KOSÉ and Niigata University develop a three-dimensional epithelial model that reproduces the human lip area
To be used for evaluating the efficacy and safety of cosmetic ingredients and products
2023-06-30
(Press-News.org)
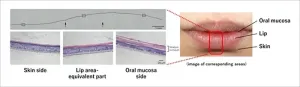
Niigata, Japan - KOSÉ Corporation (Headquarters: Chuo-ku, Tokyo; President: Kazutoshi Kobayashi) has developed in collaborative research with Professor Kenji Izumi and his colleagues at Niigata University Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences (Faculty of Dentistry) a three-dimensional epithelial model that reproduces the human lip area from the oral mucosa to the lips and surrounding skin, using cell culture.
The lips are one of the most important elements that determine the impressions of the face, and they are also an area where many people suffer from problems, such as chapped lips in winter. The lip area is the transition area between the facial skin and the oral mucosa, and has a unique structure and properties that differ from both of them, such as the stratum corneum being thinner and more delicate than in skin. However, until now, there has been no evaluation system using lip area models, and it has been necessary to use skin and oral mucosa in vitro models to evaluate the usefulness and safety of new ingredients. Therefore, the development of lip area models that reproduce its unique structure, and their use for functional analysis of the lip area and evaluation of formulations and ingredients, is a useful tool to promote better formulation development, says Prof. Izumi.
The research group developed a lip area model with the aim of enabling it to be used in cosmetics research. They used only cells derived from the epidermis and oral mucosal epithelium to develop a three-dimensional model with characteristics similar to those of the human lip area.
The immunohistochemical findings demonstrated that the lip area model developed in this research has a similar structure and differentiation mode to that of actual human lip area tissue. Prof. Izumi describes, it is expected to be used for evaluation of the effects of cosmetic ingredients on the lip area and other purposes.
The lip area model developed in this research will be used for basic research on the lips, which has only been possible until now with alternative methods using skin and oral mucosa, and for future development of lip care products and ingredients. Prof. Izumi states with confidence that we will continue our research and development to enable us to provide evidence-based solutions to customers’ lip area problems, such as clarifying the mechanisms of chapped lips and developing useful ingredients.
The results of this research have been published online in the scientific journal Histochemistry and Cell Biology in June 2023.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-30
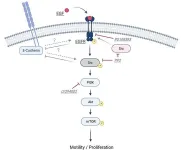
Niigata, Japan—Scientists have made significant progress in understanding the signals involved in regulating oral keratinocyte cell motility and proliferative capacity, offering new insights into potential pharmacological manipulation for regenerative medicine. A recent study, published in FEBS Open Bio, elucidated the role of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) and its downstream signaling cascade in controlling the behavior of oral keratinocytes.
Oral keratinocytes, which play a crucial role in the formation of the oral mucosa epithelial cell sheet, have long been enigmatic in terms of their signaling ...
2023-06-30
Long COVID is not a single condition, and should not be treated as such, according to new data collected in nationwide study released May 31 in the Open Forum of Infectious Diseases.
The study looked at persistent symptoms experienced by patients with COVID-19 both at three- and six-month intervals. In all, 5,963 patients participated in the study, with 4,504 of the participants testing positive for COVID-19 and 1,459 testing negative. Many of the participants, 2,000 in all, came from King County through the University of Washington School of Medicine.
The four major symptom categories for people who tested positive for COVID-19 included:
Minimal ...
2023-06-30
Sophia Antipolis, 30 June 2023: Loneliness is a bigger risk factor for heart disease in patients with diabetes than diet, exercise, smoking and depression, according to research published today in European Heart Journal, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“The quality of social contact appears to be more important for heart health in people with diabetes than the number of engagements,” said study author Professor Lu Qi of Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, New Orleans, US. “We should not downplay the important of loneliness ...
2023-06-30
ST. LOUIS - Research published in Outlook on Agriculture has shown that the population relative to available climate-suitable areas in Kenya has increased, posing a threat to the country’s economy and food security.
The study, “Spatial changes to climate suitability and availability of agropastoral farming systems across Kenya (1980-2020),” was published online on May 29.
The research team analyzed Kenya’s farming systems and climate zones between 1980-2020. Over that time, the population ...
2023-06-30
The current status and future perspectives on the successful industrialization of biobased succinic acid are discussed in a comprehensive review article in the peer-reviewed journal Industrial Biotechnology. Click here to read the article now.
Succinic acid is one of the most important platform chemicals, with applications as a pharmaceutical ingredient, food additive, precursor of various chemicals, and raw material for biobased polymers. There is increasing demand for the sustainable production of succinic acid and its derivatives.
Sang Yup Lee, from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), and coauthors, review ...
2023-06-30
In the first global assessment of TB among incarcerated people, a new study found consistently high TB case rates and low case detection in prisons, suggesting the need for health organizations to increase efforts to reduce the spread of TB among this high-risk population.
In 2019, incarcerated people across the globe developed tuberculosis (TB) at nearly 10 times the rate of people in the general population, according to a new study led by Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH).
Published in The Lancet Public Health, the study found that 125,105 of the 11 million people incarcerated worldwide developed tuberculosis in 2019, ...
2023-06-30
Research from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago promises to spare many premature infants from undergoing invasive eye exams to detect retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), the most common cause of preventable lifelong blindness in children in the U.S.
ROP is caused by an abnormal development of small blood vessels on the retina. Isabelle De Plaen, MD, and colleagues found that imaging the capillaries in the nailbed of preemies within the first month of life using a non-invasive technique, called nailbed capillaroscopy, can identify infants at high risk for developing ROP. This screening could eliminate the need to evaluate all premature infants with eye exams ...
2023-06-30
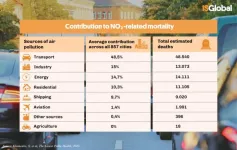
Air pollution is the largest environmental cause of death. Now, a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has estimated which sources contribute most to the mortality associated with two air pollutants - PM2.5 and NO2 - in 857 European cities.
The results of this research, which have been published in The Lancet Public Health, show great variability between the different cities studied, suggesting that, given that each one has its own particularities and its own sources of air pollution, strategies to improve air quality should be adapted to each local context.
Contributors ...
2023-06-30
A newly developed risk calculator that is based on 11 key social, demographic, and clinical factors, can correctly predict suicide risk in those who have self-harmed within the following 6 to 12 months, suggests research published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health.
Pending further validation, OxSATS, short for Oxford Suicide Assessment Tool for Self-harm, may help inform treatment decisions and the most effective targeting of resources, suggest the researchers.
Self-harm is associated with a heightened risk of suicide within the following 12 months that ...
2023-06-30
B-roll video and interview with researcher
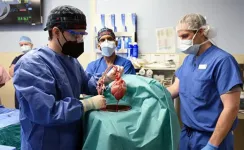
BALTIMORE, June 29, 2023– A new study published today in The Lancet has revealed the most extensive analysis to date on what led to the eventual heart failure in the world's first successful transplant of a genetically-modified pig heart into a human patient. This groundbreaking procedure was conducted by University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) physician-scientists back in January 2022 and marked an important milestone for medical science.
The patient, 57-year-old David Bennett, Sr., was treated at the University of Maryland ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] KOSÉ and Niigata University develop a three-dimensional epithelial model that reproduces the human lip area
To be used for evaluating the efficacy and safety of cosmetic ingredients and products