(Press-News.org) Board games based on numbers, like Monopoly, Othello and Chutes and Ladders, make young children better at math, according to a comprehensive review of research published on the topic over the last 23 years.
Board games are already known to enhance learning and development including reading and literacy.
Now this new study, published in the peer-reviewed journal Early Years, finds, for three to nine-year-olds, the format of number-based board games helps to improve counting, addition, and the ability to recognize if a number is higher or lower than another.
The researchers say children benefit from programs – or interventions – where they play board games a few times a week supervised by a teacher or another trained adult.
“Board games enhance mathematical abilities for young children,” says lead author Dr. Jaime Balladares, from Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, in Santiago, Chile.
“Using board games can be considered a strategy with potential effects on basic and complex math skills.
“Board games can easily be adapted to include learning objectives related to mathematical skills or other domains.”
Games where players take turns to move pieces around a board differ from those involving specific skills or gambling.
Board game rules are fixed which limits a player’s activities, and the moves on the board usually determine the overall playing situation.
However, preschools rarely use board games. This study aimed to compile the available evidence of their effects on children.
The researchers set out to investigate the scale of the effects of physical board games in promoting learning in young children.
They based their findings on a review of 19 studies published from 2000 onwards involving children aged from three to nine years. All except one study focused on the relationship between board games and mathematical skills.
All children participating in the studies received special board game sessions which took place on average twice a week for 20 minutes over one-and-a-half months. Teachers, therapists, or parents were among the adults who led these sessions.
In some of the 19 studies, children were grouped into either the number board game or to a board game that did not focus on numeracy skills. In others, all children participated in number board games but were allocated different types e.g. Dominoes.
All children were assessed on their math performance before and after the intervention sessions which were designed to encourage skills such as counting out loud.
The authors rated success according to four categories including basic numeric competency such as the ability to name numbers, and basic number comprehension e.g. ‘nine is greater than three’.
The other categories were deepened number comprehension – where a child can accurately add and subtract – and interest in mathematics.
In some cases, parents attended a training session to learn arithmetic that they could then use in the games.
Results showed that math skills improved significantly after the sessions among children for more than half (52%) of the tasks analyzed.
In nearly a third (32%) of cases, children in the intervention groups gained better results than those who did not take part in the board game intervention.
The results also show that from analyzed studies to date, board games on the language or literacy areas, while implemented, did not include scientific evaluation (i.e. comparing control with intervention groups, or pre and post-intervention) to evaluate their impact on children.
Designing and implementing board games along with scientific procedures to evaluate their efficacy, therefore, are “urgent tasks to develop in the next few years,” Dr. Balladares, who was previously at UCL, argues.
And this, now, is the next project they are investigating.
Dr. Balladares concludes: “Future studies should be designed to explore the effects that these games could have on other cognitive and developmental skills.
“An interesting space for the development of intervention and assessment of board games should open up in the next few years, given the complexity of games and the need to design more and better games for educational purposes.”
END
Board games are boosting math ability in young children
2023-07-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
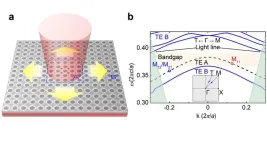
Ultra-low threshold continuous-wave quantum dot mini-BIC lasers
2023-07-07
Lasers with ultra-low threshold and compact size are highly desirable in photonic integrated circuits, aiming at the application of optical communications, chip-scale solid-state LIDAR and quantum information. The general approach to realizing such lasers is to effectively trap light and boost light-matter interaction by embedding gain materials into few- or sub-wavelength scale optical cavities with high quality (Q) factor and/or small mode volume (V-mode).
Low-threshold lasing has been realized on planar photonic crystal via introducing defect-type PhC modes or ...
Cracking the structure of a crucial neural transport protein
2023-07-07
Using Cryo-EM, a powerful microscopy technique, researchers at IISc and collaborators have decoded the molecular architecture of a transporter protein controlling the movement of a key neurotransmitter.
Neurons or nerve cells communicate by releasing chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Each neurotransmitter can activate specific sets of proteins called receptors that in turn either excite or inhibit neural communication. A balance between excitation and inhibition is vital for the neural circuitry to maintain normal structure and function. Imbalances in excitatory or inhibitory inputs can result in disorders like seizures, anxiety, and schizophrenia.
The inhibitory neurotransmitter ...
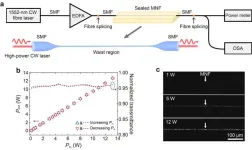
High-power optical continuous-wave waveguiding in a silica micro/nanofibre
2023-07-07
Optical MNFs are cylindrical optical waveguides with diameter below or close to the wavelength of the light. Since its first experimental demonstration [Nature 426, 816 (2003)], low-loss silica MNF has been attracting increasing attention in wide applications from optical sensors, atom optics, nonlinear optics to optomechanics. Generally, increasing the waveguiding mode power is the most effective approach to enhance light-matter interaction, and explore new opportunities for both scientific research and technological applications. However, the highest CW mode power reported so far in a MNF is ~0.4 W [AIP Adv. 4, 067124 (2014)], with typical waveguiding ...
Laser differential confocal Raman-Brillouin spectrum microscopy
2023-07-07
There are obvious differences between cancerous cells and normal cells in morphology, chemical properties and mechanical properties. The detection of cytochemical and mechanical properties of tumor tissues can provide multi-dimensional information for the pathological process of cells and human tissues. Among the existing detection methods for the morphology, mechanics and chemical properties of tissue and cells, confocal Raman spectroscopy can detect the chemical properties of micro-regions of samples without contact and label, and confocal Brillouin spectroscopy can detect ...
New Zealand kids spending one-third of after-school time on screens
2023-07-07
Regulations are urgently needed to protect children from harm in the unregulated online world, researchers at the University of Otago, New Zealand, say.
The call comes as the researchers publish the results of their study into the after-school habits of 12-year-olds. Their research, published today in the New Zealand Medical Journal, finds children are spending a third of their after-school time on screens, including more than half their time after 8pm.
Senior researcher Dr Moira Smith from the University's Department ...
It worked in the Caribbean – What about here?
2023-07-07
While there is extensive data on the high rates of HIV, STIs and unintended pregnancies among Black populations in the U.S., this racial category problematically subsumes the ethnic diversity of immigrant Black populations. Today, one in ten Black people in the U.S. are immigrants, with Caribbean immigrants accounting for approximately 46% of the total Black immigrant population.
It can’t be assumed that the variety of effective behavioral interventions (EBIs) that exist to address sexual and reproductive health for Black populations will be effective with Afro-Caribbean ...
Global diet study challenges advice to limit high-fat dairy foods
2023-07-07
Sophia Antipolis, 7 July 2023: Unprocessed red meat and whole grains can be included or left out of a healthy diet, according to a study conducted in 80 countries across all inhabited continents and published today in European Heart Journal, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 Diets emphasising fruit, vegetables, dairy (mainly whole-fat), nuts, legumes and fish were linked with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and premature death in all world regions. The addition ...
Not eating enough of these six healthy foods is associated with higher cardiovascular disease and deaths globally
2023-07-07
HAMILTON, ON (July 6, 2023) – A study led by McMaster University and Hamilton Health Sciences researchers at the Population Research Health Institute (PHRI) has found that not eating enough of six key foods in combination is associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in adults.
Consuming fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, fish and whole-fat dairy products is key to lowering the risk of CVD, including heart attacks and strokes. The study also found that a healthy diet can be achieved in various ways, ...
Vaccine candidate prevents diarrhea, improves growth in animal model
2023-07-07
PORTLAND, Oregon -- A vaccine originally developed to prevent bacteria-caused diarrhea has now also been found to help infant nonhuman primates grow faster, according to a new study published in Nature Communications.
“The 160 million people worldwide who get sick every year from Campylobacter bacteria is far too many,” said the study’s lead researcher, Mark Slifka, Ph.D., a professor at Oregon Health & Science University’s Oregon National Primate Center. “We need a new tool to prevent bacterial diarrhea in babies and to enable more children to grow into healthy adults, and this vaccine approach looks ...
Queensland native forestry can help achieve global environment goals
2023-07-07
Research conducted by The University of Queensland has revealed that Queensland native forestry, including timber harvesting, could actually help conserve biodiversity and mitigate climate risks.
Dr Tyron Venn from UQ’s School of Agriculture and Food Sustainability reviewed more than 350 publications, studying the ecological and economic impacts of Queensland native forest management, which includes everything from fire management to timber harvesting.
“Stopping forestry in Queensland’s native forests may sound like a positive outcome for the environment, but the research suggests that it would further shift our impacts offshore and increase ...