Spider mite males undress maturing females to win the first mating
2023-07-07
(Press-News.org)
In males of many species, it pays to identify females that are nearing maturity to be the first in line for mating. Now researchers reporting in the journal iScience on July 7 have found a remarkable example: male spider mites guard and then actively strip off the skin of premature females that are soon to molt and mature to make them accessible for mating sooner.
“Our study documents an exceptional male behavior in the animal kingdom, namely that male spider mites strip off the skin of premature females that are close to molting into adulthood,” said Peter Schausberger from the University of Vienna, Austria. “Such undressing behavior by the male is adaptive—that is, it increases their reproductive success—because it would be an enormous cost to the guarding male if a rival would take away the female and inseminate her instead of the male that invested time and energy in guarding her. The guards would have invested hours in guarding a potential future mate without any reward.”
In spider mites, the competition for first mating is especially intense, Schausberger explained. That’s because the first copulation partner of a female is the one that sires all the offspring. In fact, the males only sire the daughters because sons arise from unfertilized eggs. Because of this intense competition to be number one, spider mite males guard premature females for several hours before the females molt to the adult stage.
“For about one or two hours before molting, the females take on a silvery appearance because of air filling the gap between the old skin, called exuvia, and the new skin; in this phase the guarding males change their behavior—sometimes they drum with their forelegs on the females, possibly to stimulate the females to initiate the molting process, and make the females bulge and crack the exuvia,” Schausberger said.
“Upon cracking the exuvia, the guarding male becomes highly active and pulls on the hind part of the old skin with his pedipalps until it is removed from the female body and the genital opening of the female, which is located on the underside of the tip of her abdomen, is exposed so that the male can slip beneath the female and insert his aedeagus,” he continued. “Females that are undressed by a male first get rid of the hind part of the old skin because of male pulling, whereas females that molt without the help of a male first pull out from the front part of the old skin.”
Schausberger and colleagues are generally interested in sexual selection in spider mites, and especially alternative reproductive tactics by males, including fighting and sneaking. While observing and videotaping many male-male and male-female interactions, they noticed the undressing behavior they’ve now described in detail.
The findings offer yet another example of the fascinating behaviors that are driven by sexual selection, according to the researchers. They’re also a reminder that even tiny arachnids have highly sophisticated behaviors.
In future work, they hope to study the undressing behavior in more detail to find out whether fighting males differ from sneakers in this behavior. They also want to find out what happens when males in the process of undressing a female have to contend with rivals and whether the undressing behavior acts as a signal to females of a male’s quality.
####
This work was supported by the Austrian Science Fund and the Study Abroad Program from the Ministry of Education, Republic of Turkey.
iScience, Schausberger et al. “Spider mite males undress females to secure the first mating” https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(23)01189-6
iScience (@iScience_CP) is an open access journal from Cell Press that provides a platform for original research and interdisciplinary thinking in the life, physical, and earth sciences. The primary criterion for publication in iScience is a significant contribution to a relevant field combined with robust results and underlying methodology. Visit http://www.cell.com/iscience. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-07
About The Study: Deaths due to opioid toxicity increased substantially during the COVID-19 pandemic. By 2021, 1 of every 22 deaths in the U.S. was attributable to unintentional opioid toxicity, underscoring the urgent need to support people at risk of substance-related harm, particularly men, younger adults, and adolescents.
Authors: Tara Gomes, Ph.D., of the University of Toronto, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.22303)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
2023-07-07
About The Study: In this systematic review and meta-analysis, smoke-free legislation was associated with significant reductions in morbidity and mortality related to cardiovascular disease, respiratory system disease, and perinatal outcomes. These findings support the need to accelerate the implementation of smoke-free laws to protect populations against smoking-related harm.
Authors: Ryota Nakamura, Ph.D., of Hitotsubashi University in Tokyo, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
2023-07-07
Until now, scientific evidence has been inconclusive regarding the ability of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID, to replicate in the human placenta. Answering this question, as well as understanding the response of the placenta to other viral infections during pregnancy, is crucial for the development of effective preventive and therapeutic strategies for both the mother and the baby.
At Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children’s Hospital, researchers have taken a novel approach to shed light on ...
2023-07-07
The mucus in the airways is not as sticky, inflammation in the lungs significantly reduced: Triple combination therapy can achieve these positive, lasting effects in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF). Researchers from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin and the Max Delbrück Center have just recently published their findings in the European Respiratory Journal.* According to their research, this form of medication improves the symptoms of CF in many patients.
Two years ago, a research ...
2023-07-07
This study is led by Dr. Taihua Wang and Dr. Dawen Yang (Tsinghua University), together with experts in the field of both permafrost and glacier including Dr. Tandong Yao, Dr. Xin Li (Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Dr. Guodong Cheng and Dr. Huijun Jin (Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences). In a warming climate, the sustainability of cryospheric meltwater on the Tibetan Plateau has raised concerns because of its importance for the fragile ecosystem in the headwater regions and the dense populations in the downstream. Existing studies ...
2023-07-07
An apple a day not only keeps the doctor away, it also could save the United States at least $40 billion in medical bills, report Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University researchers in a new study published July 7 in the Journal of the American Heart Association. Their modeled implementation of a nationwide produce prescription program—which would provide free or discounted fruits and vegetables to eligible Americans living with diabetes—projected extensive reductions in national rates of cardiovascular disease and associated healthcare ...
2023-07-07
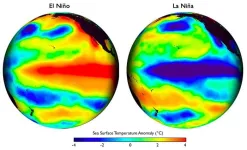
A multi-model ensemble (MME) prediction system has been recently developed by a team led by Dr. Dake Chen. This prediction system consists of 5 dynamical coupled models with various complexities, parameterizations, resolutions, initializations, and ensemble strategies, to address various possible uncertainties of ENSO prediction. One long term over past 100 year (1880-2017) ensemble hindcast demonstrated the superiority of the MME over individual models, evaluated by both deterministic and probabilistic skills, and suffered less from ...
2023-07-07
In a new study, a group from Institute of Geographic Science and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, proposed a concept of ecosystem water stress and comprehensively compared the impacts of high atmospheric vapor pressure deficit and low soil water content on vegetation growth in Eurasian drylands
Drought, a multifaceted phenomenon encompassing atmospheric and soil drought, has sparked a lively debate over which type of dryness stress exerts a more significant impact on vegetation growth. "Through our defined concept of ecosystem water stress, we can discern where water-stressed vegetation growth is dominated by ...
2023-07-07
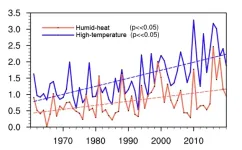
One of the main risks posed by climate change is exceeding the thermal limits of the human body. In hot environments, evaporation is considered to be the primary means by which human bodies cool down. However, atmospheric humidity is a crucial factor affecting the efficiency of evaporation, making the combination of hot and humid conditions more physiologically stressful than extreme dry-temperature conditions.
Besides the human health impacts, the occurrence of extreme-heat events also has severe socioeconomic impacts. For example, the record-breaking ...
2023-07-07
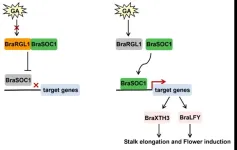
In June 2023, Prof. Riyuan Chen's team of South China Agricultural University online published a research article entitled Role of BraRGL1 in regulation of Brassica rapa bolting and flowering in the well-reputed journal Horticulture Research (Advance Access).
In this study, the authors performed highly efficient and inheritable mutagenesis using the CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing system in BraPDS (phytoene desaturase) and BraRGL1 (key DELLA protein) genes. The flower bud differentiation and bolting time ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Spider mite males undress maturing females to win the first mating