(Press-News.org) Fascination surrounding spaceflight and rockets is at an all-time high. Sites near launchpads draw crowds of spectators, eager to witness the flash of fire and feel the vibrations as the rumble of the motor becomes a roar. People, squinting and craning their necks to watch the rocket hurtle out of sight, aren’t likely thinking about the science behind the propulsion that makes it all possible.
What are the key elements that influence the combustion process? Are there advantages to utilizing solid propellants versus liquid? Simplicity, lower cost, and ease of storage and handling make solid fuel sources ideal for military and space applications.
To advance the fundamental knowledge of how polymeric solid fuels combust, the Department of Defense (DOD) has awarded $7.5 million to a multi-university partnership as part of the agency’s Multidisciplinary University Research Initiatives program.
The project, led by Virginia Tech over the next three years, will bring together leading researchers and engineers from Penn State, Georgia Tech, Iowa State University, Stanford University, University of California Riverside, and North Carolina State University to conduct experiments and develop computational models that detail how a variety of solid fuels will burn in various flow conditions.
Research on the combustion of polymeric solid fuels has a long history, but high-level studies have revealed fundamental gaps in the chemistry and physics needed to predict results for new polymeric solids and combustors. This research is being sponsored by the Office of Naval Research, as the data gathered is relevant to the U.S. Navy and can be applied to developing high speed and hypersonic vehicles.
“Our goal is to develop a unified understanding of solid fuel combustion for different fuels under a diverse set of flow conditions,” said Virginia Tech’s Gregory Young, the primary investigator leading the multi-institutional research effort. “Through detailed measurements and computations, we will have a better understanding of the fundamental processes. This knowledge will allow for the future development of revolutionary solid fuels that may operate in extreme conditions such as high speeds and altitudes.”
Young, associate professor in the Kevin T. Crofton Department of Aerospace and Ocean Engineering, is a leading expert in energetic materials, combustion, and propulsion. His research over the past decade has focused on the development, characterization, and optimization of energetic materials and propellants, specifically for applications in pyrotechnics, rocket propulsion, and high speed air breathing systems such as ramjets and scramjets.
Solid fuel combustion is crucial to hypersonic and space-propulsion systems. Fuel types and flowfields influence the combustion process – specifically heat transfer, pyrolysis, condensed phase chemistry, mixing, and gas phase chemistry.
Using a coordinated multidisciplinary approach involving novel experimental, theoretical, and numerical techniques, the research team aims to unravel complex, highly coupled combustion behavior of solid fuels over a wide range of conditions. Researchers will then integrate the obtained knowledge into a unified and reliable model for solid fuel combustion.
Large scale experimentation will be conducted at research facilities at Virginia Tech and Penn State. At Virginia Tech, Young and his graduate students will investigate aspects of solid fuel combustion in both subsonic and supersonic flows at the Advanced Propulsion and Power Laboratory. The interdisciplinary research facility is equipped with several state-of-the-art experimental rigs and diagnostic instrumentation systems.
Data derived from this study will enable scientists and engineers to better understand the characteristics and behavior of physicochemical processes in solid fuel combustion. With the comprehensive knowledge on how specific fuels burn at higher altitudes and accelerated speeds, researchers will be able to utilize the model to make predictions for revolutionary solid fuel sources as they are developed.
“These are complex issues, and we’ll be one of the first groups to tackle this problem in this level of detail,” said Young.
A community of subject matter experts
To expand the educational impact for students across institutions, the team will actively cross-train students among the various laboratories. For instance, Virginia Tech students will have the opportunity to travel to partner universities for hands-on experience with advanced diagnostics approaches, while students from other institutions will be able to participate in the large-scale experiments in Blacksburg.
Similarly, students will interact and cross-train on continuum modeling efforts and multiscale modeling improvements.
“This cross-training will be key in demonstrating the power of multidisciplinary research,” said Young. “We hope this experience will foster a collaborative relationship that the students can build upon as they enter the workforce together.”
The research will also involve collaborators from government labs, such as the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory; U.S. Naval Surface Warfare Center, Indian Head Division; U.S. Naval Air Warfare Center, China Lake; and the Air Force Research Laboratory. With a goal of training the next generation of scientists and engineers to lead the aerodynamics, combustion, and energetics communities, the project will introduce students to internship opportunities at DOD laboratories and facilities.
The model developed and knowledge gained will enable the DOD to develop revolutionary solid fuels to operate under extreme conditions of altitude and combustor residence times. The modeling and diagnostic tools developed will improve future studies on fundamental and applied combustion, and the resulting kinetic models for solid fuels represent the initial framework for binder chemistry necessary to develop composite solid-propellant models.
END
Virginia Tech leads multi-institution research on polymeric solid fuel combustion
University partners will conduct experiments and develop computational models that detail how a variety of solid fuels will burn in various flow conditions.
2023-06-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Newly discovered Jurassic fossils are a Texas first
2023-06-27
A team led by scientists at The University of Texas at Austin has filled a major gap in the state’s fossil record – describing the first known Jurassic vertebrate fossils in Texas.
The weathered bone fragments are from the limbs and backbone of a plesiosaur, an extinct marine reptile that would have swum the shallow sea that covered what is now northeastern Mexico and far western Texas about 150 million years ago.
The bones were discovered in the Malone Mountains of West Texas during two fossil hunting missions led by Steve May, a research associate at UT Austin’s Jackson School of Geosciences Museum of Earth ...
DOE and Sweden sign joint implementation agreement to increase scientific cooperation
2023-06-27
The Department of Energy (DOE) today signed an implementation agreement with Sweden to further promote and facilitate basic science research in energy and related fields.
The agreement reflects the United States and Sweden’s commitment to advancing scientific knowledge. It aims to foster joint research, shared facilities and exchanges of scientists in topics such as scientific computing, high energy physics, nuclear physics, fusion, basic energy sciences, and biological and environmental research.
Present at the ...
Researchers make a quantum computing leap with a magnetic twist
2023-06-27
FROM: James Urton
University of Washington
206-543-2580
jurton@uw.edu
(Note: researcher contact information at the end)
For immediate release
June 27, 2023
Researchers make a quantum computing leap with a magnetic twist
Quantum computing could revolutionize our world. For specific and crucial tasks, it promises to be exponentially faster than the zero-or-one binary technology that underlies today’s machines, from supercomputers in laboratories to smartphones in our pockets. But developing quantum computers hinges on building a stable network of qubits — or quantum ...
A prestigious CAREER award for UTA faculty member
2023-06-27
A University of Texas at Arlington faculty member is pioneering a transformative technique aimed at enhancing the utilization of tungsten in additive manufacturing processes, specifically overcoming significant challenges presented by tungsten’s high melting point, intrinsic brittleness and high susceptibility to cracking.
Narges Shayesteh, assistant professor in the Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Department and director of the Innovative Additive Manufacturing Laboratory, has earned a five-year, $582,358 Faculty Early Career Award Development Program (CAREER) grant from the National Science Foundation to advance her research and education initiatives.
The ...
DNA barcoding identifies the plants a person has eaten
2023-06-27
DURHAM, N.C. – What people say they’ve eaten and what they’ve actually eaten are often two very different lists of foods. But a new technique using DNA barcoding to identify the plant matter in human feces may get at the truth, improving clinical trials, nutrition studies and more.
Building on earlier studies that attempted to compare DNA found in feces with reported diets, researchers in the lab of Lawrence David, an associate professor of molecular genetics and microbiology in the Duke ...
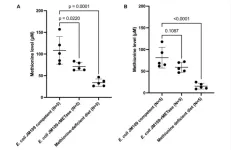
Methionine restriction reverses old-age obesity in mice
2023-06-27
“This is the first report that showed the efficacy of methionine restriction to reverse old-age-induced obesity.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 27, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 11, entitled, “Old-age-induced obesity reversed by a methionine-deficient diet or oral administration of recombinant methioninase-producing Escherichia coli in C57BL/6 mice.”
Obesity increases with aging. Methionine restriction ...
The 2023 Ogawa-Yamanaka Stem Cell Prize awarded to Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz
2023-06-27
SAN FRANCISCO, CA—Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz, PhD, was announced today as the recipient of the 2023 Ogawa-Yamanaka Stem Cell Prize by Gladstone Institutes. Zernicka-Goetz is a professor of mammalian development and stem cell biology in the Department of Physiology, Development, and Neuroscience at the University of Cambridge, as well as the Bren Professor of Biology and Biological Engineering at the California Institute of Technology.
A pioneering stem cell scientist, Zernicka-Goetz was selected for the prize because of her work uncovering fundamental mechanisms that drive the development of mammalian embryos, which led to the ...
Unsafe feeding methods spiked during infant formula shortage
2023-06-27
Nearly half of parents who relied on formula to feed their babies during the infant formula shortage last year resorted to potentially harmful feeding methods, according to a survey from researchers at the University of California, Davis. The study was published in the journal BMC Pediatrics.
In an online anonymous survey of U.S. parents, the number of individuals that used at least one unsafe feeding practice increased from 8% before the formula shortage to nearly 50% during the shortage. Unsafe practices included watering down formula, using expired or homemade formula, or using human milk from informal sharing.
The percentage of parents who shared human milk ...
Illinois study reveals genetic secrets of America's favorite snack
2023-06-27
URBANA, Ill. – In its simplest form, popcorn is pretty uncomplicated. Most supermarket varieties offer the choice of two kernel colors, yellow or white, and two kernel shapes, pointed or pearl. When popped, the flake typically expands into one of two shapes: mushroom or butterfly. But there’s more to popcorn than meets the eye. New research from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign reveals a wealth of untapped diversity lurking in popcorn’s genetic code.
Analyzing 320 publicly available popcorn lines, crop sciences researchers found variation at more ...
UC Irvine scientists develop freely available risk model for hurricanes, tropical cyclones
2023-06-27
Irvine, Calif., June 27, 2023 — As human-driven climate change amplifies natural disasters, hurricanes and typhoons stand to increase in intensity. Until now, there existed very few freely available computer models designed to estimate the economic costs of such events, but a team of researchers led by Jane W. Baldwin at the University of California, Irvine recently announced the completion of an open-source model that stands to help countries with high tropical cyclone risks better calculate just how much those storms will impact their people and their economies.
“Tropical cyclones are some of the most impactful natural disasters on Earth. They pose huge risks ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Virginia Tech leads multi-institution research on polymeric solid fuel combustionUniversity partners will conduct experiments and develop computational models that detail how a variety of solid fuels will burn in various flow conditions.