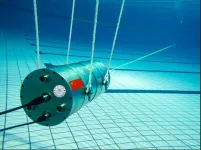
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON — Researchers report a new single-photon Raman lidar system that operates underwater and can remotely distinguish various substances. They also show that the new system can detect the thickness of the oil underwater up to 12 m away, which could be useful for detecting oil spills.
“Differentiating substances in water and detecting their distribution characteristics in the ocean are of great significance for marine monitoring and scientific research,” said research team leader Mingjia Shangguan from Xiamen University in China. “For instance, the remote sensing of underwater oil that we demonstrated could be useful for monitoring leaks in underwater oil pipelines.”
Although lidar approaches based on Raman signals have been previously used for detection of underwater substances, existing systems are impractical because they are bulky and require large amounts of power.
In the Optica Publishing Group journal Applied Optics, the researchers describe their new lidar system, which uses just 1 μJ of pulse energy and 22.4 mm of receiver aperture. The entire lidar system is 40 cm long with a diameter of 20 cm and can be operated up to 1 km underwater. To boost sensitivity, the researchers incorporated single-photon detection into their compact underwater Raman lidar system.
“Mounting an underwater Raman lidar system on an autonomous underwater vehicle or remotely operated vehicle could enable monitoring for leaks in underwater oil pipelines,” said Shangguan. “It could potentially also be used to explore oceanic resources or be applied in detecting seafloor sediment types, such as coral reefs.”
Single-photon sensitivity in underwater lidar
Traditional lidar systems designed to operate above water on ships, aircraft or satellites can achieve large-scale ocean profiling, but their detection depth is limited, especially during rough sea conditions. Raman lidar systems, however, can be used for analysis underwater at different depths without being affected by sea conditions.
Raman lidar works by emitting a pulse of green laser light into the water that interacts with substances such as oil. This excites inelastic Raman signals that can be used to identify substances. By measuring the intensity of Raman signals at specific wavelengths, lidar can provide information about the oil content in the water.
“Traditional Raman lidar systems rely on increasing laser power and telescope aperture to achieve remote sensing detection, which leads to a large system size and high-power consumption that make it difficult to integrate lidar systems onto underwater vehicles,” said Shangguan. “The use of single-photon detection technology made this work possible by improving detection sensitivity to the level of single photons.”
The researchers demonstrated their new lidar system by using it to detect varying thicknesses of gasoline oil in a quartz cell that was 12 m away from the system. Both the lidar system and the quartz cell were submerged at a depth of 0.6 m underwater in a large pool. The lidar system was able to detect and distinguish all thicknesses of gasoline, which ranged from 1 mm to 15 mm.
The researchers are now working to increase the number of detection channels and the Raman spectral resolution of the single-photon lidar system to enhance its ability to distinguish different substances in water. This would allow it to be used to analyze underwater bubble types and to detect corals and manganese nodules.
Paper: M. Shangguan, Z. Yang, M. Shangguan, Z. Lin, Z. Liao, Y. Guo, C. Liu, “Remote sensing oil in water with an all-fiber underwater single-photon Raman lidar,” Applied Optics vol. 62 issue 19 pp. 5301-5305 (2023).
DOI: doi.org/10.1364/AO.488872
About Applied Optics
Applied Optics publishes in-depth peer-reviewed content about applications-centered research in optics. These articles cover research in optical technology, photonics, lasers, information processing, sensing and environmental optics. Applied Optics is published three times per month by Optica Publishing Group and overseen by Editor-in-Chief Gisele Bennett, MEPSS LLC. For more information, visit Applied Optics .
About Optica Publishing Group
Optica Publishing Group is a division of Optica (formerly OSA), Advancing Optics and Photonics Worldwide. It publishes the largest collection of peer-reviewed content in optics and photonics, including 18 prestigious journals, the society’s flagship member magazine, and papers from more than 835 conferences, including 6,500+ associated videos. With over 400,000 journal articles, conference papers and videos to search, discover and access, Optica Publishing Group represents the full range of research in the field from around the globe.
END
New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks
System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications
2023-06-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Faster, safer target prep
2023-06-29
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers have developed a method to simplify one step of radioisotope production — and it’s faster and safer.
ORNL produces several radionuclides from irradiated radium-226 targets, including actinium-227 and thorium-228, both used in cancer treatments. Continuously improving isotopes for human health is one of the lab’s missions.
Currently, it takes workers two weeks to prepare radium-226 targets for irradiation in the High Flux Isotope Reactor. The targets are exposed to radiation throughout the process, which involves pressing radium carbonate aluminum composite into 10 pellets — one each day — and sealing ...
Health care utilization following interventions to improve social well-being
2023-06-29
About The Study: This systematic review and meta-analysis including 41 studies and 7,800 participants found that psychosocial interventions were associated with decreased health care use in most health services and increased use of outpatient care. The greatest health care decrease was among caregivers and individuals with mental illnesses and in interventions delivered 1-on-1 by health professionals.
Authors: Neta HaGani, M.S.W., of the University of Sydney in Sydney, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Transferring data with many colors of light simultaneously
2023-06-29
New York, NY—June 29, 2023—The data centers and high-performance computers that run artificial intelligence programs, such as large language models, aren’t limited by the sheer computational power of their individual nodes. It’s another problem — the amount of data they can transfer among the nodes — that underlies the “bandwidth bottleneck” that currently limits the performance and scaling of these systems.
The nodes in these systems can be separated by more than one kilometer. Since metal wires dissipate electrical signals as heat when transferring data at high speeds, these systems transfer data via fiber-optic ...
An early predictor of cognitive decline in Parkinson’s disease
2023-06-29
Have you ever felt the strong sensation that someone is behind you, so intense that you turn around, only to see that no-one is there? This is a 'presence hallucination’. Presence hallucinations are particularly frequent but underreported in patients with Parkinson’s disease and may appear early on in the course of the disease. They are sometimes ignored by the patient, by clinicians, or brushed off as a simple side-effect of medication.
Now, EPFL scientists have found that patients recently diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease and who have early hallucinations are ...
Cracking the tubulin code
2023-06-29
Tubulin is a protein that plays a crucial role in the structure and function of cells. It is the main component of microtubules, which are long, hollow fibers that provide structural support, help the cell divide, give it its shape, and act as tracks for moving molecular cargo around inside the cell.
There are two types of tubulin: alpha-tubulin and beta-tubulin. Together, they form dimeric (two-part) building blocks, spontaneously assembling into microtubules that undergo further continuous cycles of assembly and disassembly.
The tubulin code
To fine-tune microtubules, the dimers undergo various post-translational modifications (PTMs), which are chemical modifications that occur ...
Amander T. Clark takes on new role as President of the ISSCR
2023-06-29
Skokie, IL – The ISSCR is pleased to announce Amander T. Clark, PhD, Professor of Molecular, Cell and Developmental Biology, University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), USA, as its President. Dr. Clark’s one-year term of office leading the global society begins 1 July 2023.
“I will work to ensure that the society continues to defend stem cell science and the researchers working to transform lives,” Dr. Clark said at the ISSCR 2023 Annual Meeting in Boston this month. “We will expand our engagement with the public ...
New AI tool beats standard approaches for detecting heart attacks
2023-06-29
A new machine learning model uses electrocardiogram (ECG) readings to diagnose and classify heart attacks faster and more accurately than current approaches, according to a study led by University of Pittsburgh researchers that published today in Nature Medicine.
“When a patient comes into the hospital with chest pain, the first question we ask is whether the patient is having a heart attack or not. It seems like that should be straightforward, but when it’s not clear from the ECG, it can take ...
Proteins predict significant step toward development of diabetes
2023-06-29
RICHLAND, Wash.—Scientists have taken an important step forward in predicting who will develop Type 1 diabetes months before symptoms appear.
In a paper published online on June 29 in Cell Reports Medicine, researchers at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory and their colleagues identify a set of altered proteins that predict a condition known as islet autoimmunity, a precursor for everyone who will ultimately develop Type 1 diabetes.
The scientists caution that the work marks a beginning, not the end, of a search for a way to predict who will develop the disease. More work needs to be done ...
Sociogenomics: The intricate science of how genetics influences sociology
2023-06-29
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Humans contain multitudes. Each person on the planet contains enough DNA to stretch to Pluto – several times.
Studying how all this genetic material works, and especially how genes influence human behavior, is an enormously complicated undertaking – one that’s being made easier by the emergence of massive banks of genetic data and complex data science analysis techniques to parse that data.
Robbee Wedow, an assistant professor of sociology and data science in Purdue University’s College of Liberal Arts, an adjunct assistant professor of ...
City of Hope appoints David W. Craig, Ph.D., as founding chair of its new Department of Integrative Translational Sciences within its Beckman Research Institute
2023-06-29
LOS ANGELES — City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States and a leading research center for diabetes and other life-threatening illnesses, today announced that effective June 30, David W. Craig, Ph.D., will be professor and founding chair of its newly created Department of Integrative Translational Sciences within Beckman Research Institute of City of Hope. Craig also will serve as deputy director of translational sciences at Beckman Research Institute and associate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
[Press-News.org] New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaksSystem could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications