(Press-News.org) UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 16:00 LONDON TIME (BST) / 11:00 (US ET) ON TUESDAY 4TH JULY 2023
Analysis of global tracking data for 77 species of petrel has revealed that a quarter of all plastics potentially encountered in their search for food are in remote international waters – requiring international collaboration to address.
The extensive study assessed the movements of 7,137 individual birds from 77 species of petrel, a group of wide-ranging migratory seabirds including the Northern Fulmar and European Storm-petrel, and the Critically Endangered Newell’s Shearwater.
This is the first time that tracking data for so many seabird species has been combined and overlaid onto global maps of plastic distribution in the oceans.
The results show that plastic pollution threatens marine life on a scale that transcends national boundaries: a quarter of all plastic exposure risk occurs in the high seas. This is largely linked to gyres - large systems of rotating ocean currents - where vast accumulations of plastics form, fed by waste entering the sea from boats, and from many different countries.
Seabirds often mistake small plastic fragments for food, or ingest plastic that has already been eaten by their prey. This can lead to injury, poisoning and starvation, and petrels are particularly vulnerable because they can’t easily regurgitate the plastic. In the breeding season they often inadvertently feed plastic to their chicks.
Plastics can also contain toxic chemicals that can be harmful to seabirds.
Petrels are an understudied but vulnerable group of marine species, which play a key role in oceanic food webs. The breadth of their distribution across the whole ocean makes them important ‘sentinel species’ when assessing the risks of plastic pollution in the marine environment.
“Ocean currents cause big swirling collections of plastic rubbish to accumulate far from land, way out of sight and beyond the jurisdiction of any one country. We found that many species of petrel spend considerable amounts of time feeding around these mid-ocean gyres, which puts them at high risk of ingesting plastic debris,” said Lizzie Pearmain, a PhD student at the University of Cambridge’s Department of Zoology and the British Antarctic Survey, and joint corresponding author of the study.
She added: “When petrels eat plastic, it can get stuck in their stomachs and be fed to their chicks. This leaves less space for food, and can cause internal injuries or release toxins.”
Petrels and other species are already threatened with extinction due to climate change, bycatch, competition with fisheries, and invasive species such as mice and rats on their breeding colonies. The researchers say exposure to plastics may reduce the birds’ resilience to these other threats.
The north-east Pacific, South Atlantic, and the south-west Indian oceans have mid-ocean gyres full of plastic waste, where many species of threatened seabird forage.
“Even species with low exposure risk have been found to eat plastic. This shows that plastic levels in the ocean are a problem for seabirds worldwide, even outside of these high exposure areas,” said Dr Bethany Clark, Seabird Science Officer at BirdLife International and joint corresponding author of the study.
She added: “Many petrel species risk exposure to plastic in the waters of several countries and the high seas during their migrations. Due to ocean currents, this plastic debris often ends up far away from its original source. This highlights the need for international cooperation to tackle plastic pollution in the world’s oceans.”
The study also found that the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea together account for over half of petrels’ global plastic exposure risk. However, only four species of petrel forage in these enclosed, busy areas.
The study was led by a partnership between the University of Cambridge, BirdLife International and the British Antarctic Survey, in collaboration with Fauna & Flora International, the 5 Gyres Institute, and over 200 seabird researchers in 27 countries.
It is published today in the journal Nature Communications.
To get their results, the researchers overlaid global location data, taken from tracking devices attached to the birds, onto pre-existing maps of marine plastic distribution. This allowed them to identify the areas on the birds’ migration and foraging journeys where they are most likely to encounter plastics.
Species were given an ‘exposure risk score’ to indicate their risk of encountering plastic during their time at sea. A number of already threatened species scored highly, including the Critically Endangered Balearic Shearwater, which breeds in the Mediterranean, and Newell’s Shearwater, endemic to Hawaii.
Another Endangered species, the Hawaiian Petrel also scored high for plastic exposure risk, as did three species classified by the IUCN as Vulnerable: the Yelkouan Shearwater, which breeds in the Mediterranean; Cook’s Petrel, which breeds in New Zealand, and the Spectacled Petrel, which only breeds on an extinct volcano called Inaccessible Island, part of the Tristan da Cunha archipelago, a UK Overseas Territory.
“While the population-level effects of plastic exposure are not yet known for most species, many petrels and other marine species are already in a precarious situation. Continued exposure to potentially dangerous plastics adds to the pressures,” said Professor Andrea Manica at the University of Cambridge’s Department of Zoology, a co-author of the study.
He added: “This study is a big leap forward in understanding the situation, and our results will feed into conservation work to try and address the threats to birds at sea.”
This research was funded by the Cambridge Conservation Initiative’s Collaborative Fund for Conservation, sponsored by the Prince Albert II of Monaco Foundation, and the Natural Environment Research Council.
Reference
Clark, B.L. et al.: ‘Global assessment of marine plastic exposure risk for oceanic birds.’ Nature Communications, July 2023. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-38900-z
Media contacts
Jacqueline Garget, Office of External Affairs and Communications, University of Cambridge researchcommunications@admin.cam.ac.uk
Lizzie Pearmain, Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge, and British Antarctic Survey ejp69@cam.ac.uk
Bethany Clark, BirdLife International Bethany.Clark@birdlife.org
About the University of Cambridge www.cam.ac.uk
The University of Cambridge is one of the world’s top ten leading universities, with a rich history of radical thinking dating back to 1209. Its mission is to contribute to society through the pursuit of education, learning and research at the highest international levels of excellence.
The University comprises 31 autonomous Colleges and 150 departments, faculties and institutions. Its 24,450 student body includes more than 9,000 international students from 147 countries. In 2020, 70.6% of its new undergraduate students were from state schools and 21.6% from economically disadvantaged areas.
Cambridge research spans almost every discipline, from science, technology, engineering and medicine through to the arts, humanities and social sciences, with multi-disciplinary teams working to address major global challenges. Its researchers provide academic leadership, develop strategic partnerships and collaborate with colleagues worldwide.
The University sits at the heart of the ‘Cambridge cluster’, in which more than 5,300 knowledge-intensive firms employ more than 67,000 people and generate £18 billion in turnover. Cambridge has the highest number of patent applications per 100,000 residents in the UK.
About BirdLife International www.birdlife.org
BirdLife International is the world’s largest nature conservation partnership. Together we are over 115 BirdLife Partners worldwide and growing. All of BirdLife’s work is underpinned by scientific research. Our science is used to set priorities, inform action on the ground, and shape policy and advocacy. Through our unique local-to-global approach, we deliver high-impact and long-term conservation for the benefit of nature and people.
END
World’s most threatened seabirds visit remote plastic pollution hotspots, study finds
2023-07-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sea of plastic: Mediterranean is the area of the world most at risk for endangered seabirds
2023-07-04
New study reveals the areas most at risk of plastic exposure by the already endangered seabirds.
The study, now published in Nature Communications, brings together more than 200 researchers worldwide around a pressing challenge, widely recognized as a growing threat to marine life: the pollution of oceans by plastic. Coordinated by Dr. Maria Dias, researcher at the Centre for Ecology, Evolution and Environmental Changes (cE3c) at the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon (Ciências ULisboa), ...
Omega-3 oil counteracts toxic effects of pesticides in pollinators
2023-07-04
New research suggests that the use of an omega-3 rich oil called “ahiflower oil” can prevent damage to honey bee mitochondria caused by neonicotinoid pesticides. This research is part of an ongoing project by PhD student Hichem Menail of the Université de Moncton in New Brunswick, Canada.
“Pesticides are a major threat to insect populations and as insects are at the core of ecosystem richness and balance, any loss in insect biodiversity can lead to catastrophic outcome,” says Mr Menail, adding that pesticide-related pollinator declines are also a huge concern for food crops globally.
Imidacloprid, ...
Global efforts to reduce infectious diseases must extend beyond early childhood
2023-07-04
Global efforts to reduce infectious disease rates must have a greater focus on older children and adolescents after a shift in disease burden onto this demographic, according to a new study.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute and the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, has found that infectious disease control has largely focused on children aged under five, with scarce attention on young people between five and 24 years old.
Published in The Lancet, the study found three million children and adolescents die from infectious diseases every year, equivalent to one death every 10 seconds. It looked at data across 204 countries ...
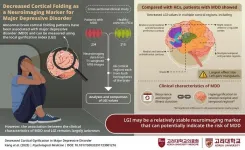
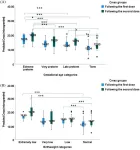
Korea University Medicine study highlights a new biomarker for major depressive disorder
2023-07-04
In appearance, the human brain’s outermost layer, called the cortex, is a maze of tissue folds. The peaks or raised surfaces of these folds, called gyri, play an important role in the proper functioning of the brain. Improper gyrification—or the development of gyri—has been implicated in various neurological disorders, one of them being the debilitating and widespread mental illness, major depressive disorder (MDD). Although prior studies have shown that abnormal cortical folding patterns are associated with MDD, ...
Luísa Figueiredo was elected as an EMBO member
2023-07-04
The European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO) has announced today that it will award the lifetime honor of EMBO Membership to Luísa Figueiredo, group leader at the Instituto de Medicina Molecular João Lobo Antunes (iMM, Lisbon, Portugal), in recognition of the excellence of her research and outstanding achievements in the life sciences. EMBO is an international organization of more than 2000 life scientists in Europe and around the world, committed to build a European research environment where scientists can achieve their best work. Aside from Luísa Figueiredo, 68 other EMBO Members have been elected this year.
Luísa ...
Fat-free mass-based dosing: A superior antibiotic regimen for newborns
2023-07-04
Gentamicin is a common antibiotic used to treat critically ill neonates. It is water soluble and is primarily eliminated from the body through urine. For this reason, total body weight, which factors in the weight of the body’s water content, is used to determine gentamicin dosage. However, the total water content of a healthy neonate differs significantly from that of a premature baby. As such, using total body weight to calculate gentamicin dose may lead to non-optimal dose prescription. Premature babies also have weaker kidneys, which means that discrepancy in ...
How mercury emissions from industry can be greatly reduced
2023-07-04
Sulphuric acid is the world’s most used chemical. It is an important reagent used in many industries and it is used in the manufacture of everything from paper, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics to batteries, detergents and fertilisers. It is therefore a worldwide challenge that sulphuric acid often contains one of the most toxic substances – mercury. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have now developed a method that can reduce the levels of mercury in sulphuric acid by more than 90 per cent – even from low levels.
“Until now, there has been no viable method for purifying finished sulphuric ...
Long COVID not caused by COVID-19 immune inflammatory response, new research finds
2023-07-04
Long Covid, which affects nearly two-million people in the UK1, is not caused by an immune inflammatory reaction to COVID-19, University of Bristol-led research finds. Emerging data demonstrates that immune activation may persist for months after COVID-19.
In this new study, published in eLife today [4 July], researchers wanted to find out whether persistent immune activation and ongoing inflammation response could be the underlying cause of long Covid.
To investigate this, the Bristol team collected and analysed immune responses in blood samples from 63 patients hospitalised ...
How the ear can inform the brain of whether hearing is impaired
2023-07-04
A cochlear signal, the exact role of which has been unclear since its discovery around 70 years ago, probably gives the brain information on whether the ear is functioning normally or not. This is the conclusion of a study from Linköping University, Sweden. Its findings are an important piece of the puzzle in explaining what happens in the ear in hearing impairment caused by harmful noise, and may in the long run contribute to diagnosing noise-induced hearing injury.
When the ear is exposed to loud sounds, as at a concert or when being in a noisy environment, hearing can be temporarily impaired. Being repeatedly exposed to loud sounds may cause permanent ...
Nanosheet technology developed to boost energy storage dielectric capacitors
2023-07-04
A research group led by Professor Minoru Osada at the Institute for Materials and Systems for Sustainability (IMaSS), Nagoya University in Japan, in collaboration with NIMS, has developed a nanosheet device with the highest energy storage performance yet seen. Their results were published in Nano Letters.
Innovations in energy storage technology are vital for the effective use of renewable energy and the mass production of electric vehicles. Current energy storage technology, such as lithium-ion batteries, has long charging times ...