(Press-News.org) Washington, D.C. – Bacteria found in 74 kitchens spread among 5 European countries were mostly harmless according to new research published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
“We have previously found considerable variations in kitchen standards, food preparation practices, and cleaning regimes between France, Norway, Portugal, Romania, and Hungary,” said Birgitte Moen, Ph.D., Scientist—Department of Food Safety and Quality, Nofima—Norwegian Institute of Food, Fisheries, and Aquaculture Research, Ås, Norway.
In the study, the researchers sampled bacteria populations from sinks, cutting boards, counter tops, handles and cleaning utensils—sponges and cloths—used in kitchens.
Despite large numbers of species and considerable differences in bacterial diversity between samples, the researchers identified 8 bacterial genera commonly associated with environmental sources in most of the kitchens they sampled, which they characterized as “core microbiota.” These included Acinetobacter, Pseudomonas, Enhydrobacter, Enterobacteriaceae, Psychrobacter, Chryseobacterium, Bacillus and Staphylococcus.
In the report, the authors stressed that the core microbiota persisted despite considerable differences between kitchens in the study. Some kitchens lacked running water, some lacked an indoor sink and some lacked dishwashers. They also persisted despite differing food preparation methods, dietary habits and differences in hand and kitchen hygiene, both of which affect the probability of infection.
The study was motivated by the authors’ curiosity, said Moen. Bacteria in food, in the gut, in hospitals and in professional food production had been well researched, but little was known about the microbes that inhabit the domestic kitchen. With an already existing collaboration across countries, “we had a unique opportunity to dig into this,” Moen added.
The team knew that harmful bacteria enter kitchens via contaminated food, and that the type of these bacteria varied across countries. For example, Salmonella is not a problem in Norway, but it is the most commonly reported cause of foodborne illness in mainland Europe. Knowledge of the bacteria inhabiting the domestic kitchen could be used to help prevent human illness, and perhaps could even lead to more hygienic kitchen designs and better cleaning utensils, said Moen.
###
The American Society for Microbiology is one of the largest professional societies dedicated to the life sciences and is composed of 30,000 scientists and health practitioners. ASM's mission is to promote and advance the microbial sciences.
ASM advances the microbial sciences through conferences, publications, certifications, educational opportunities and advocacy efforts. It enhances laboratory capacity around the globe through training and resources. It provides a network for scientists in academia, industry and clinical settings. Additionally, ASM promotes a deeper understanding of the microbial sciences to diverse audiences.
END
Bacteria in kitchen may not be as harmful as you think
2023-07-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Allen Institute for Neural Dynamics launches first-ever crowdsourced neuroscience experiment
2023-07-11
The aim is to maximize impact by turning to the combined talent and insight of the broader international neuroscience community.
SEATTLE — July 11, 2023 — Today, scientists from the Allen Institute for Neural Dynamics, a division of the Allen Institute, launched the world’s first completely open- and crowd-sourced neuroscience experiment—inviting researchers from around the world to publicly design a shared experiment that will run on the Allen Brain Observatory, as part of the Institute’s OpenScope program. Experiments will probe ...
Marine fossils are a reliable benchmark for degrading and collapsing ecosystems
2023-07-11
Biologists attempting to conserve and restore denuded environments are limited by their scant knowledge of what those environments looked like before the arrival of humans. This is especially true of coastal ecosystems, many of which had already been drastically altered by pollution and overharvesting hundreds of years before scientists began monitoring them.
According to a new study published in the journal PeerJ, a faithful analogue of modern marine ecosystems lies just beneath the surface. Building on more than 20 years of conservation paleobiology, the results suggest that fossils of various marine groups — including worms, mollusks, crabs and sea urchins — are ...
Mount Sinai Queens opens new Cardiac Catheterization Lab to expedite care for heart attack patients
2023-07-11
Click here to watch a video on the new Cath Lab
Mount Sinai Queens today announced the opening of a new cardiac catheterization lab that will provide rapid and comprehensive care to hundreds of heart patients every year for life-threatening emergencies and scheduled cardiac procedures. The first cardiac catheterization lab in Astoria, it will transform treatment for patients in the growing communities of western Queens by vastly improving access to cardiac care in the borough and beyond.
Atul Kukar, DO, has been named the Director of the Mount Sinai Queens Catheterization Lab and leads a team of 14 specialists including interventional cardiologists, nurses, and technicians.
“Our ...
The ground is deforming, and buildings aren’t ready
2023-07-11
There is a “silent hazard” lurking underneath our major global cities, and our buildings were not designed to handle it.
A new Northwestern University study has, for the first time, linked underground climate change to the shifting ground beneath urban areas. As the ground heats up, it also deforms. This phenomenon causes building foundations and the surrounding ground to move excessively (due to expansions and contractions) and even crack, which ultimately affects structures’ long-term operational performance and durability. Researchers also report that past building damage ...
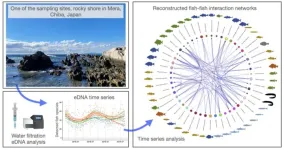
Deciphering fish species interactions for climate change insights
2023-07-11
A team led by the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has developed a technique to study how different fish species interact with each other in a coastal region, a breakthrough that helps explain the complex relationships among marine species and how global warming impacts fish populations.
By analyzing minute traces of fish DNA from samples of seawater, the team combined the use of environmental DNA – known as eDNA – and advanced statistical analysis to not only detect ...
Simple oxygen intervention could help patients ‘dramatically improve’ after brain injuries
2023-07-11
Motor learning skills let us move through the world: we use them to teach ourselves how to walk, how to pick up a drink, how to run. But age or sickness can weaken our ability to learn motor tasks. Scientists studying the impact of oxygen supplementation on motor learning have found a promising treatment that could help patients who have experienced neurological trauma recover old skills.
“A simple and easy to administer treatment with 100% oxygen can drastically improve human motor learning processes,” said Dr Marc Dalecki, now at the German University of Health and Sports in Berlin, senior author of the study in Frontiers in Neuroscience.
Repurposing ...
3D bioprinting technology to be used for removing cancer cells
2023-07-11
A three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting technology capable of eliminating cancer cells using the function of immune cells has been developed for the first time in the world.
Through joint research with the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (President Sang Jin Park, hereinafter referred to as KIMM), the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (President Jang Seong Kim, hereinafter referred to as KRIBB), institute under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Science and ICT, developed a 3D bioprinting technology using natural killer cells (NK cells)* as a new method of immunotherapy for treating cancer, and ...
New book explores the psychology of being duped
2023-07-11
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — According to two psychologists who study memory and perception, fraudsters tend to exploit the common habits of thought and decision-making that make us susceptible – and often oblivious – to their fabrications. Their book, “Nobody’s Fool: Why We Get Taken In and What We Can Do About It,” gives readers an overview of dozens of types of scams, hoaxes and strategies used by cheaters to deceive, and explains how to evaluate their ploys and avoid becoming a victim.
The authors, Daniel Simons, a professor of psychology at the University ...
New guidance: Bridging the gap between what we know and what we do
2023-07-11
ARLINGTON, Va. (July 11, 2023) — Five medical societies have published a set of recommendations for operationalizing strategies for infection prevention in acute care settings that account for conditions within the facility, including the culture and communications style of teams, hospital policies, resources available, leadership support and staff buy-in.
“There is no best way to implement a practice, but implementation need not be overly complex,” said Joshua Schaffzin, MD, a pediatric infectious disease physician and a senior author of Implementing Strategies to Prevent ...
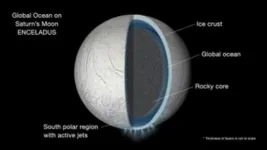
Study increases probability of finding water on other worlds by x100
2023-07-11
A new analysis shows that there are probably many more Earth-like exoplanets with liquid water than had been thought, significantly increasing the chance of finding life. The work finds that even where the conditions are not ideal for liquid water to exist at the surface of a planet, many stars will harbour geological conditions suitable for liquid water under the planet’s surface.
Presenting the work at the Goldschmidt geochemistry conference in Lyon, lead researcher Dr Lujendra Ojha (Rutgers University, New Jersey, USA) said “We know that the presence of liquid water is essential for life. Our work shows that this water can be found in places ...