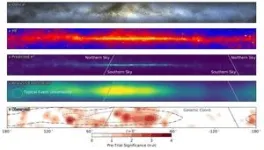
(Press-News.org) The Milky Way galaxy is an awe-inspiring feature of the night sky, dominating all wavelengths of light and viewable with the naked eye as a hazy band of stars stretching from horizon to horizon. Now, for the first time, the IceCube Neutrino Observatory has produced an image of the Milky Way using neutrinos — tiny, ghostlike astronomical messengers.
In a June 30 article in the journal Science, the IceCube Collaboration — an international group of more than 350 scientists — presents this new evidence of high-energy neutrino emission from the Milky Way. The findings indicate that the Milky Way produces far fewer neutrinos than the average distant galaxies.
“What’s intriguing is that, unlike the case for light of any wavelength, in neutrinos, the universe outshines the nearby sources in our own galaxy,” says Francis Halzen, a professor of physics at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and principal investigator at IceCube.
The IceCube search focused on the southern sky, where the bulk of neutrino emission from the galactic plane is expected near the center of the galaxy. However, until now, a background of neutrinos and other particles produced by cosmic-ray interactions with the Earth’s atmosphere made it difficult to parse out neutrinos originating from galactic sources — a significant challenge compounded by relatively sparse neutrino production in general.
To overcome these challenges, IceCube collaborators at Drexel University developed analyses that select for detections of astrophysical neutrinos from the southern sky. Machine learning methods developed by IceCube collaborators at TU Dortmund University further improved the identification of astrophysical neutrinos, along with their direction and energy reconstruction. The observation of neutrinos from the Milky Way is a hallmark of the emerging critical value that machine learning provides in data analysis and event reconstruction in IceCube.
The dataset used in the study included 60,000 neutrinos spanning 10 years of IceCube data. These neutrinos were compared to previously published prediction maps of locations in the sky where the galaxy was expected to shine in neutrinos.
The observation of the galactic plane with IceCube has profound implications. An analysis by Halzen and UW–Madison IceCube colleagues Ke Fang and Jay Gallagher indicates that the Milky Way is 10 to 100 times dimmer in neutrinos than the average of distant galaxies. This may be an important clue to solve the ongoing mystery of precisely where and how extremely high-energy cosmic rays are produced.
“One implication is that our galaxy has not hosted the type of sources that produced the bulk of high-energy neutrinos for the past few million years,” says Fang, “which is roughly the time since the last jet activity of the black hole of our own galaxy.”
Planned and future follow-up analyses by IceCube will further understanding of the particle accelerators of the Milky Way galaxy.
“As is so often the case, significant breakthroughs in science are enabled by advances in technology,” says Denise Caldwell, director of NSF’s Physics Division. “The capabilities provided by the highly sensitive IceCube detector, coupled with new data analysis tools, have given us an entirely new view of our galaxy — one that had only been hinted at before. As these capabilities continue to be refined, we can look forward to watching this picture emerge with ever-increasing resolution, potentially revealing hidden features of our galaxy never before seen by humanity."
Read more about this news and the science that produced it. Learn more about these results in person by joining UW–Madison physics professor Justin Vandenbroucke on July 5 at 7 p.m. for Wednesday Nite @ The Lab.
The IceCube Neutrino Observatory is funded and operated primarily through an award from the National Science Foundation to the University of Wisconsin–Madison. The IceCube Collaboration, with over 350 scientists in 58 institutions from around the world, runs an extensive scientific program that has established the foundations of neutrino astronomy. IceCube’s research efforts, including critical contributions to the detector operation, are funded by agencies in Australia, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Germany, Italy, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, the United Kingdom and the United States, including NSF. IceCube construction was also funded with significant contributions from the National Fund for Scientific Research (FNRS & FWO) in Belgium; the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and the German Research Foundation (DFG) in Germany; the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, the Swedish Polar Research Secretariat and the Swedish Research Council in Sweden; and the Wisconsin Alumni Research Fund in the U.S.
###
—Alisa King-Klemperer, amking3@wisc.edu
END
IceCube shows Milky Way galaxy is a neutrino desert
For the first time, the IceCube Neutrino Observatory has produced an image of the Milky Way using neutrinos — tiny, ghostlike astronomical messengers.
2023-06-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
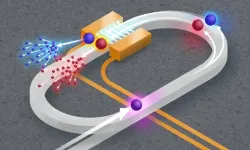
Scientists edge toward scalable quantum simulations on a photonic chip
2023-06-29
Scientists have made an important step toward developing computers advanced enough to simulate complex natural phenomena at the quantum level. While these types of simulations are too cumbersome or outright impossible for classical computers to handle, photonics-based quantum computing systems could provide a solution.
A team of researchers from the University of Rochester’s Hajim School of Engineering & Applied Sciences developed a new chip-scale optical quantum simulation system that ...
Push to green energy is not without consequences, PSU prof explores
2023-06-29
From a proposed lithium mine near the Oregon-Nevada border to a proposed pumped hydropower facility in Washington, the transition from fossil fuels to renewables is not all clean and green. The extraction, manufacturing, storage and recycling of metals and minerals needed for electric cars, wind and solar has impacts on land, water, wildlife and people — and thanks to a new grant, a Portland State professor will take a closer look at those impacts, both good and bad.
Alida Cantor, associate professor of geography, ...
Honey bees more faithful to their flower patches than bumble bees
2023-06-29
Kim Kaplan
301-588-5314
Kim.Kaplan@usda.gov
Honey Bees More Faithful to Their Flower Patches Than Bumble Bees
MADISON, WI, June 29, 2023—Honey bees are more faithful to their flower patches than bumble bees when it comes to returning to collect more pollen and nectar, according to a study by U.S. Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service scientists.
Overall, 76 percent of honey bees in the study revisited the same plot of alfalfa flowers in contrast to just 47 percent of eastern bumble bees.
But size does matter, especially to bumble bees. They were more faithful to larger flower patches, while the likelihood of honey bees returning to a flower patch ...
Where there’s smoke, there’s fire – and normal numbers of national park visitors
2023-06-29
More Americans than ever are heeding the call of the outdoors – spending time recreating outside and enjoying national parks. Simultaneously, smoky skies are worsening as the size and severity of wildfires increase and adversely affect air quality across the country.
Wildfire smoke threatens human health and welfare, especially if humans are exposed to smoke for long periods or while exercising – such as during a hiking trip to one of America’s beloved national parks.
Matthew Clark, a doctoral student at Boise State University studying how social and environmental ...
HIV patients in DC reported intense distress during pandemic
2023-06-29
The COVID-19 pandemic had substantial psychological impacts on the nation and around the world. New research shows patients with HIV were particularly susceptible to psychosocial challenges like depression, anxiety, substance abuse, loneliness and more. The study was co-authored by HIV/AIDS expert Michael Horberg, MD, and published in AIDS Research and Therapy.
Researchers analyzed the results from a 2020 survey of nearly 900 Washington, D.C.-based participants diagnosed with HIV. The survey asked patients to rate the degree to which they experienced challenges with financial stability, mental health, social connections ...
Researchers teach an AI to write better chart captions
2023-06-29
Chart captions that explain complex trends and patterns are important for improving a reader’s ability to comprehend and retain the data being presented. And for people with visual disabilities, the information in a caption often provides their only means of understanding the chart.
But writing effective, detailed captions is a labor-intensive process. While autocaptioning techniques can alleviate this burden, they often struggle to describe cognitive features that provide additional context.
To help people author high-quality chart captions, MIT researchers have developed a dataset to improve automatic ...
What Genetics is Telling Us About Substance Use Disorders - A Free Webinar from the Brain & Behavior Research Foundation
2023-06-29
The Brain & Behavior Research Foundation (BBRF) is hosting a free webinar, “What Genetics is Telling Us About Substance Use Disorders” on Tuesday, July 11, 2023, at 2:00 pm EST. The presenter will be Sandra Sanchez-Roige, Ph.D. Dr. Sanchez-Roige is an Associate Professor at the Department of Psychiatry at the University of California San Diego, and the Department of Medicine, Division of Genetic Medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center. She is also the recipient of a 2018 BBRF Young Investigator Grant. The webinar will be hosted by Jeffrey Borenstein, M.D., President & CEO of the Brain & ...
Tobacco smoke exposure may increase heavy metal levels in children’s saliva
2023-06-29
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Secondhand tobacco smoke continues to be a major source of indoor air pollution that causes more than 41,000 nonsmoking adults to die every year in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The exposure is even more dire for children, who can be more affected by less smoke. It can increase frequency and severity of asthma attacks, respiratory infections, cancer, sudden infant death syndrome and behavioral problems. Now, for the first time, Penn State-led research has shown exposure to tobacco smoke increases the presence of heavy metals in children’s saliva.
The ...
Staging pancreatic cancer early with minimally invasive surgery shows positive results in patient prognosis, Mayo Clinic study finds
2023-06-29
ROCHESTER, Minn. — A study published in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons reveals that performing a minor surgical procedure on patients newly diagnosed with pancreatic cancer helps to identify cancer spread early and determine the stage of cancer. The researchers add that the surgery ideally should be performed before the patient begins chemotherapy.
"This is an important study because it supports that staging laparoscopy may help with determining a patient's prognosis and better inform treatment so that patients ...
Cyanotriazole compounds can rapidly cure trypanosome infections in mice
2023-06-29
Cyanotriazole compounds are fast-acting topoisomerase II poisons that can selectively and rapidly kill trypanosome parasites that cause Chagas disease and African sleeping sickness, according to a new study. Millions who live in Latin America and sub-Saharan Africa are at risk for trypanosomatid infections – pathogenic protozoan parasites that cause Chagas disease and human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), which are potentially fatal if not treated. Although treatments for HAT have improved in recent years, Chagas therapies remain limited and rely on lengthy regimens of toxic drugs. More effective, safer, and shorter-duration ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
[Press-News.org] IceCube shows Milky Way galaxy is a neutrino desertFor the first time, the IceCube Neutrino Observatory has produced an image of the Milky Way using neutrinos — tiny, ghostlike astronomical messengers.