(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO — July 5, 2023 —The Southwest Research Institute-led Ultraviolet Spectrograph (UVS) aboard ESA’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) spacecraft has successfully completed its initial commissioning following the April 14 launch. The UVS instrument is one of three instrument projects comprising NASA’s contribution to the JUICE mission. The mission’s science goals focus on Jupiter and its system, making multiple flybys of the planet’s large, ocean-bearing satellites with a particular emphasis on investigating Ganymede as a potentially habitable planetary body.
UVS is one of 10 science instruments and 11 investigations for the JUICE spacecraft. The mission has overarching goals of investigating potentially habitable worlds around the gas giant and studying the Jupiter system as an archetype for gas giants in our solar system and beyond. As it begins a roundabout 4.1-billion-mile (6.6-billion-kilometer), eight-year journey to the Jupiter system, the spacecraft has been busy deploying and activating its antennas, booms, sensors and instruments to check out and commission all its important subsystems. SwRI’s UVS instrument is the latest to succeed in this task.
“Our team of SwRI scientists traveled to Darmstadt, Germany, to put JUICE-UVS through its paces,” said Dr. Randy Gladstone, JUICE-UVS principal investigator. “On June 20, we opened the UVS aperture door to collect UV light from space for the first time. Soon after, we observed a swath of the sky to verify the instrument was performing well.” The team imaged a segment of this data, as the instrument scanned a swath of the Milky Way.
SwRI has provided ultraviolet spectrographs for other spacecraft, including ESA’s Rosetta comet orbiter, as well as NASA’s New Horizons mission to Pluto, Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter mission in orbit around the Moon and Juno mission to Jupiter.
“JUICE-UVS is the fifth in this series, and it benefits greatly from the design experience gained by our team from the Juno-UVS instrument, launched in 2011, as it pertains to operating in Jupiter’s harsh radiation environment," said Steven Persyn, program manager for UVS. “Each successive instrument we build is more capable than its predecessor.”
Weighing just over 40 pounds and drawing only 7.5 watts of power, UVS is smaller than a microwave oven, yet this powerful instrument will determine the relative concentrations of various elements and molecules in the atmospheres of Jupiter’s moons once in the Jovian system. A similar instrument, Europa-UVS, will launch in 2024 aboard NASA’s Europa Clipper, which will take a more direct route to arrive at the Jupiter system 15 months before JUICE and focus on studying the potential habitability of Europa.
“Having two UVS instruments making measurements in the Jupiter system at roughly the same time will offer exciting complementary science possibilities,” said Dr. Kurt Retherford, principal investigator of Europa-UVS and deputy PI for JUICE-UVS.
Aboard JUICE, UVS will get close-up views of the Galilean moons Europa, Ganymede and Callisto, all thought to host liquid water beneath their icy surfaces. UVS will record ultraviolet light emitted, transmitted and reflected by these bodies, revealing the composition of their surfaces and tenuous atmospheres and how they interact with Jupiter and its giant magnetosphere. Additional scientific goals include observations of Jupiter itself as well as the gases from its volcanic moon Io that spread throughout the Jovian magnetosphere.
JUICE is the first large-class mission in ESA’s Cosmic Vision 2015–2025 program. The spacecraft and science instruments were built by teams from 15 European countries, Japan and the United States. SwRI’s UVS instrument team includes additional scientists from the University of Colorado Boulder, the SETI institute, the University of Leicester (U.K.), Imperial College London (U.K.), the University of Liège (Belgium), the Royal Institute of Technology (Sweden) and the Laboratoire Atmosphères, Milieux, Observations Spatiales (France). The Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center oversees the UVS contribution to ESA through the agency’s Solar System Exploration Program. The JUICE spacecraft was developed by Airbus Defence and Space.
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/planetary-science.
END
First ultraviolet data collected by ESA’s JUICE mission
SwRI-led UVS instrument demonstrated en route to Jupiter system
2023-07-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Investigational three-month TB regimen is safe but ineffective, NIH study finds
2023-07-05
The first clinical trial of a three-month tuberculosis (TB) treatment regimen is closing enrollment because of a high rate of unfavorable outcomes with the investigational course of treatment. AIDS Clinical Trials Group 5362, also known as the CLO-FAST trial, sought to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a three-month clofazimine- and high-dose rifapentine-containing regimen. An interim data analysis showed that participants taking the investigational regimen experienced ongoing or recurring TB at rates above thresholds set in the study protocol. Based on these findings, ...
Public support for militarily defending NATO allies
2023-07-05
Voters in North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) member states are far more willing to militarily defend another country if the country joins NATO, versus if the same country does not join NATO, according to a study. To explore the possible consequences of expanding NATO membership, Michael Tomz and colleagues surveyed 14,000 voters in 13 NATO countries. Each survey participant was presented with a hypothetical Russian attack on one of four possible targets: Bosnia, Finland, Georgia, or Sweden—the four countries (other than Ukraine) furthest along in their bids for NATO accession at the time of ...
Mount Sinai launches Center for Ophthalmic Artificial Intelligence and Human Health
2023-07-05
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has launched the Center for Ophthalmic Artificial Intelligence and Human Health, the first of its kind in New York and one of the first in the United States. The Center is dedicated to advancing artificial intelligence (AI) in the field of ophthalmology, further positioning the Mount Sinai Health System as a leader in providing patient care through pioneering innovations and technologies.
In partnership with the Windreich Department of Artificial Intelligence and Human Health at Icahn Mount Sinai, the Center aims to ...
Sunscreen leaching poses minimal threat to aquatic wildlife
2023-07-05
New research reveals that sunscreen contamination may be less harmful to wildlife than previously thought. This study by Aaron Boyd, a PhD candidate at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Canada, demonstrates how exposure to sunscreen is actually a low risk for small aquatic animals compared to some of the suncream’s individual chemicals.
Sunscreens contain ultraviolet filters (UVFs) which have been found to be toxic to marine life such as corals, leading to the ban of some UVFs in Hawaii and Palau. If sunscreen is applied to the skin before swimming in lakes and rivers, these UVFs and other chemicals will leach into surrounding waters.
Mr ...
Exterminating greenhouse pests with bat-inspired drones
2023-07-05
Researchers have been testing real-life Batman-style gadgets to eradicate moth pests from greenhouses, including bat-inspired flying drones that hunt down and destroy moths – but new research reveals that the noise from drones can alter moth flight behaviour.
“The idea of using drones as an alternative solution to eliminating moths all started in the bedroom of one of the co-owners of the PATS startup company,” says Dayo Jansen, a PhD student from student from Wageningen University and Research in the Netherlands. ...
New telehealth certification available to health care professionals
2023-07-05
Embargoed until 8 a.m. ET/ 7 a.m. CT on Wednesday, July 5, 2023
DALLAS, July 5, 2023 — The COVID-19 pandemic radically changed the way health care professionals serve their patients. Over the past three years, a huge proportion of care has shifted to the virtual landscape as clinicians and patients search for a safe, reliable way to receive needed care.[1]
As part of its longstanding commitment to ensuring equitable access to high-quality health care, the American Heart Association has launched its first individual ...
An easier way to learn quantum processes
2023-07-05
Imagine a world where computers can unravel the mysteries of quantum mechanics, enabling us to study the behavior of complex materials or simulate the intricate dynamics of molecules with unprecedented accuracy.
Thanks to a pioneering study led by Professor Zoe Holmes and her team at EPFL, we are now closer to that becoming a reality. Working with researchers at Caltech, the Free University of Berlin, and the Los Alamos National Laboratory, they have found a new way to teach a quantum computer how to understand and predict the behavior of quantum systems, even with a few simple examples.
Quantum neural networks (QNNs)
The researchers worked on “quantum neural networks” ...
Fast, automated, affordable test for cement durability developed at U of I
2023-07-05
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Engineers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a new test that can predict the durability of cement in seconds to minutes – rather than the hours it takes using current methods. The test measures the behavior of water droplets on cement surfaces using computer vision on a device that costs less than $200. The researchers said the new study could help the cement industry move toward rapid and automated quality control of their materials.
The results of the study, led by Illinois civil and environmental engineering professor Nishant ...
Study finds younger kidney cancer survivors at significant risk for heart problems
2023-07-05
New research out of VCU Massey Cancer Center indicates that many adolescent and young adult kidney cancer survivors are at a significantly elevated risk for heart issues.
Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of health complications and death among adolescents and young adults (AYAs) diagnosed with cancer, where AYAs are characterized as patients between the ages of 15 and 39.
A study publishing July 5 in the Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network assessed the incidence and risk of hypertension — high blood pressure — and heart failure among AYA patients diagnosed ...
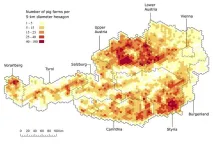
Researchers map Austria's pig trade network for the first time
2023-07-05
The transfer of pigs from one place to another poses the risk of spreading infectious diseases. Knowing how holdings (e.g., farms, markets, etc.) are connected is therefore of crucial importance. In a study by the Complexity Science Hub, the University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna, and the Austrian Agency for Health and Food Safety (AGES), researchers are now drawing a map of the Austrian pig trade for the first time.
Every year, around 250,000 transfers of pigs take place in Austria. Each of these transfers carries a certain risk of spreading swine infectious diseases. To identify possible risks of disease spread and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] First ultraviolet data collected by ESA’s JUICE missionSwRI-led UVS instrument demonstrated en route to Jupiter system