A novel peptide ‘T14’ reflects age and photo-aging in human skin
2023-07-05
(Press-News.org)
“[...] the results suggest a possible novel approach [for] exploring skin disorders [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 5, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 12, entitled, “A novel peptide ‘T14’ reflects age and photo-aging in human skin.”
T14 is a 14mer peptide derived from the C-terminus of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Once cleaved, it is independently bioactive of the parent molecule and enhances calcium influx in different cell types, in a range of scenarios: it binds to an allosteric site selectively on the alpha-7 receptor, where it modulates calcium influx and is thus a potential trophic agent, as already reported in a range of normal developmental scenarios. However, if inappropriately activated, this erstwhile beneficial effect converts to a toxic one, resulting in pathologies as disparate as Alzheimer’s and various metastatic cancers.
In this new study, given that epidermal keratinocyte cells have the same ectodermal origin as brain cells, as well as expressing AChE and the alpha-7 receptor, researchers Sheila Rocha, Sara Garcia Ratés, Tumisang Moswete, Kristopher Kalleberg, Anna Villa, Jason P. Harcup, and Susan A. Greenfield from Unilever Research and Development and Neuro-Bio explored whether T14 plays a comparable role.
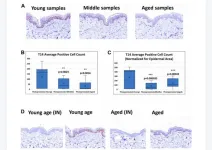
“The first aim of this study was therefore to see if T14-ir could be detected in keratinocytes using an antibody that would not recognize the parent AChE itself, and thus be readily differentiated from it. [...] Hence the second aim of the study was to investigate the possibility that T14 was not only present in keratinocytes but could be regarded as an index reflecting not just age but also photo-induced aging.”
The team reports that the T14 immunoreactivity is detectable in human keratinocytes with levels inversely related to age: this decrease is even more apparent with chronic photo-exposure and thus accelerated skin aging. They concluded that T14, an agent promoting cell growth and renewal in other parts of the body, also operates in skin. Moreover, monitoring of keratinocyte T14 levels might offer further insights into the now well reported link between degenerative diseases and epidermal cell profile.
“Hence further exploration of the T14 system in the epidermis might prompt new insights into the treatment of hyperproliferative skin disorders, as well as into the mechanisms of normal skin age and ageing.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204844
Corresponding Author: Sara Garcia Ratés
Corresponding Email: sara.garciarates@neuro-bio.com
Keywords: skin, age, photo-aging, acetylcholinesterase peptide, keratinocyte
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.204844
About Aging-US:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
SoundCloud
Facebook
Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LabTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-05
There has been much buzz about the warming planet’s melting Arctic region opening shipping routes and lengthening travel seasons in ocean passageways that ice once blocked. Expanded fishing, trade and tourism is envisioned.
Operative word: Envisioned.
Scientists at Michigan State University (MSU), University of Waterloo, and University of Alaska Fairbanks report in Climatic Change where vessels are traveling in the ice-covered waters of the Arctic between Alaska and Russia, and what those reports may mean for important wildlife and communities in the region.
“Even with climate change, sea ice is still a substantial barrier to Arctic vessel traffic,” said Kelly Kapsar, ...
2023-07-05
AUSTIN, Texas — As public concerns mount over lack of transparency in political giving, a new study from researchers at The University of Texas at Austin is the first to illuminate how and why corporations choose to legally conceal their lobbying and campaign contributions.
U.S. companies are required to disclose the total amount they spend on political activity, but beyond that, the disclosure is incredibly vague, according to Tim Werner, associate professor of business, government and society at the McCombs ...
2023-07-05
WASHINGTON (July 5, 2023)--Although the situation is improving, Latinos and especially Mexican Americans, remain very underrepresented in U.S. health professions that require advanced degrees, according to a study published today in the journal Health Affairs. The study by George Washington University researchers is the first to examine the representation of the four largest Latino populations in the U.S. health workforce and the findings raise concerns about the lack of diversity in the U.S. health workforce.
The study ...
2023-07-05
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JULY 5, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – Older people who have fluctuating levels of cholesterol and triglycerides may have a higher risk of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias compared to people who have steady levels, according to new research published in the July 5, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. While the study found a link, it does not prove that fluctuating levels of cholesterol and triglycerides cause dementia.
“Prevention strategies for Alzheimer’s and related dementias are urgently needed,” ...
2023-07-05
Amid heightened demand for mental health care, a new study finds that nearly two-thirds of Medicare Advantage psychiatrist networks contain less than 25% of all psychiatrists in a given service area.
“This means that many people who have coverage through Medicare Advantage plans may not actually have access to psychiatrists, given how few are considered in-network,” said lead author Jane Zhu, M.D., assistant professor of medicine (general internal medicine and geriatrics) in the School of Medicine at Oregon Health & Science University.
The research published today in the July issue of the journal Health Affairs.
Medicare is the federal ...
2023-07-05
ATLANTA, July 5, 2023 – More people with advanced cancers in the United States received critical palliative care services, according to new findings by researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS). Palliative care includes supportive care managed by a healthcare team, such as relief from symptoms, pain, and stress. Researchers also found where a patient lives in the U.S. may determine their use of palliative care. Medicaid expansion under the ACA was associated with the largest increases in palliative care use. The study was published today in the July issue of the journal Health Affairs.
“Our findings are encouraging, especially with growing evidence of the important ...
2023-07-05
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JULY 5, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – Taking good care of your teeth may be linked to better brain health, according to a study published in the July 5, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study found that gum disease and tooth loss were linked to brain shrinkage in the hippocampus, which plays a role in memory and Alzheimer’s disease. The study does not prove that gum disease or tooth loss causes Alzheimer’s disease; it only shows an association.
“Tooth ...
2023-07-05
July 5, 2023-- Health departments have a historic opportunity to bolster their workforce due to new funding but often do not have accurate or updated job descriptions or short, attention-grabbing job postings to use as marketing tools for recruitment. New research by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health will help lead to evidence-based job descriptions and postings that health departments can now use.
The study is the first attempt to compile existing occupation-specific job task analyses, lists of competencies, and certifications across multiple job types within governmental public health that can allow comparisons of ...
2023-07-05
AMHERST, Mass. – Computer scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently found that data-visualization experts have no agreed-upon understanding of who makes up one of their largest audiences—novice users. The work, which recently won a coveted Best Paper Award at the Association for Computing Machinery’s conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (ACM CHI), is an important first step in ensuring more inclusive data visualizations, and thus data visualization that works for all users.
Data visualization is the representation of data in a ...
2023-07-05
Malaria remains one of the world’s deadliest diseases. Each year malaria infections result in hundreds of thousands of deaths, with the majority of fatalities occurring in children under five. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently announced that five cases of mosquito-borne malaria were detected in the United States, the first reported spread in the country in two decades.
Fortunately, scientists are developing safe technologies to stop the transmission of malaria by genetically editing mosquitoes that spread the parasite that causes the disease. Researchers at the University of California San Diego led by Professor Omar Akbari’s laboratory have engineered ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A novel peptide ‘T14’ reflects age and photo-aging in human skin