(Press-News.org) With a flick of a switch, current technologies allow you to quickly change materials from being dark to light, or cold to hot, just by blocking or transmitting specific wavelengths. But now, inspired by squid skin, researchers in ACS Nano report a soft film that can regulate its transparency across a large range of wavelengths — visible, infrared and microwave — simultaneously. They demonstrated the material in smart windows and in health monitoring and temperature management applications.
Unique to the skin of squid and other cephalopods, iridocytes and chromatophores reversibly change their orientation and alter the animals’ appearance. Similarly, scientists have developed artificial materials that transition from reflecting to transmitting visible and infrared wavelengths by shifting from wrinkly to cracked. Because microwaves are much larger than these surface structures, they aren’t impacted. However, researchers recently found that dense networks of electrically conductive materials, such as silver nanowires, could block microwaves. So, Yi Yang, Guangbin Ji, Zhichuan J. Xu and colleagues wanted to integrate surface structures with a conductive network in a soft film that could quickly transition between shielding visible-to-microwave bands and allowing them through.
The researchers created a two-layer film by spraying a thin coating of silver nanowires onto a stretched elastomer. Stretching and contracting the material produced cracks and bumpy wrinkles, respectively, in the metal surface. Then, when the researchers contracted the material to a -30% strain, it blocked light, trapped infrared heat and shielded up to 99.9% of microwaves that could interfere with devices. And as the material stretched apart, the expansion was directly related to an increase in optical transparency and heat and microwaves it transmitted. Additionally, the team demonstrated how the material could be used for various applications:
To transmit or block wireless electrocardiography signals.
As a blanket to trap body heat or allow it to escape.
For tracking movements because the materials produce temperature changes that are detectable by infrared cameras.
The researchers say that their system’s ability to modify its transparency repeatedly and rapidly could benefit dynamic camouflage technologies, energy-efficient buildings, and adaptive personal and healthcare devices.
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Nature Science Foundation of China and the National Science and Technology Major Project of China.
The paper’s abstract will be available on June 28 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs /10.1021/acsnano.3c01836
For more of the latest research news, register for our upcoming meeting, ACS Fall 2023. Journalists and public information officers are encouraged to apply for complimentary press registration by completing this form.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
Squid-inspired soft material is a switchable shield for light, heat, microwaves
2023-06-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
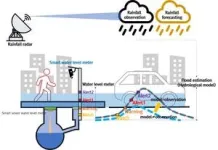
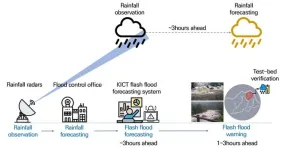
Forecasting flash floods an hour in advance
2023-06-28
Korea has recently seen a surge in localized torrential rain and floods due to global warming. Frequent flash floods are hard to forecast and, when forecast, the accuracy is low. This often leads to major disasters that take hundreds of lives, as seen in Germany and China (Henan) in July 2021. Floods are one of the deadliest types of natural disasters, but climate change has made the forecasting of them even more challenging.
Researchers at the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-Suk) have developed a system that can forecast ...
SNMMI keeps “Eye on the Patient” at 2023 Annual Meeting
2023-06-28
Reston, VA (July 28, 2023)—The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) hosted nearly 8,000 physicians, technologists, pharmacists, laboratory professionals, scientists and others at its 2023 Annual Meeting, themed “Eye on the Patient,” held in Chicago, Illinois.
“This year’s meeting offered attendees world-class scientific research, education, and exhibits as well as one-of-a-kind networking opportunities that will ultimately help us serve our patients better,” said Helen ...
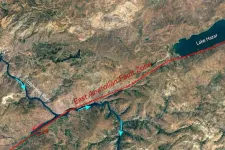
Researchers unearth the mysteries of how Turkey’s East Anatolian fault formed
2023-06-28
An international team led by the University of Minnesota Twin Cities has, for the first time, accurately determined the age and formation process of the East Anatolian fault, which runs from eastern to south-central Turkey and was involved in the creation of the Anatolian tectonic plate.
The fault zone was the site of two devastating earthquakes that occurred in Turkey and Syria in February 2023. While the researchers’ findings won’t help predict timing or size of earthquakes, it allows geologists to learn more about how long the area has been seismically active and how major earthquakes have shaped the landscape over time, which can help drive ...
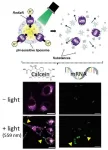
Towards new light-responsive carriers for intracellular substance delivery
2023-06-28
Artificial lipid bilayer vesicle liposomes, also called proteoliposomes, are specialized systems capable of incorporating various molecules, such as chemicals and drugs. Their unique properties make them ideal carriers for delivering substances inside cells. However, they must possess the dual characteristics of high stability in extracellular environments and low stability in intracellular environments.
Several techniques have been developed to regulate the stability of liposomes in a condition-dependent manner, with pH-sensitive liposomes being widely employed. A standard measure of acidity or basicity, the ...
Women with adenomyosis face increased risk of pregnancy and childbirth complications
2023-06-28
Copenhagen, Denmark: Women with adenomyosis – a chronic condition that can cause pelvic pain and heavy menstrual bleeding – are at increased risk of infertility as well as problems in pregnancy and during birth, according to research presented at the 39th annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) [1].
Data from the first study of its kind based on more than nine million women show that mothers-to-be with adenomyosis experienced higher rates of complications.
The greatest risk was for caesarean section delivery – ...
Prisoners ‘trading rare jaguar parts for fashion items’
2023-06-28
Prisoners in Bolivia are trading in jaguar skins and other wild animal body parts to produce wallets, hats, and belts for sale in local markets. The fangs and bones of jaguars are being illegally exported for use as traditional Asian medicine.
The trade, which further threatens the future of this species, has been uncovered by researchers investigating reports of illegal trading at Mocoví prison, in Trinidad, Bolivia.
As the largest big cat in the Americas the jaguar (Panthera Onca) has ecological and cultural significance in the landlocked country of Bolivia, but numbers are declining fast due to reasons including habitat loss – as ...
Group-based performing arts therapies reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression - review
2023-06-28
Performing arts performed in groups appears to lower anxiety and depression, according to a review of available evidence.
Researchers at the University of Exeter looked at the effect of group-based performing arts-based therapies on symptom severity, wellbeing, quality of life, functional communication or social participation. In a study published in BMJ Open, the researchers reviewed 171 studies, and took 12 forward to inclusion, which met the screening criteria.
Published from 2004 to 2021, the studies involved a total of 669 participants with anxiety and/or depression, from nine countries and covered ...
That essential morning coffee may be a placebo
2023-06-28
For many people, the day doesn’t start until their coffee mug is empty. Coffee is often thought to make you feel more alert, so people drink it to wake themselves up and improve their efficiency. Portuguese scientists studied coffee-drinkers to understand whether that wakefulness effect is dependent on the properties of caffeine, or whether it’s about the experience of drinking coffee.
“There is a common expectation that coffee increases alertness and psychomotor functioning,” said Prof Nuno Sousa of the University of Minho, corresponding author of the study ...
Virginia pediatric hospital prevented central line infections for nearly a year
2023-06-28
Orlando, Fla., June 28, 2023 – A Virginia pediatric hospital eliminated central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSI) among its most vulnerable patients for 300 days during 2021 and 2022. Their results are being presented at the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology’s (APIC’s) Annual Conference in Orlando Florida, June 26-28.
When the infection prevention and quality departments at Inova L.J. Murphy Children’s Hospital, part of the Inova Health System and located in Falls Church, Virginia, benchmarked their CLABSI rates against other pediatric hospitals, ...
US public pensions could be $21 billion richer right now
2023-06-28
New research shows that U.S. public pension funds would be $21 billion richer had they divested from fossil fuels a decade ago.
The study, out of the University of Waterloo in partnership with Stand.earth, analyzed the public equity portfolios of six major U.S. public pension funds, which collectively represent approximately 3.4 million people, to determine the effect divesting from their energy holdings would have had. In total, researchers estimate that the pension funds would have seen a return on their investments that was 13 per cent higher on average.
Another analysis of the same eight U.S. public pension funds included in the report found that ...