beagrie says. “It is clear that these complex interactions were much more common than we had previously appreciated.”
END
A new tool to study complex genome interactions
2023-06-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Assessment of how climate scientists communicate risk shows imperfections, improvements
2023-06-19
Scientists have long struggled to find the best way to present crucial facts about future sea level rise, but are getting better at communicating more clearly, according to an international group of climate scientists, including a leading Rutgers expert.
The consequences of improving communications are enormous, the scientists said, as civic leaders actively incorporate climate scientists’ risk assessments into major planning efforts to counter some of the effects of rising seas.
Writing in Nature Climate Change, the scientists ...
De facto decriminalization of drug possession reduces the overall arrest toll on the Black community, although racial disparities persist
2023-06-19
Ann Arbor, June 19, 2023 – De facto decriminalization of drug possession may be a good first step in addressing the disproportionate impact of an overburdened United States criminal justice system on the Black community. According to a new study in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, published by Elsevier, this strategy was associated with significant and sustained reductions in low-level arrests. These arrests too often prevent drug users from obtaining needed treatments and services. The findings also suggest that while these policies may effectively reduce the overall arrest toll, striking disparities persist in how police are applying the directives across racial ...
Combatting stress to improve the heart health of the Hispanic/Latino community
2023-06-19
Embargoed until 8am Eastern Time on Monday, June, 19, 2023
DALLAS, June 19, 2023 — Constant or chronic stress can affect overall well-being and may even impact heart health. Chronic stress can lead to increased blood pressure, heart rate and inflammation, which can contribute to developing chronic diseases.[1] The American Heart Association, the leading global voluntary health organization dedicated to fighting heart disease and stroke for all, today launches a new campaign to help the Hispanic/Latino community protect its overall well-being by addressing common stressors that ...
Bridging traditional economics and econophysics
2023-06-19
How do asset markets work? Which stocks behave similarly? Economists, physicists, and mathematicians work intensively to draw a picture but need to learn what is happening outside their discipline. A new paper now builds a bridge.
In a new study, researchers of the Complexity Science Hub highlight the connecting elements between traditional financial market research and econophysics. "We want to create an overview of the models that exist in financial economics and those that researchers in physics and mathematics have developed ...
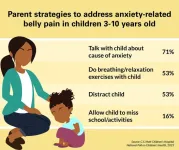
1 in 6 parents say child reports tummy pain at least monthly but many haven’t consulted with a doctor
2023-06-19
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Tummy aches are common among kids, with one in six parents in a new national poll saying their child experiences them at least once a month.
But not all parents seek professional advice when belly pain becomes a regular occurrence and just one in three are sure they’d know when it might be a sign of a serious problem, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
“Tummy complaints are common among children. This type of pain may be a symptom for a range of health issues, but it can be difficult to know if it’s ...
Pandemic took a major, prolonged toll on university students’ mental health, finds study
2023-06-19
Undergraduates at UK universities experienced prolonged and high levels of psychological distress and anxiety during the pandemic, according to a new study, tracking wellbeing over the course of 2020 to 2021.
They also reported significantly lower levels of wellbeing, happiness and life satisfaction compared to pre-pandemic levels.
Published in the British Journal of Educational Studies, the University of Bolton research highlights how the stringent lockdown measures – including ...
Significant acceleration of humanities and social sciences open access through Taylor & Francis and Jisc Transformative Agreement
2023-06-19
The power of transformative agreements (TAs) to drive the transition to open access (OA), especially in the Humanities and Social Sciences, is revealed in a new report published by Taylor & Francis. Accelerating open access in the UK explores in detail the first two years of Taylor & Francis’ OA partnership with the Jisc consortium and how it has boosted the global impact of research from UK institutions.
Supporting Humanities and Social Sciences researchers to publish OA
One of the report’s standout findings is the benefit of the TA for Humanities and Social Science ...
A probiotic could help mitigate mercury absorption in the gut
2023-06-18
Houston, TX – New research by a team at Pennsylvania State University suggests that microbes in the human gut could be harnessed to block absorption of toxic metals like mercury and help the body absorb useful nutritional ones, like iron. The group presents their findings at ASM Microbe 2023, the annual meeting of the American Society for Microbiology.
Methylmercury, a neurotoxin, is particularly worrisome, said Daniela Betancurt-Anzola, a graduate student at Penn State who led the new study. It ...
An oral probiotic can treat dry eye disease
2023-06-18
Houston, TX – In a study by a research group at Baylor College of Medicine, oral administration of a commercially available probiotic bacterial strain was found to improve dry eye disease in an animal model. The findings were presented at ASM Microbe 2023, the annual meeting of the American Society for Microbiology.
Dry eye, a common condition in which tears produced by the eye can’t keep the eye adequately lubricated, afflicts approximately 1 in 20 people in the United States. It can cause eye stinging and burning, inflammation, blurry vision and light sensitivity. Extreme cases can result in damage ...
People with alcohol use disorder impaired after heavy drinking, despite claims of higher tolerance
2023-06-18
While heavy drinkers can tolerate a certain amount of alcohol better than light or moderate drinkers, the concept of “holding your liquor” is more nuanced than commonly believed, according to new research from the University of Chicago.
The researchers conducted the study with three groups of young adults in their 20s with different drinking patterns. They found that drinkers with alcohol use disorder (or AUD, traditionally known as alcoholism) displayed less impairment on fine motor and cognitive tasks than light or heavy social drinkers after consuming a standard intoxicating dose—equivalent ...