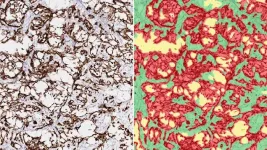
(Press-News.org) Immunotherapy is among the newest and most potent weapons against cancer. It prompts the immune system to recognize tumors as intruders in the body and attack. But not all patients respond well to immunotherapy. Why? Scientists aren’t always sure.
Sometimes, immunotherapy patients experience side effects that steroids called glucocorticoids (GCs) can treat. GCs are often used to regulate the immune response in conditions such as asthma, Crohn’s disease, and even COVID-19. Yet just how they work is also a mystery.
Now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) researchers may be closer to answering both questions. Their new research indicates GCs may indirectly lead to some immunotherapy treatment failures by driving the production of a protein called Cystatin C (CyC). Higher levels of CyC are linked to poorer outcomes of this type of therapy.
CSHL Assistant Professor Tobias Janowitz says, “GCs are very powerful suppressors of immunity and are consequently used to treat autoimmunity,” which is when the immune system attacks healthy cells. “We’ve previously shown that GCs can also break cancer immunotherapy. Now, here’s perhaps a clue into how they’re doing it.”
Janowitz’s lab studies the whole-body response to cancer. For this study, he and a Ph.D. student in his lab, physician-turned-researcher Sam Kleeman, teamed with a third CSHL scientist, Assistant Professor Hannah Meyer, an expert in quantitative biology. Together, they analyzed a massive genetic dataset from the UK Biobank. How massive? Almost 500,000 volunteers, including patients with cancer. Kleeman also reached out to researchers overseas to gather even more patient data.
The scientists found that patients who were more likely to produce CyC in response to GCs had a worse overall survival rate. These patients were also less likely to benefit from treatment. This suggests CyC production within a tumor may contribute to the failure of cancer immunotherapy.
To confirm CyC’s connection with cancer, the researchers turned to good old-fashioned lab work. In mice, they deleted a CyC-producing gene so it was no longer present in cancer cells. They found that tumors without CyC grew slower.
“It’s really powerful to come at this from multiple angles and support the findings through many approaches,” Meyer says. “Clever genetic models gave us some indication of which experiments to design to help us answer the question of what this molecule does.”
Janowitz says he plans to continue studying CyC. He hopes this could greatly help future patients.
“The research has given me an impetus to find out more about the function of this molecule, specifically in the context of cancer immunotherapy,” he says. “Perhaps its function can be targeted to enhance the success of cancer immunotherapy.”
END
How popular steroids could mess up some cancer treatments
2023-06-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Treatment for opioid use disorder varies widely among states, study finds
2023-06-23
Despite a national opioid overdose epidemic supercharged by a surge of illicit fentanyl, new research from Oregon Health & Science University reveals wide discrepancies among U.S. states in effectively treating opioid use disorder among people covered by Medicaid.
The study, published today in the journal JAMA Health Forum, found that in many states, fewer than half of people diagnosed with opioid use disorder received proven medications to treat it.
“We fail people by not providing adequate treatment to people with opioid use disorder enrolled in Medicaid,” said lead author Stephan Lindner, Ph.D., associate professor in ...
Patterns, characteristics of nicotine dependence among adults with cigarette use
2023-06-23
About The Study: There were significant reductions in nicotine dependence prevalence from 2006 to 2019 among U.S. adults with cigarette use and all examined subgroups 26 years and older. Adults 50 years and older (especially those with major depressive episode and/or substance use disorder) had the highest nicotine dependence prevalence compared with other age groups, highlighting the importance of assisting with smoking cessation efforts and addressing nicotine dependence for this older population. Evidence-based tobacco cessation strategies tailored to age and comorbidities are ...
Characteristics of medical evacuation by train in Ukraine
2023-06-23
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that medical evacuation in a war zone by converted trains is possible and can improve access to health care for war-affected patients. The presence of intensive care capacity on board allows for transport of more severely ill or injured individuals. However, the target population should not be limited to trauma patients, as health care institutions affected host a much broader population whose needs and urgency for evacuation may change over time.
Authors: James ...
BU researcher receives NIH grant to study stress, depression
2023-06-23
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, June 23, 2023
Contact: Gina DiGravio, 617-3508-7838, ginad@bu.edu
BU Researcher Receives NIH Grant to Study Stress, Depression
(Boston)—Michael Wallace, PhD, assistant professor of anatomy & neurobiology at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, was awarded a $2.8 million from the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Mental Health. The award will fund his project "Serotonergic modulation of the circuits and cell-types of the lateral habenula."
The award, which runs from 2023-2028, supports his research into the cellular and circuit impacts of serotonin on a brain region implicated in chronic stress and ...
Global warming accelerates CO2 emissions from soil microbes
2023-06-23
The rise in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration is a primary catalyst for global warming, and an estimated one fifth of the atmospheric CO2 originates from soil sources. This is partially attributed to the activity of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that decompose organic matter in the soil utilizing oxygen, such as deceased plant materials. During this process, CO2 is released into the atmosphere. Scientists refer to it as heterotrophic soil respiration.
Based on a recent study published in the scientific journal Nature Communications, a team of researchers from ...
UVA Health launches effort to improve HIV care across America
2023-06-23
A UVA Health doctor is launching an ambitious effort to assess and improve HIV care for people with low incomes across the nation, a campaign that could also help prevent transmission.
Kathleen McManus, MD, MS, of the University of Virginia School of Medicine, and her collaborators plan to identify specific policies and programs that can increase the numbers of patients who keep the HIV virus in their blood at undetectable levels. This desirable state, known as being “undetectable” or having “sustained viral suppression,” is associated with better health outcomes for individuals ...
Young Editor recruitment for journal Space: Science & Technology
2023-06-23
Introduction
Science Partner Journal Space: Science & Technology is an online-only Open Access journal published in affiliation with Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT) and distributed by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). BIT cooperates with China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) in managing the journal. The mission of Space: Science & Technology is to promote the exploration and research of space worldwide, to lead the rapid integration and technological breakthroughs of interdisciplinary sciences in the space field, and to build a high-level academic platform for discussion, cooperation, technological progress and information dissemination ...
New type of computer memory could greatly reduce energy use and improve performance
2023-06-23
Researchers have developed a new design for computer memory that could both greatly improve performance and reduce the energy demands of internet and communications technologies, which are predicted to consume nearly a third of global electricity within the next ten years.
The researchers, led by the University of Cambridge, developed a device that processes data in a similar way as the synapses in the human brain. The devices are based on hafnium oxide, a material already used in the semiconductor industry, and tiny self-assembled barriers, which can be raised or lowered ...
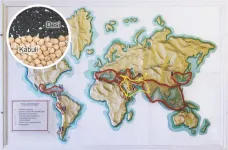
Study reveals genetic signatures of chickpea's cultural crossroads
2023-06-23
With its nutty flavor and dense nutrient profile, the humble chickpea has captivated palates and nourished civilizations for millennia. From its ancient origins to its widespread use in modern kitchens and restaurants around the world, this legume demonstrates both culinary versatility and cultural significance. Despite prominence in traditional cuisines across several continents, the origin, diversification, and spread of chickpeas throughout the Middle East, South Asia, Ethiopia, and the western Mediterranean have remained a mystery. A new study in Molecular Biology and Evolution titled “Historical ...
Supermarket trolleys set to help diagnose common heart rhythm disorder and prevent stroke
2023-06-23
Edinburgh, UK – 23 June 2023: It could be the shopping trip that saves your life: supermarket trolleys are helping to diagnose atrial fibrillation which can then be treated to prevent disabling or fatal strokes. The research is presented today at ACNAP 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“This study shows the potential of taking health checks to the masses without disrupting daily routines,” said study author Professor Ian Jones of Liverpool John Moores University, UK. “Over ...