(Press-News.org) In October, the excavation work for the superlative construction project began. What some consider an ideal ecological city, others call a promotional gimmick. Researchers from the Complexity Science Hub now show why The Line should not be a showcase for future cities.
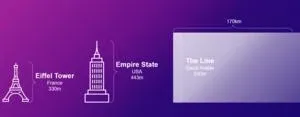
"It's the embodiment of the dream to start from scratch and completely rethink a city," says Rafael Prieto-Curiel, who researches cities at the Complexity Science Hub. The Line is planned to be a city built from nothing in the desert. It is to consist of two gigantic, unbroken rows of skyscrapers, with living space in between. 170 kilometers long. 200 meters wide. 500 meters high, higher than any building in Europe, Africa, and Latin America. String straight ahead from the Red Sea to the east.
TEN TIMES DENSER THAN MANHATTAN
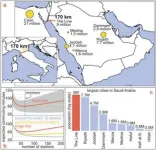
Nine million people are expected to live in it - more than in any other city in Saudi Arabia. This translates into a population density of 265,000 people per square kilometer - ten times denser than Manhattan and four times denser than the inner districts of Manila, currently estimated to be the densest urban neighborhoods on Earth. "How you can attract that many people in a medium-sized country at all is yet to be observed," Prieto-Curiel points out.
SIXTY MINUTES FOR A TRIP
Further questions arise in terms of mobility. “A line is the least efficient possible shape of a city,” says Prieto-Curiel. “There's a reason why humanity has 50,000 cities, and all of them are somehow round,” he emphasizes.
If we randomly pick two people in The Line, they are, on average 57 kilometers apart. In Johannesburg, which is 50 times larger in area, two random people are only 33 kilometers apart. Assuming a walking distance of one kilometer, only 1.2% of the population is within walking distance from each other. This hinders active mobility, so people will depend on public transport.
The backbone of public transportation is planned to be a high-speed rail system. "For everyone to be within walking distance of a station, there must be at least 86 stations," explains CSH researcher Dániel Kondor. As a result, trains spend considerable time in stations and will not be able to reach high travel speeds between any two stations. According to the researchers, a trip, therefore, is expected to take 60 minutes on average, and at least 47% of the population would have an even longer commute. Even with additional express lines, gains are limited due to the additional transfers necessary. The result is that people would still be traveling longer than in other major cities, such as Seoul, where 25 million people commute for less than 50 minutes.
A CITY IS MORE THAN A NEIGHBOURHOOD
Research shows that people want to spend a limited amount of time commuting, so efficient transportation plays a key role in the success of cities. But can these trips through the city be avoided because high density allows everything (jobs, shopping, amenities, etc.) to be available locally? "Cities are more than a collection of semi-isolated 15-minute neighborhoods located next to each other. What sets a city apart from smaller settlements is not just its size but additional opportunities outside the immediate neighborhood - such as concerts or an extended job search. For this reason, we need to consider citywide transportation,” explains Kondor.
WHY NOT “THE CIRCLE”?
If you take The Line and make it The Circle with a radius of 3.3 kilometers, the distance between any two people would be only 2.9 kilometers, and 24% of the population would be within walking distance of each other. Most mobility could be active (walking, cycling, or similar), making a high-speed rail system unnecessary. Alternatively, The Circle could allow good connectivity even with lower densities, avoiding the need for supertall buildings.
IS THERE SOMETHING POSITIVE?
"This project gets people discussing urban forms, and that's immensely important because cities, especially in Africa, are growing,” says Prieto-Curiel. Historically, cities often grew in organic ways, while planned cities often did not live up to expectations; thus, there is a need for more public engagement about urban design on a human scale.
Additionally, sustainability is emphasized in many aspects of the project. For example, there will be no cars for distances that are no more than a five-minute walk. This not only saves a lot of space in terms of infrastructure and parking but also reduces the number of cars. Moreover, all energy will be produced with zero carbon emissions. What is not taken into account here, however, is the construction of the skyscrapers, which requires a lot of material and energy.
“Overall, it stands to reason that other considerations may have played a role in choosing this unique form, such as branding or creating engaging social media videos. However, it is important to understand the consequences, especially if The Line is treated as a showcase for modern building and urban planning technologies”, emphasizes Prieto-Curiel.
_____
FIND OUT MORE
The opinion paper “Arguments for building The Circle and not The Line in Saudi Arabia” has been published in the Journal npj Urban Sustainability.
_____
ABOUT THE COMPLEXITY SCIENCE HUB
The mission of the Complexity Science Hub (CSH Vienna) is to host, educate, and inspire complex systems scientists dedicated to making sense of Big Data to boost science and society. Scientists at the Complexity Science Hub develop methods for the scientific, quantitative, and predictive understanding of complex systems.
The CSH Vienna is a joint initiative of AIT Austrian Institute of Technology, Central European University CEU, Danube University Krems, Graz University of Technology, Medical University of Vienna, TU Wien, VetMedUni Vienna, Vienna University of Economics and Business, and Austrian Economic Chambers (WKO). https://www.csh.ac.at
END
Why Saudi Arabia's "The Line" isn’t a revolution in urban living
2023-06-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Magnetic bacteria point the way
2023-06-27
Magnetotactic bacteria, which can align with the Earth’s magnetic field, have been discovered in a new location. Previously observed on land and in shallow water, analysis of a hydrothermal vent has proven that they can also survive deep under the ocean. The bacteria were able to exist in an environment that was not ideal for their typical needs. Magnetotactic bacteria are of interest not only for the role they play in Earth’s ecosystem, but also in the search for extraterrestrial life. Evidence of their existence can remain in rocks for billions of years. Their magnetic inclinations can also provide ...
Over 100 leaders in aging and longevity to present their latest research at the 10th ARDD
2023-06-27
June 27, 2023, the University of Copenhagen is excited to reveal the speakers, program and travel grants for the 10th Aging Research & Drug Discovery Meeting, the World's Largest Conference on Aging Research in the biopharmaceutical industry that will transpire on August 28 - September 1, 2023 on-site at the Ceremonial Hall, University of Copenhagen, and online.
According to the United Nations, the proportion of people aged over 65 now outnumber children younger than 5. The enormous growth in the elderly population is posing a socioeconomic challenge to societies worldwide, and necessitates new sweeping interventions for age-associated ...
A new method to keep thickening agents tiny in transport and big in application
2023-06-27
Osaka, Japan – Many commercial products such as food, cosmetics, and inks contain cellulose nanofiber (CNF) as a thickening agent. However, CNFs have some limitations that prevent their more widespread use. Now, researchers from Osaka University have demonstrated a method of dehydrating CNFs to a dense powder without affecting their three key properties. Their findings are published in Macromolecular Rapid Communications.
Video for your easy understanding
https://youtu.be/PAEd36v_SjI
CNFs are a popular thickening agent because small amounts in water have high transparency, high viscosity, and the viscosity ...
Two technology-based approaches that improved hand hygiene compliance are featured at infection prevention conference
2023-06-27
Orlando, Fla., June 27, 2023 – Hand hygiene is the simplest, most effective way to prevent the spread of infections in healthcare, yet healthcare worker adherence is often low. Infection preventionists at two health systems will present their successful hand hygiene interventions at the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology’s (APIC’s) Annual Conference in Orlando Florida, June 26-28.
University of Michigan Health sustains 95% hospital-wide hand hygiene compliance through creation ...
Updated guidance shows how hospitals should protect patients from resistant infections
2023-06-27
ARLINGTON, Va. (June 27, 2023) — A group of five medical organizations have released updated recommendations for the prevention of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, known as MRSA, transmission and infection. MRSA causes approximately 10% of hospital-associated infections in the United States and such infections are associated with an increased risk of death. Certain infections caused by MRSA rose by as much as 41% during the pandemic after falling in preceding years.
Strategies to Prevent Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Transmission and Infection in Acute Care Hospitals provides evidence-based, ...
How secure are voice authentication systems really?
2023-06-27
Computer scientists at the University of Waterloo have discovered a method of attack that can successfully bypass voice authentication security systems with up to a 99% success rate after only six tries.
Voice authentication – which allows companies to verify the identity of their clients via a supposedly unique “voiceprint” – has increasingly been used in remote banking, call centers and other security-critical scenarios.
“When enrolling in voice authentication, ...
Synthesis of peripherally annulated phenanthroporphyrins
2023-06-27
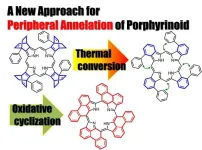
Prof. Okujima, in collaboration with Prof. Kobayashi at Shinshu University, reported the synthesis, molecular structure, optical properties and electronic structure of unusual phenanthrene-fused porphyrins.
Precursor porphyrins fused with aryl-substituted bicyclo[2.2.2]octadiene afforded the corresponding arylbenzoporphyrins (arylBPs) by retro Diels–Alder reaction. Unusual phenanthroporphyrins were obtained via the intramolecular Scholl reaction of arylBPs. We analyzed the optical and electronic structures using magnetic circular dichroism spectroscopy and time-dependent density functional theory calculations.
Our ...
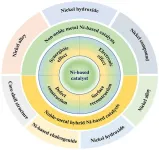
Recent progress of Ni-based catalysts for methanol electrooxidation reaction in alkaline media
2023-06-27
The study is led by Ligang Feng (School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University).
The rapid development of the economy driven by the large consummation of traditional fossil fuels is not sustainable, and global attention is shifted to the utilization of renewable energy sources, and biomass fuels. Methanol is considered a good biomass fuel to realize energy storage and conversion, which is convenient for storage and transportation; more importantly, it is much safer than other fuels such as gasoline, diesel, and natural gas. In addition, it can be prepared with wide sources in low-cost and ...
Move over diamond. hBN is quantum’s new best friend.
2023-06-27
Diamond has long been the go-to material for quantum sensing due to its coherent nitrogen-vacancy centres, controllable spin, sensitivity to magnetic fields, and ability to be used at room temperature. With such a suitable material so easy to fabricate and scale, there’s been little interest in exploring diamond alternatives. But this GOAT of the quantum world has one Achilles Heel… It’s too big. Just as an NFL linebacker is not the best sportsperson to ride in the Kentucky Derby, diamond is not an ideal material when exploring quantum sensors and information processing. ...
Personalized dosing in prostate cancer treatment improves patient outcomes
2023-06-27
Chicago, Illinois (Embargoed until 3:45 p.m. CDT, Tuesday, June 27, 2023)—By monitoring early-response biomarkers in men undergoing 177Lu-PSMA prostate cancer treatment, physicians can personalize dosing intervals, significantly improving patient outcomes. In a study presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2023 Annual Meeting, early stratification with 177Lu-SPECT/CT allowed men responding to treatment to take a “treatment holiday” and allowed those not responding the option to switch to another treatment.
Approved by the U.S. Food ...