(Press-News.org) “Listen, if there's one thing the history of evolution has taught us is that life will not be contained. Life breaks free. It expands to new territories, and it crashes through barriers painfully, maybe even dangerously, but . . . life finds a way,” said Ian Malcolm, Jeff Goldblum's character in Jurassic Park, the 1993 science fiction film about a park with living dinosaurs.
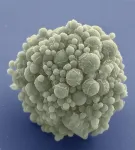
You won't find any Velociraptors lurking around evolutionary biologist Jay T. Lennon's lab; however, Lennon, a professor in the College of Arts and Sciences Department of Biology at Indiana University Bloomington, and his colleagues have found that life does indeed find a way. Lennon's research team has been studying a synthetically constructed minimal cell that has been stripped of all but its essential genes. The team found that the streamlined cell can evolve just as fast as a normal cell—demonstrating the capacity for organisms to adapt, even with an unnatural genome that would seemingly provide little flexibility.
“It appears there’s something about life that’s really robust,” says Lennon. “We can simplify it down to just the bare essentials, but that doesn’t stop evolution from going to work.”
For their study, Lennon's team used the synthetic organism, Mycoplasma mycoides JCVI-syn3B—a minimized version of the bacterium M. mycoides commonly found in the guts of goats and similar animals. Over millennia, the parasitic bacterium has naturally lost many of its genes as it evolved to depend on its host for nutrition. Researchers at the J. Craig Venter Institute in California took this one step further. In 2016, they eliminated 45 percent of the 901 genes from the natural M. mycoides genome—reducing it to the smallest set of genes required for autonomous cellular life. At 493 genes, the minimal genome of M. mycoides JCVI-syn3B is the smallest of any known free-living organism. In comparison, many animal and plant genomes contain more than 20,000 genes.
In principle, the simplest organism would have no functional redundancies and possess only the minimum number of genes essential for life. Any mutation in such an organism could lethally disrupt one or more cellular functions, placing constraints on evolution. Organisms with streamlined genomes have fewer targets upon which positive selection can act, thus limiting opportunities for adaptation.
Although M. mycoides JCVI-syn3B could grow and divide in laboratory conditions, Lennon and colleagues wanted to know how a minimal cell would respond to the forces of evolution over time, particularly given the limited raw materials upon which natural selection could operate as well as the uncharacterized input of new mutations.
“Every single gene in its genome is essential,” says Lennon in reference to M. mycoides JCVI-syn3B. “One could hypothesize that there is no wiggle room for mutations, which could constrain its potential to evolve.”
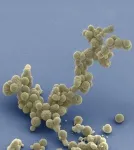
The researchers established that M. mycoides JCVI-syn3B, in fact, has an exceptionally high mutation rate. They then grew it in the lab where it was allowed to evolve freely for 300 days, equivalent to 2000 bacterial generations or about 40,000 years of human evolution.
The next step was to set up experiments to determine how the minimal cells that had evolved for 300 days performed in comparison to the original, non-minimal M. mycoides as well as to a strain of minimal cells that hadn't evolved for 300 days. In the comparison tests, the researchers put equal amounts of the strains being assessed together in a test tube. The strain better suited to its environment became the more common strain.
They found that the non-minimal version of the bacterium easily outcompeted the unevolved minimal version. The minimal bacterium that had evolved for 300 days, however, did much better, effectively recovering all of the fitness that it had lost due to genome streamlining. The researchers identified the genes that changed the most during evolution. Some of these genes were involved in constructing the surface of the cell, while the functions of several others remain unknown.
Details about the study can be found in a paper recently featured in Nature [link to paper]. Roy Z. Moger-Reischer, a Ph.D. student in the Lennon lab at the time of the study, is first author on the paper.
Understanding how organisms with simplified genomes overcome evolutionary challenges has important implications for long-standing problems in biology—including the treatment of clinical pathogens, the persistence of host-associated endosymbionts, the refinement of engineered microorganisms, and the origin of life itself. The research done by Lennon and his team demonstrates the power of natural selection to rapidly optimize fitness in the simplest autonomous organism, with implications for the evolution of cellular complexity. In other words, it shows that life finds a way.
END
Artificial cells demonstrate that "life finds a way"
2023-07-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers find eruption date of Laacher See volcano is wrong by 130 years
2023-07-05
-With pictures-
In a new study, a group of scientists argue that the new high precision radiocarbon-based date set for Laacher See volcano eruption of 13,000 years before present is probably not correct.
They argue that the correct age of the Laacher See volcano eruption is 12,880 years ago, 130 years after the date presented by Reinig et al., in 2021.
The research team, which included scientists from Durham University, University of Oxford, Royal Holloway University of London, SYSTEMIQ Ltd. and Teesside University ...
Vaccine delivers a boost to T cell therapy
2023-07-05
CAMBRIDGE, MA — Engineering T cells to destroy cancer cells has shown success in treating some types of cancer, such as leukemia and lymphoma. However, it hasn’t worked as well for solid tumors.
One reason for this lack of success is that the T cells target only one antigen (a target protein found on the tumors); if some of the tumor cells don’t express that antigen, they can escape the T cell attack.
MIT researchers have now found a way to overcome that obstacle, using a vaccine that boosts the response of ...
Internet searches for self-managed abortion after Roe v Wade overturned
2023-07-05
About The Study: This study used Google Trends data to estimate public interest in self-managed abortions and whether this interest differs depending on the legality of abortion in a state.
Authors: Sean D. Young, Ph.D., of the University of California, Irvine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2023.2410)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and ...
Cannabis use disorder and perioperative complications
2023-07-05
About The Study: Cannabis use disorder was associated with a modest increased risk of perioperative morbidity and mortality after major elective, inpatient, noncardiac surgery. In the context of increasing cannabis use rates, these findings support preoperative screening for cannabis use disorder as a component of perioperative risk stratification. However, further research is needed to quantify the perioperative impact of cannabis use by route and dosage and to inform recommendations for preoperative cannabis cessation.
Authors: Paul P. ...
Perspectives about racism and patient-clinician communication among Black adults with serious illness
2023-07-05
About The Study: This study found that Black patients’ experiences with racism, specifically epistemic injustice, were associated with their perspectives on medical care and decision making during serious illness and end of life. These findings suggest that race-conscious, intersectional approaches may be needed to improve patient-clinician communication and support Black patients with serious illness to alleviate the distress and trauma of racism as these patients near the end of life.
Authors: Crystal ...
Association of population well-being with cardiovascular outcomes
2023-07-05
About The Study: Assessing the association of well-being and cardiovascular outcomes, higher well-being, a measurable, modifiable, and meaningful outcome, was associated with lower cardiovascular disease mortality, even after controlling for structural and cardiovascular-related population health factors, indicating that well-being may be a focus for advancing cardiovascular health.
Authors: Erica S. Spatz, M.D., M.H.S., of the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.21740)
Editor’s ...
From atoms to materials: Algorithmic breakthrough unlocks path to sustainable technologies
2023-07-05
New research by the University of Liverpool could signal a step change in the quest to design the new materials that are needed to meet the challenge of net zero and a sustainable future.
Publishing in the journal Nature, the Liverpool researchers have shown that a mathematical algorithm can guarantee to predict the structure of any material just based on knowledge of the atoms that make it up.
Developed by an interdisciplinary team of researchers from the University of Liverpool’s Departments of Chemistry and Computer Science, the algorithm systematically evaluates entire sets of possible structures at once, rather than considering them one at a time, to accelerate identification ...
An international team identifies the mutations that cause the most frequent congenital heart defects
2023-07-05
Bicuspid aortic valve is the most common congenital defect in humans, affecting between 1% and 2% of the population. Instead of the usual three symmetric leaflets, affected individuals have two asymmetric valve leaflets. This defect is a frequent cause of aortic stenosis and endocarditis and is associated with early calcification of the aortic valve. Currently the only effective treatment is valve replacement surgery.
But this situation could be changed by the results of a new study published by an international team co-led by CNIC group leader Dr. José ...
Utah seismologist peer into Earth's inner core
2023-07-05
Media contacts:
--Keith Koper, professor, Department of Geology and Geophysics, University of Utah, keith.koper@utah.edu 801-585-3669
--Brian Maffly, research communications, University of Utah, brian.maffly@utah.edu 801-573-2382
--Syl Kacapyr, Cornell Engineering, Associate Director, Marketing and Communications
vpk6@cornell.edu 607.339.6450
At the center the Earth is a solid metal ball, a kind of “planet within a planet,” whose existence makes life on the surface possible, at least as we know it.
How Earth’s inner core formed, grew and evolved over ...
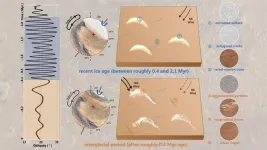
Martian dunes eroded by a shift in prevailing winds after the planet's last ice age
2023-07-05
Detailed analysis of data obtained by the Zhurong rover of dunes located on the southern Utopian Plain of Mars suggests the planet underwent a major shift in climate that accompanied changes in prevailing winds. This shift likely occurred about 400,000 years ago, which coincides with the end of the last glacial period on Mars.
Researchers from the National Astronomical Observatories, Institute of Geology and Geophysics and Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with colleagues from Brown University, assessed the surface structure and chemical composition of Martian dunes to ...