(Press-News.org) The rate of eating disorder diagnoses among girls aged 13–16-years-old in the UK during the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic (from March 2020–March 2022) was 42% higher than the expected rate based on previous trends, suggests a study published in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health journal. The rate of self-harm diagnoses in the same cohort was 38% higher than the expected rate for the two-year period.
As the largest and most targeted nationwide study in the adolescent population, and the first to cover two years of the pandemic, these findings are the best available evidence on eating disorder and self-harm diagnoses among young people in the UK since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The researchers analysed the health records of more than 9 million young patients (male and female, ages 10–24 years) from more than 1,800 general practices across the UK to assess diagnosis rates at the first point of care. Using data from 2010–2020, the study predicted the expected rates of eating disorders and self-harm, had the pandemic not occurred, from March 2020, to March 2022. The actual rates of documented diagnoses during the pandemic were then compared with the projected rates.
Between March 2020, and March 2022, in 13–16-year-old girls, the rate of eating disorder diagnoses was 42% higher than expected, with 3,862 observed cases compared with 2,713 projected cases if the pandemic had not occurred. In the same cohort, the rate of self-harm diagnoses was 38% higher than expected, with 9,174 observed cases compared with 6,631 projected cases.
The study also provides novel insight into how the pandemic affected pre-existing socioeconomic differences in the rates of eating disorders and self-harm. During the pandemic, the higher than expected rates of eating disorders and self-harm in girls aged 13–16 years were largely due to increases within less deprived communities, although the authors highlight the need for further research into the reasons for these findings.
The authors argue the apparent increase in eating disorders and self-harm among teenage girls is a long-term consequence of the pandemic that remains to be addressed. They call for improved measures around early identification of mental health difficulties, timely access to treatments, scaling up of services, and ongoing support from GPs and mental health services, to reduce the potential of ongoing issues into adulthood.
Notes to Editors:
For interviews with the Article authors, please contact: Michael Addelman, Media Relations Officer, University of Manchester P) 07717 881567 E) michael.addelman@manchester.ac.uk
For embargoed access to the Article and Comment, please see: www.thelancet-press.com/embargo/GirlsMentalHealth.pdf
For embargoed access to the Appendix, please see: www.thelancet-press.com/embargo/GirlsMentalHealthAPPX.pdf
After the embargo lifts, the paper will be available at: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanchi/article/PIIS2352-4642(23)00126-8/fulltext
END
THE LANCET CHILD & ADOLESCENT HEALTH: Prolonged rise in eating disorders and self-harm among adolescent girls in the UK following the COVID-19 pandemic, best evidence to date suggests
2023-06-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Screening newborns for deadly immune disease saves lives
2023-06-21
Introducing widespread screening of newborns for a deadly disease called severe combined immunodeficiency, or SCID, followed by early treatment boosted the five-year survival rate of children with the disorder from 73% before the advent of screening to 87% since, researchers report. Among children whose disease was suspected because of newborn screening rather than illness or family history, 92.5% survived five years or more after treatment. These findings demonstrate for the first time that newborn screening facilitated the early identification of infants with SCID, leading to prompt ...
Sustainability of a 12-month lifestyle intervention delivered by community health workers in reducing blood pressure in Nepal: 5-year follow-up of an open-label, cluster randomised (COBIN) trial
2023-06-21
The sustainability and scalability of limited duration interventions in low- and middle-income countries remain unclear. A study published in The Lancet Global Health aimed to investigate the sustainability in reduction of blood pressure (BP) through a 12-month lifestyle intervention by community health workers (CHWs) to reduce BP in Nepal four years after the intervention ceased.
During the 12-month intervention, female community health volunteers (FCHVs) visited participants in the intervention groups and provided lifestyle counselling and BP measurement every 4 months.
At the end of the 12-month intervention, ...
Air pollution, even at low levels, made Covid worse for patients and hospitals
2023-06-21
Exposure to air pollution meant an average of around four extra days in hospital for Covid-19 patients, further increasing the burden on health care systems, according to a study published today (Wednesday) in the European Respiratory Journal [1].
The researchers say the effect of pollution on patients’ time in hospital was equivalent to being a decade older. Conversely, the effect of reducing exposure to pollution was 40 to 80% as effective in reducing patients’ time in hospital as some of the best available treatments.
In ...
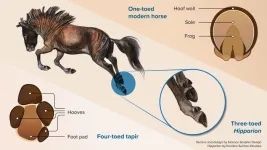
Modern horses have lost their additional toes, scientists confirm
2023-06-21
The distant ancestors of modern horses had hooved toes instead of a single hoof, which vanished over time, according to researchers.
The animals, such as the Eocene Hyracotherium, had feet like those of a modern tapir: four toes in front and three behind, each individually hooved with an underlying foot pad.
In contrast, modern equids such as horses, asses, and zebras, have only a single toe, the left over original third toe on each foot, encased in a thick-walled keratinous hoof, with an underlying triangular frog on the sole that acts as a shock absorber.
An international ...
Scientists discover critical factors that determine the survival of airborne viruses
2023-06-21
Critical insights into why airborne viruses lose their infectivity have been uncovered by scientists at the University of Bristol. The findings, published in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface today [21 June], reveal how cleaner air kills the virus significantly quicker and why opening a window may be more important than originally thought. The research could shape future mitigation strategies for new viruses.
In the first study to measure differences in airborne stability of different variants of SARS-CoV-2 in inhalable particles, ...
UK's young people at risk of leaving school without vital knowledge of reproductive health, study finds
2023-06-21
Pupils in the UK are not learning about potentially life-changing issues such as endometriosis, infertility, and miscarriage, according to a new study of curricula in science and in relationships and sex education.
Researchers from University College London (UCL) looked at what schools are expected to teach 14–18-year-olds across the UK, using curriculum requirements and specifications set by exam boards. Findings, published today in the peer-reviewed journal Human Fertility, demonstrate significant gaps and variations in what pupils are taught ...
Study explores climate change impacts on seagrass meadows
2023-06-21
Hidden beneath the waves of coastal waters lies an important member of the marine food chain – seagrasses. These marine meadows are in many ways the unsung heroes of the ocean, benefiting humans and the planet by producing oxygen, removing carbon dioxide from the air, and providing food and habitat for marine life. But these submerged savannahs may be in danger of disappearing, according to a new Stanford study that modeled the distribution of seagrass species around the world at two different timepoints in the future.
Climate change is expected to hit marine species hard, in part because oceans absorb an estimated ...
Helping define the impact of “art” in education
2023-06-20
Growing up, Brian Kisida always enjoyed going to school. He especially enjoyed the broad spectrum of subjects he was able to explore, including the arts. Now, as an assistant professor in the Truman School of Government and Public Affairs at the University of Missouri, he is researching the relationship between arts education and student success.
Over the years, Kisida, an expert on education policy, has seen the culture of education shift dramatically.
“I saw the impact that the test obsessed culture had on schooling, students’ mental health and enjoyment of learning,” Kisida said. “I wanted to know why we were seeing these changes that seem to not be in line ...
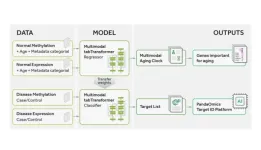
Precious1GPT: multimodal transfer learning for aging clock development and target discovery
2023-06-20
“The development of Precious1GPT [...] has demonstrated the potential of our approach in deciphering the molecular mechanisms of aging.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 20, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 11, entitled, “Precious1GPT: multimodal transformer-based transfer learning for aging clock development and feature importance analysis for aging and age-related disease target discovery.”
Aging is a complex ...
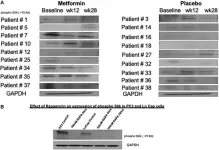
Metformin's role in preventing metabolic syndrome during androgen deprivation therapy: a Phase II study
2023-06-20
“[...] we found no impact of the addition of metformin to [androgen deprivation] therapy on risk of metabolic syndrome associated with castration therapy and no additional anti-tumor effects.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 20, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on June 19, 2023, entitled, “Utilizing metformin to prevent metabolic syndrome due to androgen deprivation therapy (ADT): a randomized phase II study of metformin in non-diabetic men initiating ADT for advanced prostate cancer.”
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) can lead to metabolic syndrome (MS) and is implicated in ADT-resistance. Metformin showed antineoplastic ...