(Press-News.org) University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have discovered how the cells that let us hear can repair themselves after being damaged. That important insight could benefit efforts to develop new and better ways to treat and prevent hearing loss.
“Hair cells” found in the inner ear, are important both for our ability to hear and our sense of balance. They are known as hair cells because the cells are covered in hair-like structures that serve as mechanical antennas for sound detection. When auditory hair cells are killed, as we learn in school, they are gone for good. But the new UVA Health research shows these delicate cells have the ability to repair themselves from damage caused by loud noises or other forms of stress.
“For many years, auditory research has placed considerable emphasis on the regeneration of sensory hair cells. Although these efforts continue, it is equally important to enhance our comprehension of the intrinsic mechanisms that govern the repair and maintenance of these cells. By gaining a deeper understanding of these inherent repair processes, we can uncover strategies to fortify them effectively. One such approach in the future might involve the utilization of drugs that stimulate repair programs,” said researcher Jung-Bum Shin, PhD, of UVA’s Department of Neuroscience. “In essence, when replacement of hair cells proves challenging, the focus shifts towards repairing them instead. This dual strategy of regeneration and repair holds strong potential in advancing treatments for hearing loss and associated conditions.”
Hearing Repair
Hair cells are naturally fragile – they must be delicate so they can sense sound, but they also must withstand the continuous mechanical stress inherent in their jobs.
Prolonged exposure to loud noise harms hair cells in a variety of ways, and one of those is by damaging the cores of the “hairs” themselves. These hair-like structures are known as stereocilia, and Shin’s new research shows a process they use to repair themselves.
The hair cells do this by deploying a protein called XIRP2, which has the ability to sense damage to the cores, which are made of a substance called actin. Shin and his team found that XIRP2 first senses damage, then migrates to the damage site and repairs the cores by filling in new actin.
“We are especially excited to have identified a novel mechanism by which XIRP2 can sense damage-associated distortions of the actin backbone,” Shin said. “This is of relevance not only for hair cell research, but the broader cell biology discipline.”
The pioneering work has netted Shin and his colleagues more than $2.3 million from the National Institutes of Health, grant R01DC021176, to fund additional research into how the cores are repaired. By understanding this, scientists will be better positioned to develop new ways to battle hearing loss – even the kind that comes from aging, the researchers say.
“Age-related hearing loss affects at least a third of all older adults,” Shin said. “Understanding and harnessing internal mechanisms by which hair cells counteract wear and tear will be crucial in identifying ways to prevent age-related hearing loss. Furthermore, this knowledge holds potential implications for associated conditions such as Alzheimer's disease and other dementia conditions.”
Findings Published
The researchers have published their findings in the scientific journal eLife. The article is open access, meaning it is free to read.
The research team consisted of Elizabeth L. Wagner, Jun-Sub Im, Stefano Sala, Maura I. Nakahata, Terence E. Imbery, Sihan Li, Daniel Chen, Katherine Nimchuk, Yael Noy, David W. Archer, Wenhao Xu, George Hashisaki, Karen B. Avraham, Patrick W. Oakes and Shin. The researchers have no financial interest in the work.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders, grants R01DC014254, R56DC017724, R01DC018842, R01DC011835 and 1F31DC017370-01. Additional support was provided by the Owens Family Foundation, the Virginia Lions Hearing Foundation, and a National Science Foundation CAREER Award.
To keep up with the latest medical research news from UVA, subscribe to the Making of Medicine blog.
END
Scientists discover natural repair process that fixes damaged hearing cells
2023-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tracking down social determinants of health in electronic health records
2023-07-10
INDIANAPOLIS – Information on the nonmedical factors that influence health outcomes, known as social determinants of health, is often collected at medical appointments. But this information is frequently recorded as text within the clinical notes written by physicians, nurses, social workers, and therapists.
Researchers from Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University Fairbanks School of Public Health recently published one of the first studies in which natural language processing was applied to social determinants of health. The researchers developed three new natural language processing algorithms to successfully extract information from text data related to housing ...
Association for Molecular Pathology publishes clinical CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 genotyping assay recommendations
2023-07-10
ROCKVILLE, Md. – July 10, 2023 – The Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP), the premier global molecular diagnostic professional society, today published consensus recommendations to aid in the design and validation of clinical CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 genotyping assays, promote standardization of testing across different laboratories, and improve patient care. The manuscript, “CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 Genotyping Recommendations: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the AMP, Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC), College of American Pathologists (CAP), Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) of the Royal Dutch Pharmacists ...
First ladies from African countries convene at inaugural executive leadership program to advance health and development
2023-07-10
NEW YORK, NEW YORK, July 10, 2023 – First Ladies from countries across Africa and experts from the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health will meet the week of July 10, 2023 to discuss current trends, critical research, and sustainable, evidence-based approaches to promote population health and well-being. From July 10th to the 13th, First Ladies and their senior advisors will participate in an executive leadership program to advance critical health and development issues in their countries and regions, including communicable and chronic disease ...
Carnegie Mellon University offers new online graduate certificate in computational data science to meet AI demand
2023-07-10
Artificial intelligence has transformed how industries and organizations operate, putting data professionals in high demand. To meet this increasing need, Carnegie Mellon University recently launched an online Graduate Certificate in Computational Data Science Foundations program.
"Everything we teach will translate into skills that enable mobilization of data for significant impact in your organization," said Carolyn Rosé, the faculty program director and a professor in both the Human-Computer ...
Sharp rise in severe, alcohol-related liver injury during pandemic
2023-07-10
SEATTLE, Wash. – A boom in alcohol sales during the pandemic appears to have had dire consequences for some as hospital admissions for alcohol-related hepatitis, a life-threatening liver inflammation, increased dramatically, according to a study of national hospitalization data.
Researchers found increasing cases of the alcohol-related liver illness from 2016 through 2020, but the rise was particularly pronounced the year COVID-19 arrived in the U.S. in 2020, which saw a 12.4% increase over 2019 levels. It was worse in younger patients, ages 18 to 44, a group that had a nearly 20% ...
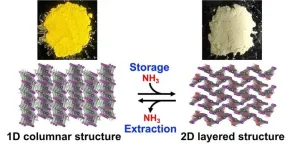
A safe, easy, and affordable way to store and retrieve hydrogen
2023-07-10
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS) in Japan have discovered a compound that uses a chemical reaction to store ammonia, potentially offering a safer and easier way to store this important chemical. This discovery, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on July 10, makes it possible not only to safely and conveniently store ammonia, but also the important hydrogen is carries. This finding should help lead the way to a decarbonized society with a practical hydrogen economy.
For society to make the switch from carbon-based to hydrogen-based energy, we need a safe way to store and transport hydrogen, which by itself ...
These lollipops could ‘sweeten’ diagnostic testing for kids and adults alike
2023-07-10
A lollipop might be a sweet reward for a kid who’s endured a trip to the doctor's office, but now, this candy could make diagnostic testing during a visit less invasive and more enjoyable. Researchers publishing in ACS’ Analytical Chemistry have shown, for the first time, that a lollipop-based saliva collection system can capture bacteria from adults and remain shelf-stable for up to a year. Study participants also preferred the candies over conventional collection systems.
Throat swabs are commonly used to collect samples for the diagnosis of a wide variety of illnesses, including strep throat. A less-gag-inducing method is saliva sampling, in which technicians ...
Air monitor can detect COVID-19 virus variants in about 5 minutes
2023-07-10
Now that the emergency phase of the COVID-19 pandemic has ended, scientists are looking at ways to surveil indoor environments in real time for viruses. By combining recent advances in aerosol sampling technology and an ultrasensitive biosensing technique, researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have created a real-time monitor that can detect any of the SARS-CoV-2 virus variants in a room in about 5 minutes.
The inexpensive, proof-of-concept device could be used in hospitals and health care facilities, schools and ...
Policy guidance offers strategies to shift to value-based health care and payment
2023-07-10
Statement Highlights:
The American Heart Association supports a value-based care and payment (VBP) system that is person-centered, equitable, coordinated and seeks to improve equity, patient and provider experience, and individual and population health while controlling costs.
Defining and improving clinician understanding of value-based payment program design and best practices promotes informed decisions for participating and successfully engaging in these models.
Embargoed until 4:00 a.m. CT/5:00 a.m. ET, Monday, July 10, 2023
DALLAS, July 10, 2023 — The American Heart Association, a global force for longer, healthier lives for all, ...
Study identifies prostate cancer–related disparities between Indigenous and non-Indigenous men in a universal health care system
2023-07-10
Indigenous Peoples in Canada have higher illness rates and lower life expectancies than non-Indigenous Canadians. A new study reveals that Indigenous men in the country who have prostate cancer are being diagnosed with more advanced and more aggressive tumors than their non-Indigenous counterparts. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
To identify disparities in prostate cancer screening, diagnoses, management, and outcomes between Indigenous and non-Indigenous men in Canada, a team led by Adam Kinnaird, MD, PhD, of the University of Alberta, ...