(Press-News.org) Increasing access to prescription opioid painkillers may reduce opioid overdose deaths in the United States, according to a Rutgers study.
“When access to prescription opioids is heavily restricted, people will seek out opioids that are unregulated,” said Grant Victor, an assistant professor in the Rutgers School of Social Work and lead author of the study published in the Journal of Substance Use and Addiction Treatment. “The opposite may also be true; our findings suggest that restoring easier access to opioid pain medications may protect against fatal overdoses.”
America’s opioid crisis has evolved across several waves, with each increasingly fatal. Wave one, which began in the 1990s, was associated with overdose deaths because of the misuse of opioid medications.
A policy implemented during the initial wave was the creation of prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs), state-based initiatives that track controlled substance prescribing. While the policy made it more difficult to access prescription opioids and rates of prescribing did decrease, it had the unintended consequence of pushing people toward off-market opioids, raising the risk of accidental death, said Victor.
This led to wave two of the crisis, a surge in heroin-related deaths, beginning around 2010, followed by wave three (which started in 2013), fueled by synthetic opioids such as fentanyl.
To measure trends and sociodemographic disparities in access to buprenorphine – a common treatment for opioid use disorder – and opioid painkillers, the researchers examined toxicology data, death records, and available PDMPs from 2,682 accidental overdose deaths that occurred from 2016 to 2021 in Indianapolis, Indiana.
The researchers found fewer than half of all decedents (43.3 percent) had a PDMP record of any kind, meaning they didn’t even try to access prescription opioids. Of the 10.6 percent that had been prescribed buprenorphine, most (64.7 percent) were prescribed treatment more than 30 days prior to death, suggesting they were not actively seeking treatment.
Victor and collaborators also found racial disparities in buprenorphine and opioid prescription trends, with dispersal for Blacks significantly lower than whites (7.3 percent and 21.9 percent versus 92.7 percent and 77.7 percent, respectively).
“Buprenorphine uptake is associated with significantly reduced rates of nonfatal and fatal overdose,” the researchers wrote. “Despite these positive treatment outcomes, several barriers remain to the widespread uptake of [medications for opioid use disorder] in the United States,” such as stigma and cost.
“For these reasons, a lack of adequate buprenorphine prescribing, combined with reductions in the availability of opioid analgesics, have left individuals contending with [opioid use disorder] at an elevated risk of overdose,” they concluded.
Given these trends and past research, Victor said it is time to re-evaluate policies that make it nearly impossible to obtain opioid prescriptions, even for those with a legitimate need.
“A big reason that we have such a problem with addiction in this country is because people can't access legitimate pain medication,” he said. “Our findings support a change in policy.”
END
Easier access to opioid painkillers may reduce opioid-related deaths
2023-06-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fear of being exploited is stagnating our progress in science
2023-06-27
Science is a collaborative effort. What we know today would have never been, had it not been generations of scientists reusing and building on the work of their predecessors.
However, in modern times, academia has become increasingly competitive and indeed rather hostile to the individual researchers. This is especially true for early-career researchers yet to secure tenure and build a name in their fields. Nowadays, scholars are left to compete with each other for citations of their published work, awards and funding.
So, understandably, many scientists have grown unwilling ...
New findings on hepatitis C immunity could inform future vaccine development
2023-06-27
A new USC study that zeros in on the workings of individual T cells targeting the hepatitis C virus (HCV) has revealed insights that could assist in the development of an effective vaccine.
Every year, hepatitis and related illnesses kill more than one million people around the world. If unaddressed, those deaths are expected to rise—and even outnumber deaths caused collectively by HIV, tuberculosis and malaria by 2040.
For that reason, the World Health Organization and other leading groups have pledged to work toward eliminating viral hepatitis by 2030. While there are vaccines for two of the three most common ...
Cooperation between muscle and liver circadian clocks, key to controlling glucose metabolism
2023-06-27
Collaborative work by teams at the Department of Medicine and Life Sciences (MELIS) at Pompeu Fabra University (UPF), University of California, Irvine (UCI), and the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) has shown that interplay between circadian clocks in liver and skeletal muscle controls glucose metabolism. The findings reveal that local clock function in each tissue is not enough for whole-body glucose metabolism but also requires signals from feeding and fasting cycles to properly maintain glucose levels in the ...
Bias in health care: study highlights discrimination toward children with disabilities
2023-06-27
Children with disabilities, and their families, may face discrimination in in the hospitals and clinics they visit for their health care, according to a new study led by researchers at University of Utah Health. These attitudes may lead to substandard medical treatment, which could contribute to poor health outcomes, say the study’s authors.
“They mistreated her and treated her like a robot. Every single time a nurse walked in the room, they treated her like she was not even there,” said one mother who was interviewed about her child’s health care encounters.
The findings, published in the journal Pediatrics, ...
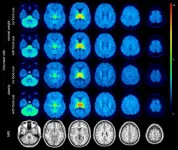
Molecular imaging identifies brain changes in response to food cues; offers insight into obesity interventions
2023-06-27
Chicago, Illinois (Embargoed until 10:05 a.m. CDT, Tuesday, June 27, 2023)—Molecular imaging with 18F-flubatine PET/MRI has shown that neuroreceptors in the brains of individuals with obesity respond differently to food cues than those in normal-weight individuals, making the neuroreceptors a prime target for obesity treatments and therapy. This research, presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2023 Annual Meeting, contributes to the understanding of the fundamental mechanisms underlying obesity ...
Flexible, supportive company culture makes for better remote work
2023-06-27
The pandemic made remote work the norm for many, but that doesn’t mean it was always a positive experience. Remote work can have many advantages: increased flexibility, inclusivity for parents and people with disabilities, and work-life balance. But it can also cause issues with collaboration, communication, and the overall work environment.
New research from the Georgia Institute of Technology used data from the employee review website Glassdoor to determine what made remote work successful. Companies that catered to employees’ interests, ...
BU study unpacks how medical systems harm the intersex community
2023-06-27
(Boston)— Intersex people’s (people whose sex characteristics do not fit within the strict binary categorizations of male or female) healthcare has received a lot of media attention recently, particularly with the uptick in anti-transgender legislation, which often also targets this community. Discrimination and mistreatment in social and medical settings, largely due to the stigma of not conforming to binary views of sex, results in many intersex individuals experiencing isolation, secrecy and shame, which can have a lasting impact on their mental health.
A new study from researchers at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine highlights the need ...
Follow the leader: Researchers identify mechanism of cancer invasion
2023-06-27
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A cancerous tumor is the accumulation of cells uncontrollably dividing, some of which can invade other parts of the body. The process is difficult to predict in detail, and eradicating the cells poses even greater difficulty. Now, a Penn State-led research team has revealed how the exodus initiates, shedding light on a potential therapeutic target to halt the invasion and providing a prognostic marker to help clinicians select the best treatment option.
They published their findings on June 26 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“Cancer cells don’t randomly detach from the primary tumor and disseminate ...
New enzyme could aid anticancer drug development
2023-06-27
HOUSTON – (June 27, 2023) – Many of the drugs we use to treat cancer and infectious disease are ⎯ or derive from ⎯ natural products, but it’s difficult to know exactly how nature assembles them.
Retracing nature’s steps, Rice University chemical engineer Xue Gao and her team mapped out the full series of enzyme-powered reactions a marine fungus uses to produce 21R-citrinadin A, a complex molecule with anticancer properties.
In the process, Gao and her collaborators identified a new enzyme, CtdY, which is the only one ...
Penn State researchers develop digital test to directly measure HIV viral load
2023-06-27
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A milliliter of blood contains about 15 individual drops. For a person with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), each drop of blood could contain anywhere from fewer than 20 copies of the virus to more than 500,000 copies. Called the viral load, this is what is measured to allow clinicians to understand how patients are responding to anti-viral medications and monitor potential progression.
The time-consuming viral load testing needs to be repeated several times as a patient undergoes treatment. Now, a Penn State research team has developed a time and cost-efficient digital assay that can directly measure the presence of HIV in ...