(Press-News.org) WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – June 20, 2023 – An estimated 3 million patients visit emergency departments each year with acute chest pain and mildly elevated troponin levels. High levels of troponin, a protein, occur when the heart muscle is damaged from a heart attack. How best to evaluate and treat patients with chest pain with detectable or mildly elevated troponin remains unclear.
Now, a new study from researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine reveals that cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), is a safe and valuable tool to help evaluate these complex patients.
The study findings appear online today in Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging, a journal of the American Heart Association.
“Patients who present to the emergency room with chest pain and mildly elevated troponin often fall into a diagnostic gray zone,” said Chad Miller, M.D., professor and chair of emergency medicine at Wake Forest University School of Medicine and emergency medicine physician at Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist. “It’s not readily clear whether they should have angiography or other forms of testing when being evaluated in the emergency department.”
Angiography is used to check the health of blood vessels and how blood flows through them, but angiography procedures are more invasive than MRI. For example, during cardiac catheterization, a catheter is guided through a patient’s blood vessel to the heart. Providers use the test to identify conditions such as clogged arteries.
For the study, researchers randomized 312 participants at four sites in the U.S. to either cardiac MRI or more invasive-based interventions with modification as needed when conditions evolved. The sites included William Beaumont Hospital in Royal Oak, Mich., the University of Mississippi in Jackson; The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus; and Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center in Winston-Salem.
Participants were followed for 2.8 years. The average age of study participants was 61; 60% were men, 64% were white, and 34% were Black. All participants experienced acute chest pain and troponin levels between detectable and 1.0 ng/ml.
The research team compiled data on heart attacks, deaths, and cardiac-related hospital readmission or emergency visits.
“We did not detect any differences in clinical or safety event rates between cardiac MRI and the invasive-based care pathway,” Miller said. “We also found that using cardiac MRI reduced the need for invasive angiography over the long-term follow-up period.”
In the cardiac MRI group, 58% of participants were safely discharged based on negative imaging and did not have angiography or an intervention such as revascularization within 90 days. Revascularization involves treatment to restore blood flow to a section of the heart that is blocked.
“These findings confirm that cardiac MRI is a highly accurate test that can be reliably used as first-line testing in this complex patient population,” Miller said.
Support from the study was provided by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute grant No. R01HL118263
END
Less-invasive cardiac MRI is a valuable diagnostic tool in the early evaluation of patients with acute chest pain
Randomized clinical trial enrolled patients with acute chest pain, mildly elevated troponin
2023-06-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
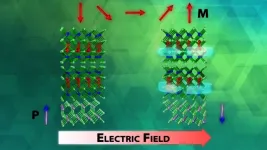
Novel way to manipulate exotic materials
2023-06-20
An advance in a topological insulator material — whose interior behaves like an electrical insulator but whose surface behaves like a conductor — could revolutionize the fields of next-generation electronics and quantum computing, according to scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
Discovered in the 1980s, a topological material is a new phase of material whose discoverers received a Nobel Prize in 2016. Using only an electric field, ORNL researchers have transformed a normal insulator into a magnetic topological insulator. This exotic material allows electricity ...
Research pilot sets the stage for better, more equitable aortic stenosis care
2023-06-20
DALLAS, June 20, 2023 — New research published today in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes examines the pilot phase of the American Heart Association quality improvement program Target: Aortic Stenosis™. The program aims to lay the groundwork to more reliably measure performance on the quality of aortic stenosis (AS) care from diagnosis to treatment. The Target: Aortic Stenosis program focuses on closing care gaps for patients who are not appropriately diagnosed and referred for initial ...
Community spaces may promote healthy aging for rural Black, Hispanic adults
2023-06-20
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Millions of Americans over the age of 65 lack access to the social and emotional support they need for healthy aging, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Non-white individuals in rural communities are especially susceptible. New research from Penn State found that the presence of social infrastructure — shared community spaces that are free or low cost to visit — in rural communities may help provide social and emotional support and promote healthy aging among older, ...
Concluding remarks & perspectives of Targeting Phage Therapy 2023
2023-06-20
The 6th World Congress on Targeting Phage Therapy 2023 that was held on June 1-2 in Paris, and gathered more than 150 attendees from 30+ different countries. Targeting Phage Therapy 2023 included more than 71 presentations between major talks, short orals, and posters.
The Chairman of the scientific committee Dr. Marvin Edeas Université de Paris, Cochin Institute, France, and Dr. Domenico Frezza, University of Roma Tor Vergata, Italy, stated: “It’s wonderful to hear that the speakers at the Targeting Phage Therapy 2023 conference delivered excellent presentations on a variety of fantastic topics. The fact ...
CEHD researchers receive funding for Appalachian Conservation Strategy Feasibility Pilot
2023-06-20
Sammie Powers, Assistant Professor, Recreation Management, School of Sport, Recreation, and Tourism Management (SRTM); Hung-Ling Liu, Associate Professor, Recreation Management, SRTM; and Ellen Rodgers, Associate Dean, College of Education and Human Development (CEHD), received funding from the Appalachian Trail Conservancy (ATC) for the project: "Appalachian Conservation Strategy Feasibility Pilot: Conservation and Human Dimensions Stakeholder Engagement Action Plan Project."
They are collaborating with Nate Trauntvein, Associate Professor, ...
Menon & Maribojoc receive funding for evaluation services for step ahead 2.0 – housing first support services pilot
2023-06-20
Menon & Maribojoc Receive Funding For Evaluation Services For Step Ahead 2.0 – Housing First Support Services Pilot
Nirup Menon, Professor, Information Systems and Operations Management (ISOM), and Roderick Maribojoc, Executive Director, Real Estate Entrepreneurship, received funding for: "Evaluation Services for Step Ahead 2.0 – Housing First Support Services Pilot."
Menon and Maribojoc are being funded to evaluate the impact of services in reducing homelessness in Fairfax ...
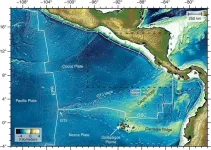
Scientists unearth 20 million years of ‘hot spot’ magmatism under Cocos plate
2023-06-20
Ten years ago, Samer Naif made an unexpected discovery in Earth’s mantle: a narrow pocket, proposed to be filled with magma, hidden some 60 kilometers beneath the seafloor of the Cocos Plate.
Mantle melts are buoyant and typically float toward the surface — think underwater volcanoes that erupt to form strings of islands. But Naif’s imaging instead showed a clear slice of semi-molten rock: low-degree partial melts, still sandwiched at the base of the plate some 37 miles beneath the ocean floor.
Then, the observation provided an explanation for how tectonic plates can gradually slide, ...
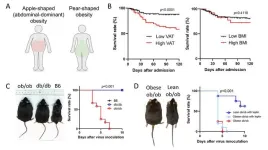
When it comes to COVID-19, belly fat upsets the apple cart
2023-06-20
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that apple-shaped obesity is associated with cytokine storm and a higher risk of death in COVID-19 patients
Tokyo, Japan – Eating an apple a day may keep the doctor away, but having an apple shape is not nearly as healthy. Now, researchers from Japan have shown that people who carry their weight in their bellies may be at greater risk of poor outcomes if they catch COVID-19.
In a study published last month in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), researchers from Tokyo Medical ...
Company culture shapes willingness of workers to act sustainably, research shows
2023-06-20
Amidst rising concerns about the global climate crisis, Princeton researchers have uncovered the surprisingly large role that companies play in shaping sustainable behaviors among employees, as well as a link between eco-friendly behaviors and happier workers.
In research published in Current Research in Ecological and Social Psychology, the Princeton team reported the results from a nationwide study of employees to understand the factors that influence whether workers take sustainable actions and incorporate the environment into their day-to-day decision making.
The results ...
USF Health researchers show how the placenta protects fetus in the womb against viral infections
2023-06-20
Give credit to your dad’s gene for keeping you safe during those long months in your mother’s womb.
Because without this genetic warrior, you might have succumbed to any number of viral infections that otherwise could be fatal to a fetus. A new paper published this week in the journal Cell Host & Microbe explains the mechanisms behind this anti-viral protection.
“What’s unique about this gene is how it produces a form of defense for the baby in the womb,’’ said Hana Totary-Jain, PhD., associate professor of Molecular ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Less-invasive cardiac MRI is a valuable diagnostic tool in the early evaluation of patients with acute chest painRandomized clinical trial enrolled patients with acute chest pain, mildly elevated troponin