(Press-News.org) Orangutans can make two separate sounds simultaneously, much like songbirds or human beatboxers, according to a study led by the University of Warwick.
Academics say the findings provide clues around the evolution of human speech, as well as human beatboxing.
Scientists observed two populations of vocalising orangutans in Borneo and Sumatra across a total of 3800 hours and found primates within both groups used the same vocal phenomenon.
Dr Adriano Lameira, Associate Professor of Psychology at the University of Warwick said: “Humans use the lips, tongue, and jaw to make the unvoiced sounds of consonants, while activating the vocal folds in the larynx with exhaled air to make the voiced, open sounds of vowels.
“Orangutans are also capable of producing both types of sounds—and both at once.
“For example, large male orangutans in Borneo will produce noises known as “chomps” in combination with “grumbles” in combative situations. Female orangutans in Sumatra produce “kiss squeaks” at the same time as “rolling calls” to alert others of a possible predator threat.
“The fact that two separate populations of orangutans were observed making two calls simultaneously, is proof that this is a biological phenomenon.”
Co-author and independent researcher Madeleine Hardus added: “Humans rarely produce voiced and voiceless noises simultaneously. The exception is beatboxing, a skilled vocal performance which mimicks the complex beats of hip hop music.
“But the very fact that humans are anatomically able to beatbox, raises questions about where that ability came from. We know now the answer could lie within the evolution of our ancestors.”
According to the authors, the vocal control and coordination abilities of wild great apes have been underestimated compared to the focus on the vocal abilities of birds.
“Producing two sounds, exactly how birds produce song, resembles spoken language but bird anatomy has no similarity to our own so it is difficult to make links between birdsong, and spoken human language,” continued Dr Hardus.
The new research has implications for the vocal capabilities of our shared ancestors and for the evolution of human speech—as well as human beatboxing. Dr Lameira said: “Now that we know this vocal ability is part of the great ape repertoire, we can’t ignore the evolutionary links.
“It could be possible that early human language resembled something that sounded more like beatboxing, before evolution organised language into the consonant – vowel structure that we know today.”
The paper, Wild orangutans can simultaneously use two independent vocal sound sources similarly to songbirds and human beatboxers, is published by PNAS Nexus.
ENDS
END
Orangutans can make two sounds at the same time, similar to human beatboxing, study finds
2023-06-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Beatboxing orangutans and the evolution of speech
2023-06-27
Orangutans can make two separate sounds simultaneously, much like songbirds or human beatboxers, according to a study. Adriano Lameira and Madeleine Hardus observed vocalizing orangutans in the wild. Humans use the lips, tongue, and jaw to make the unvoiced sounds of consonants, while activating the vocal folds in the larynx with exhaled air to make the voiced, open sounds of vowels. Orangutans are capable of producing both types of sounds—and both at once. For example, large male orangutans in Borneo will produce noises known as “chomps” in combination with “grumbles” in combative situations. Females in Sumatra produce “kiss squeaks” atop ...
What math can teach us about standing up to bullies
2023-06-27
In a time of income inequality and ruthless politics, people with outsized power or an unrelenting willingness to browbeat others often seem to come out ahead.
New research from Dartmouth, however, shows that being uncooperative can help people on the weaker side of the power dynamic achieve a more equal outcome—and even inflict some loss on their abusive counterpart.
The findings provide a tool based in game theory—the field of mathematics focused on optimizing competitive strategies—that could be applied to help equalize the balance of power in labor negotiations or international ...
Study identifies risk factors for early onset colorectal cancer in males
2023-06-27
INDIANAPOLIS – Colorectal cancer incidence and deaths are declining for individuals age 50 and older, but are increasing for those under 50.
A new study, led by researcher-clinician Thomas Imperiale, M.D., of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine, identifies seven risk factors for early onset colorectal cancer in males. The risk evaluation model the researchers developed may help 45- to 49-year-olds accept and adhere to new national screening recommendations and may also identify younger men for whom earlier screening should be considered.
“This study is important because ...
Air pollution speeds snowmelt
2023-06-27
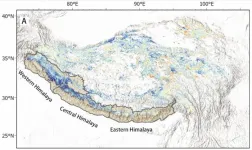
Diminished anthropogenic pollutant emissions during 2020 Covid-19 lockdowns reduced snowmelt in the Himalayas, according to a study. Liqiang Zhang and colleagues used multiple satellite data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI), as well as a coupled atmosphere-chemistry-snow model (GEOS-Chem-SNICAR) to explore how the sudden, dramatic reduction in particulate pollution in the region affected snow and ice melt. Snow and ice on the Tibetan plateau act as a water source for over 20% of the global population. However, ice and snow in the Himalayas have been melting at an accelerating rate in recent decades. ...
Unveiling the secrets of liquid iron under extreme conditions
2023-06-27
Iron is the most abundant element by mass on Earth. Despite being so common and well-studied, iron still manages to puzzle scientists by exhibiting electric and magnetic behaviors that are not fully comprehensible. In particular, the physical properties of liquid iron—which makes up most of the Earth’s core—have been the subject of much debate among physicists and geoscientists.
The problem is that certain predictions about liquid iron’s properties are difficult to experimentally verify due to the extreme conditions required to ascertain them. For example, liquid iron’s resistivity, which is the inverse of electrical conductivity, has ...
New study reveals key to sustainable, eco-friendly next-generation polymers for various uses
2023-06-27
Supramolecular polymers are a new class of polymers that are currently being evaluated for material applications. These interesting compounds also play an important role in cellular activities in the body. "Supra," as the name suggests, is attributed to some unique properties that go beyond those of conventional polymers. Unlike traditional polymers, which are held together by strong, irreversible covalent bonds, supramolecular polymers are held together by weaker, reversible hydrogen bonds. They can reversibly assemble and disassemble, are highly versatile, and can be used for developing targeted drug delivery therapies, sensors to detect pollutants, diagnostic ...
Light or moderate alcohol consumption does not guard against diabetes, obesity
2023-06-27
WASHINGTON—People who have just one or two drinks per day are not protected against endocrine conditions such as obesity and type 2 diabetes, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Alcohol consumption is a significant public health concern because it is related to many medical conditions such as diabetes, obesity, liver conditions and heart disease. While it is widely accepted that excessive alcohol consumption causes a wide range of health issues, whether modest alcohol consumption has beneficial health effects remains controversial.
“Some research ...
NUTRITION 2023 features leading nutrition experts and groundbreaking research
2023-06-27
Join us at NUTRITION 2023 for an exciting lineup of scientific symposia, educational sessions, hot-topic discussions, and award lectures covering the latest developments in nutrition science. NUTRITION 2023, the annual flagship meeting of the American Society for Nutrition (ASN), will be held July 22-25 at the Sheraton Boston.
Explore the meeting schedule and register for a press pass to attend.
The meeting will feature distinguished leaders in the field and important discussions that are helping to move nutrition science forward. Highlights include:
Ultra-processed foods – Observational studies ...
A surprise chemical find by ALMA may help detect and confirm protoplanets
2023-06-27
Scientists using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) to study the protoplanetary disk around a young star have discovered the most compelling chemical evidence to date of the formation of protoplanets. The discovery will provide astronomers with an alternate method for detecting and characterizing protoplanets when direct observations or imaging are not possible. The results will be published in an upcoming edition of The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
HD 169142 is a young star located in the constellation ...
AI model could help improve outcomes of prostate cancer focal therapy
2023-06-27
FINDINGS
A new study shows that an artificial intelligence (AI) model co-developed by researchers in the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center and department of Urology at UCLA can help doctors determine the extent of cancer within the prostate.
In a series of tests, the AI model was found to be more accurate at predicting tumor margins than magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), potentially improving the effectiveness of focal therapy, standardizing treatment margin definition, and reducing the chance of cancer recurrence.
BACKGROUND
Focal therapy, a minimally invasive treatment approach used for localized tumors, is an alternative ...